The Cellular Feast: The Remarkable Power of the FGF Family Growth Factors

Introduction to the FGF Family
The FGF family, also known as the Fibroblast Growth Factor family, comprises a group of proteins that play a crucial regulatory role in cell growth, development, and differentiation. These growth factors are widely distributed in the human body and exert stimulatory or inhibitory effects on various cell types. Members of the FGF family function during the earliest stages of embryonic development and organogenesis, maintaining progenitor cells and mediating their growth, differentiation, survival, and patterning. In adult tissues, FGFs also play roles, often by reactivating developmental signaling pathways to mediate metabolic functions, tissue repair, and regeneration.
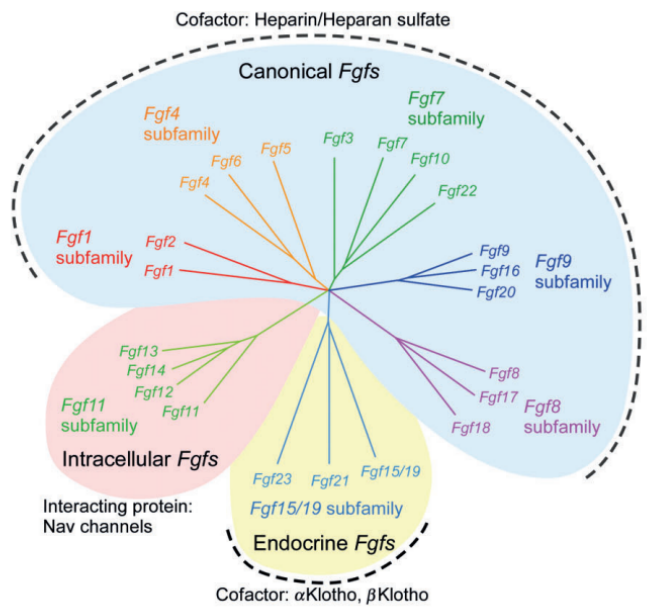
Source: DOI: 10.1002/wdev.176
Phylogenetic analysis reveals that the 22 Fgf genes can be divided into 7 subfamilies, each containing 2 to 4 members. The branch lengths are proportional to the evolutionary distance between each gene. The Fgf1, Fgf4, Fgf7, Fgf8, and Fgf9 subfamily genes encode secreted canonical FGFs, which bind to heparin/heparan sulfate (HS) as cofactors and activate FGFRs. The Fgf15/19 subfamily members encode endocrine FGFs, which bind to Klotho family proteins as cofactors and activate FGFRs. The Fgf11 subfamily genes encode intracellular FGFs, which are non-signaling proteins acting as cofactors for voltage-gated sodium channels and other molecules.
A schematic diagram of the FGFR protein structure is shown. FGFRs are receptor tyrosine kinases of approximately 800 amino acids, featuring multiple domains, including three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains (I, II, and III), a transmembrane domain (TM), and two intracellular tyrosine kinase domains (TK1 and TK2). SP denotes a cleavable secretory signal sequence. The Fgfr gene family consists of four members: Fgfr1-Fgfr4. Among these, Fgfr1-Fgfr3 produce two major splice variants of the immunoglobulin-like domain III, known as IIIb and IIIc, which are critical determinants of ligand-binding specificity.
A schematic diagram of the FGFRL1/FGFR5 protein structure is shown. FGFRL1 is structurally similar to FGFRs and is a membrane protein of approximately 500 amino acids, featuring three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains (I, II, and III), a transmembrane domain (TM), and a short intracellular tail lacking tyrosine kinase domains. SP denotes a cleavable secretory signal sequence.
Cell Types and Functions of Different FGF Subtypes
| FGF | Cell Types | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| FGF-1 | Fibroblasts, endothelial cells, etc. | Promotes cell proliferation, maintains cellular homeostasis, angiogenesis |
| FGF-2 | Stem cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells | Promotes cell proliferation, regulates differentiation, angiogenesis |
| FGF-3 | Fibroblasts, bone marrow mesenchymal cells | Promotes cell proliferation, skeletal development |
| FGF-4 | Embryonic stem cells, fibroblasts | Promotes cell proliferation, regulates embryonic development |
| FGF-5 | Neuroepithelial cells, fibroblasts | Regulates cell proliferation, neural and skin development |
| FGF-6 | Fibroblasts, muscle cells | Promotes muscle cell proliferation and repair, muscle development |
| FGF-7 | Epithelial cells, keratinocytes | Promotes epithelial cell proliferation and repair, skin and mucosa maintenance |
| FGF-8 | Embryonic stem cells, fibroblasts | Regulates embryonic development, neural and organ formation |
| FGF-9 | Fibroblasts, chondrocytes | Promotes chondrocyte proliferation, skeletal development and repair |
| FGF-10 | Epithelial cells, glandular cells | Promotes epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation, organ development and tissue repair |
| FGF-11 | Neurons, cardiomyocytes | Regulates neuronal growth, cardiac development and repair |
| FGF-12 | Neurons, cardiomyocytes | Modulates neuronal electrical activity, regulates cardiomyocyte contraction |
| FGF-13 | Fibroblasts, neurons | Regulates cell polarity and neuronal development |
| FGF-14 | Neurons, cardiomyocytes | Modulates neuronal electrical activity, cardiac development and repair |
| FGF-15 | Hepatocytes, intestinal cells | Regulates embryonic development, liver and intestinal function |
| FGF-16 | Cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelial cells | Cardiac and vascular development, vascular structure maintenance |
| FGF-17 | Brain tissue, cardiomyocytes | Regulates neural and cardiac development, tissue repair |
| FGF-18 | Chondrocytes, osteocytes | Promotes cartilage and bone development and repair |
| FGF-19 | Hepatocytes, intestinal epithelial cells | Regulates bile acid synthesis and insulin sensitivity |
| FGF-20 | Neurons, embryonic stem cells | Neural development and tissue repair |
| FGF-21 | Hepatocytes, adipocytes | Regulates energy metabolism and lipolysis |
| FGF-22 | Skin cells, epithelial cells | Promotes skin and epithelial tissue growth and repair |
| FGF-23 | Osteocytes, renal tubular cells | Regulates phosphate and calcium metabolism, skeletal and renal function |
Note: The table above summarizes the common applications and functions of FGF1 to FGF23 in cell culture. Specific conditions and effects may vary depending on experimental design and cell type. Researchers should adjust protocols based on specific requirements.
Summary and Outlook
The growth factors of the FGF family hold broad application prospects in the field of cell culture. They play pivotal roles in the cultivation of stem cells, organoids, and other advanced models. With further research into the FGF family, we anticipate discovering additional members with significant value, thereby advancing cell culture technologies and their applications. In the future, FGF family growth factors are expected to play an even greater role in tissue engineering, drug development, regenerative medicine, and other fields, contributing significantly to improving human health and quality of life.
1.David M. Ornitz,Nobuyuki Itoh.The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Periodicals.2015,May-Jun;4(3):215-66.
2.Hu MC, Shiizaki K, Kuro-o M, Moe OW. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Klotho: physiology and pathophysiology of an endocrine network of
mineral metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 2013, 75:503–533.
3.Itoh N. FGF21 as a hