The Interleukin Family: The Director of Immune Regulation

The interleukin family is a group of cytokines that play a critical role in the immune system. This family includes a variety of interleukins, which are indispensable in regulating immune responses, inflammatory processes, and cellular communication. Below is a detailed overview of the members of the interleukin family:
The Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Family
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a central mediator of innate immunity and inflammation. The IL-1 family includes seven ligands with agonist activity (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ), three receptor antagonists (IL-1Ra, IL-36Ra, IL-38), and an anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-37). The IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) family consists of six receptor chains that form four signaling receptor complexes, two decoy receptors (IL-1R2, IL-18BP), and two negative regulators (TIR8 or SIGIRR, IL-1RAcPb). Tight regulation through receptor antagonists, decoy receptors, and signaling inhibitors ensures a balance between the amplification of innate immunity and uncontrolled inflammation. All cells of the innate immune system express IL-1 family members and/or are influenced by them. Additionally, IL-1 family members play a key role in polarizing the differentiation and function of innate and adaptive lymphocytes.
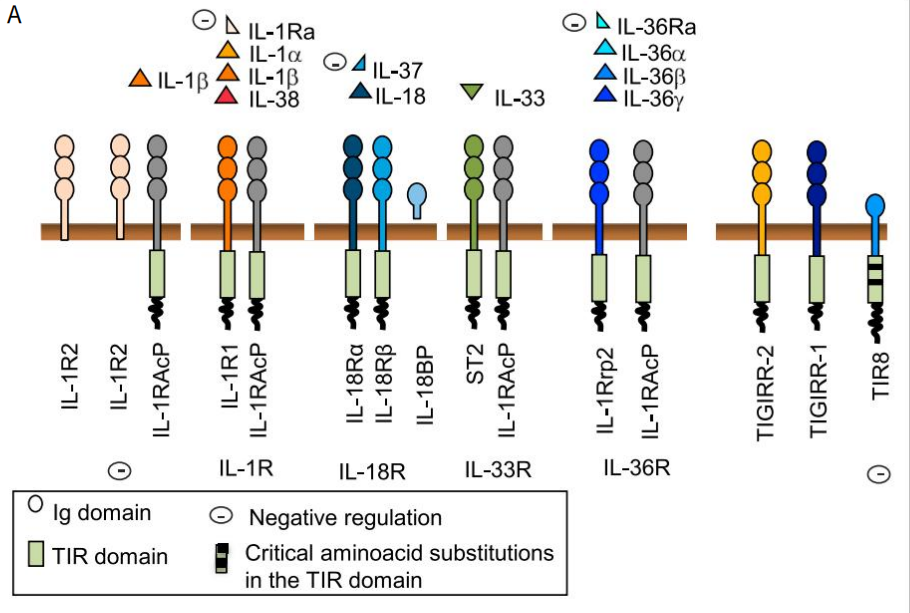
Ligands and Receptors in the IL-1 FamilyA schematic representation of ligands and receptor chains in the IL-1 family. The minus sign indicates inhibition.
Source: doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
IL-1α and IL-1β
IL-1α and IL-1β are two important members of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) family, both produced by immune cells such as monocytes and macrophages. IL-1α exhibits biological activity both intracellularly and extracellularly. As an inflammatory mediator, it can trigger inflammatory responses, promote immune cell activation, and release inflammatory mediators. IL-1α also regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and other immune and inflammatory processes. IL-1β primarily functions by inducing inflammatory responses, guiding immune cell migration and activation, and promoting local tissue inflammation. IL-1β is also associated with a range of immune- and inflammation-related physiological and pathological processes, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and chronic inflammation. Both IL-1α and IL-1β bind to the IL-1 receptor, activating downstream signaling pathways, including the NF-κB pathway, thereby regulating inflammation and immune responses. They are key regulators in inflammatory processes, enabling the body to respond to infections and tissue damage with immune and inflammatory reactions.
IL-18
IL-18 is a cytokine produced by various immune cells, primarily monocytes, macrophages, and other immune cells, with increased expression during infections and inflammation. Initially identified as "interferon-γ-inducing factor," IL-18 has the ability to induce interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production. IL-18 is a polypeptide protein whose precursor requires enzymatic cleavage (typically mediated by caspase-1) to become active. Its biological effects are mediated through binding to its receptor, the IL-18 receptor (IL-18R). IL-18 plays a significant role in immune regulation by enhancing natural killer (NK) cell activity, promoting T cell differentiation and activation, stimulating the production of inflammatory mediators, and regulating inflammatory responses. It also influences Th1/Th2 immune responses, working synergistically with IL-12 to promote Th1 cell differentiation while also affecting Th2 responses. Dysregulated IL-18 expression is closely associated with various immune-related diseases, such as autoimmune disorders, allergic reactions, and certain cancers.
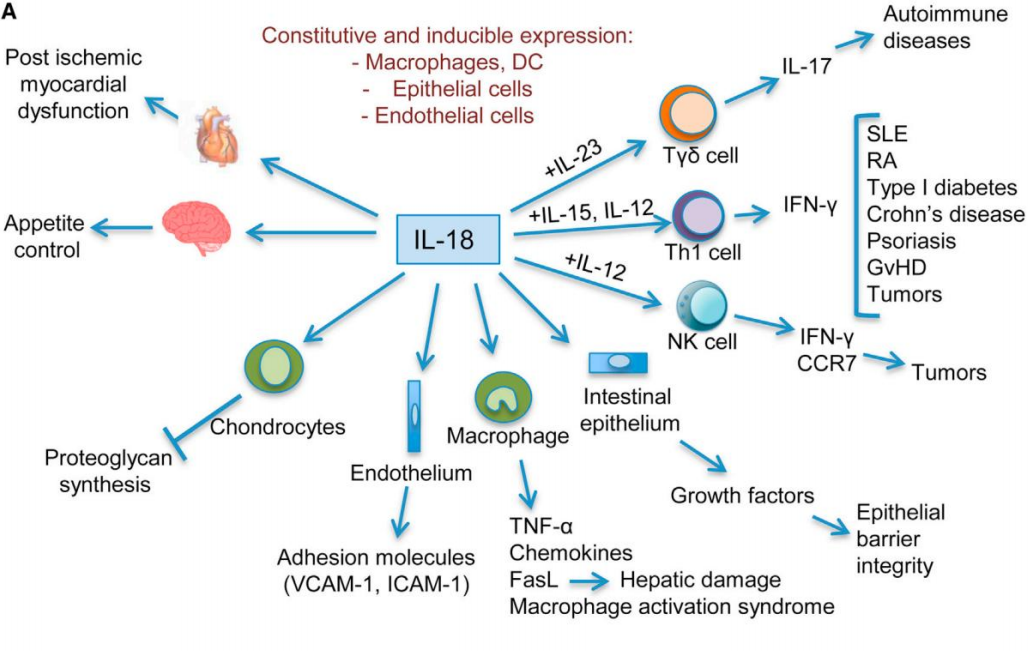
Source: doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
IL-33
IL-33 is a polypeptide protein with features common to the IL-1 family. It contains an IL-1-like N-terminus and a C-terminal nuclear localization sequence. Initially identified as a "nuclear factor," IL-33 is localized within the nucleus. Subsequent studies revealed that IL-33 can be secreted extracellularly during cell damage and inflammation, exerting various biological functions. IL-33 is primarily produced by tissue cells such as epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages, with upregulated expression during injury or inflammation. Its biological effects are mediated through binding to its receptor, ST2 (IL-1R4), which forms a complex with IL-1R ligands. IL-33 plays a regulatory role in the immune system, particularly in Th2 immune responses, and can induce and enhance allergic reactions by activating mast cells and promoting Th2 cell cytokine production. It also contributes to tissue repair by promoting epithelial cell proliferation. Dysregulated IL-33 expression is associated with various inflammatory and allergic diseases, such as asthma and allergic rhinitis.
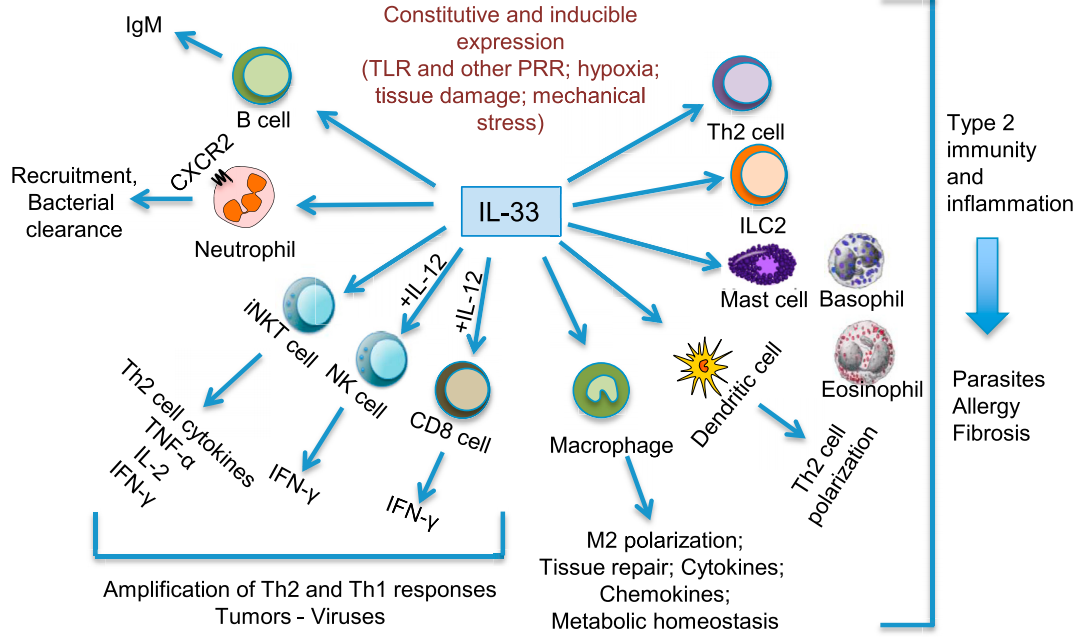
Source: doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.010
The Interleukin-2 (IL-2) Family
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a pleiotropic cytokine that drives T cell growth, enhances NK cell cytotoxic activity, induces regulatory T cell differentiation, and mediates activation-induced cell death. Like IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21, IL-2 shares the common cytokine receptor γ-chain (γc), which is mutated in patients with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Recent studies have highlighted IL-2's complex role in broadly regulating T cells to promote T helper cell differentiation. IL-2 does not specify the type of Th differentiation; instead, it regulates the expression of other cytokine and transcription factor receptors, thereby promoting or inhibiting cytokine cascades associated with each Th differentiation state. In this manner, IL-2 can initiate and potentially sustain Th1 and Th2 differentiation while expanding these cell populations, whereas it suppresses Th17 differentiation but can also expand Th17 cells.
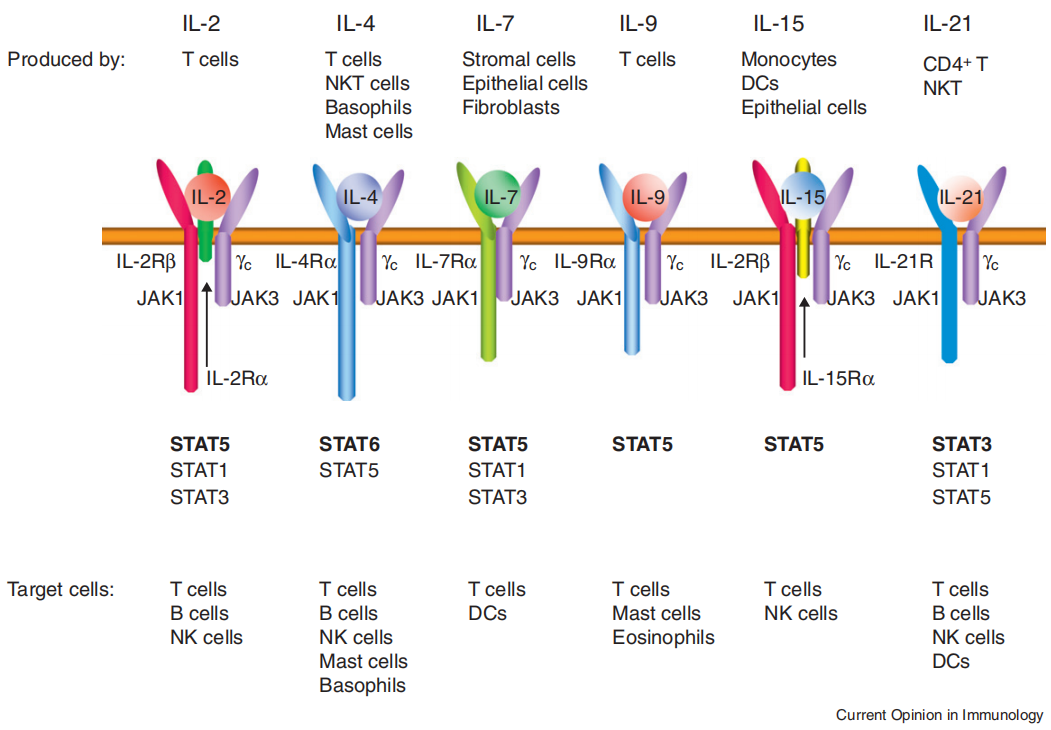
Source: Current Opinion in Immunology
Receptors of IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21.The figure illustrates the receptors for IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. These cytokines activate STAT proteins through phosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK3. The primary STAT proteins activated by each cytokine are indicated in bold. DC, dendritic cells; NK cells, natural killer cells; NKT cell, natural killer T cells. STAT5 refers to both STAT5A and STAT5B, closely related head-to-head tandem genes.
The Interleukin-17 (IL-17) Family
The interleukin-17 (IL-17) family, consisting of IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E (IL-25), and IL-17F, is a subgroup of cytokines that play a crucial role in host defense against microbes and the development of inflammatory diseases. While IL-17A is the hallmark cytokine produced by Th17 cells, IL-17A and other IL-17 family cytokines have diverse sources, ranging from immune cells to non-immune cells. IL-17 family members signal through their respective receptors, activating downstream pathways, including NF-κB, MAPKs, and C/EBP, to induce the expression of antimicrobial peptides, cytokines, and chemokines. The proximal adaptor Act1 is a common mediator in all IL-17 cytokine signaling pathways, thus participating in IL-17-mediated host defense and IL-17-driven autoimmune diseases. This section reviews the IL-17 family, the activation and regulation of IL-17 signaling, and diseases associated with this cytokine family.
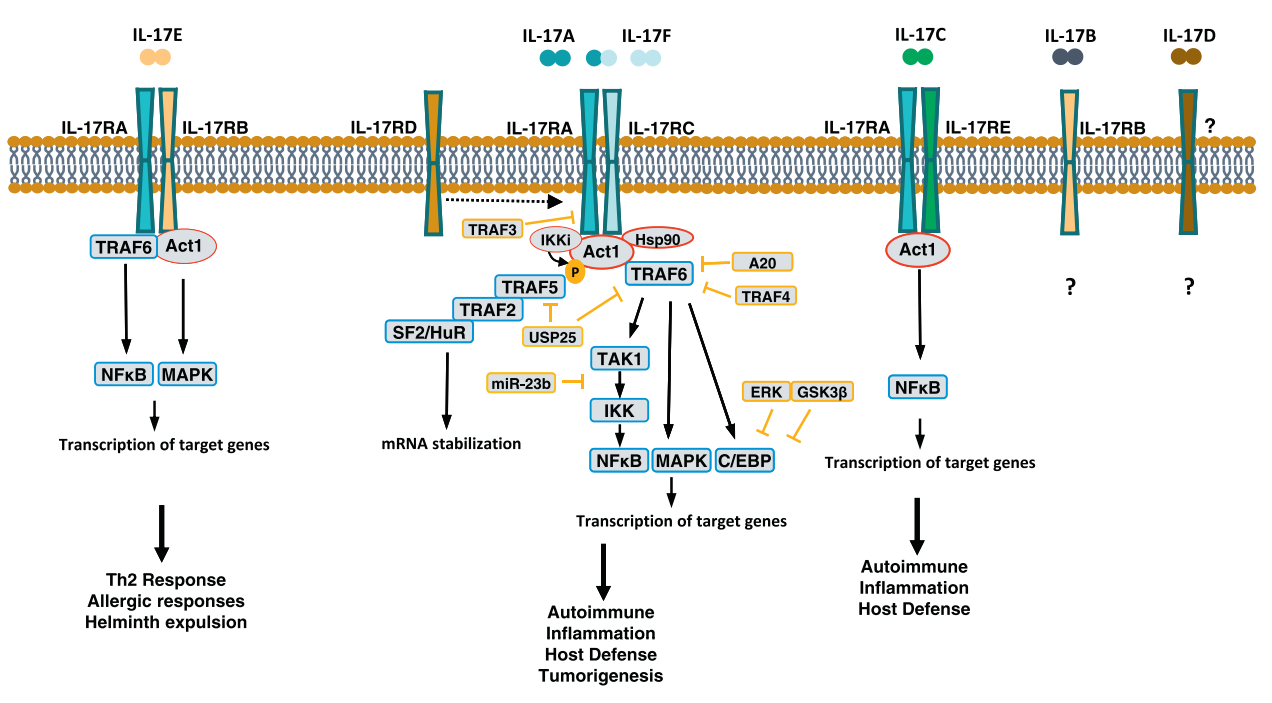
Source: www.journals.elsevier.com/cytokine
IL-17 Cytokines, Receptors, and Signaling
The IL-17 family consists of six members (IL-17A-F), while the IL-17 receptor family comprises five members (IL-17RA to IL-17RE). IL-17RA is a common receptor that can form heterodimeric complexes with IL-17RB, IL-17RC, and IL-17RE. All IL-17 receptors recruit Act1 as an adaptor molecule for downstream signaling. IL-17A and IL-17F signal through the IL-17RA-RC complex, triggering TRAF6-dependent target gene transcription and TRAF6-independent IKKi-dependent mRNA stabilization, both of which are important for host defense and contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and cancer. IL-17 signaling is tightly regulated at various levels of the signaling cascade. At the receptor level, IL-17RD interacts with Act1, sequestering it from IL-17RA and TRAF6 until IL-17 stimulation. TRAFs such as TRAF3 and TRAF4 disrupt downstream signaling complex formation. TRAF3 binds to IL-17R to prevent Act1 and TRAF6 recruitment, while TRAF4 competes with TRAF6 for Act1 binding. Deubiquitinating enzymes such as USP25 and A20 regulate the ubiquitination status of TRAFs (e.g., TRAF5 and TRAF6), thereby suppressing the signaling cascade. IL-17A-dependent micro-RNA (miR-23b) regulates NF-κB activation. IL-17A-induced transcription factors (e.g., C/EBPδ) suppress inflammatory gene expression. IL-17E (IL-25) signals through the IL-17RA-RB receptor complex, inducing Th2 responses via activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways. IL-17C signals through the IL-17RA-RE complex, mediating host defense and contributing to autoimmune disease pathogenesis, similar to IL-17A. IL-17B has been shown to interact with IL-17RB, but its biological functions remain unclear. The receptor for IL-17D is unknown.
Other Families
IL-6 Family
Interleukin-6 (IL-6): A cytokine with broad biological activities, involved in immune regulation, inflammatory responses, and hematopoiesis.
Interleukin-11 (IL-11): Shares biological functions with IL-6, primarily related to hematopoiesis, inflammation, and bone metabolism.
Interleukin-27 (IL-27): Composed of IL-27p28 and EBI3 subunits, regulates T cell function and suppresses inflammatory responses.
IL-10 Family
Interleukin-10 (IL-10): An anti-inflammatory cytokine that inhibits immune cell activation and inflammatory responses, playing a key role in immune regulation.
Interleukin-19 (IL-19): Involved in immune regulation and associated with inflammatory responses and tissue repair.
Interleukin-20 (IL-20): Plays a role in immune regulation, inflammation, and skin pathology.
Interleukin-22 (IL-22): Protects epithelial cells and intestinal mucosa, contributing to immune balance and tissue repair.
IL-12 Family
Interleukin-12 (IL-12): Along with IL-23 and IL-27, regulates Th1 cell differentiation and activation, participating in antimicrobial immune responses.
Interleukin-23 (IL-23): Involved in inflammatory responses and autoimmune diseases, closely associated with Th17 cells.
Other interleukin members not discussed here also play significant roles. These interleukins regulate immune system activity by binding to their respective receptors and activating specific signaling pathways. Studying the functions and interactions of these cytokines is essential for understanding immune regulation mechanisms, disease pathogenesis, and therapeutic strategies.
Reference
1.Dinarello, C. A. (2009). Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annual Review of Immunology, 27, 519-550.
2.Cecilia Garlanda. (2013). The Interleukin-1 Family: Back to the Future. Cell PRESS, Immunity 39, December 12, 1003-1018.
3.W.J. IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011. 23(5):598-604
4.GuC, Wu L&LiX. (2013) IL-17 family: cytokines, receptors and signaling. to i 64: 477-485.
5.Korn, T., Bettelli, E., Oukka, M., & Kuchroo, V. K. (2009). IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annual Review of Immunology, 27, 485-517.
6.Liew, F. Y., Pitman, N. I., & McInnes, I. B. (2010). Disease-associated functions of IL-33: the new kid in the IL-1 family. Nature Reviews Immunology, 10(2), 103-110.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA040200 | IL-12 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $270 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040218 | IL-12 Protein,Mouse | Host : Mouse | $264.60 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040112 | IL-13 Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $180 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040158 | IL-13 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $192 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040010 | IL-15 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $480 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040024 | IL-17 RA Protein, Human | Host : Human | $400 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040182 | IL-17A Protein, Human | Host : Human | $89 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040111 | IL-18 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $164 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040195 | IL-18 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $176 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040226 | IL-18 Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $296 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040152 | IL-19 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $134 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040009 | IL-21 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $216 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040199 | IL-28B/IFNL3 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $256 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040060 | IL-22 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,200 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040063 | IL-22 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $1,200 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040125 | IL-22 Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $180 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040207 | IL-23 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $240 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040181 | IL-23 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $324 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040179 | IL-33 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $190 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040215 | IL-36Rα Protein, Human | Host : Human | $176 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040208 | IL-36α Protein, Human | Host : Human | $176 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040203 | IL-36β Protein, Human | Host : Human | $196 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040210 | IL-36γ Protein, Human | Host : Human | $236 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| UA040202 | IL-1α Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $236 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040151 | IL-1β Protein, Human | Host : Human | $164 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040223 | IL-2(Cys145Ser) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $76 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040057 | IL-2 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $76 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040108 | IL-2 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $76 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040171 | IL-2 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $106 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040008 | IL-3 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $2,400 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040219 | IL-3 Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $176 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040026 | IL-4 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $180 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040192 | IL-4 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $152 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040205 | IL-6 Protein, Canine | Host : Canine | $356 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040052 | IL-6 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $960 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040155 | IL-6 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $236 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040118 | IL-7 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $236 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040193 | IL-7 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $236 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040174 | IL-7 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $240 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040103 | IL-8 (28-99) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $162 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040093 | IL-8(28-99) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $696 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040196 | IL-8/CXCL8 Protein, Canine | Host : Canine | $316 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040220 | IL-9 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $236 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040176 | IL-10 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $240 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




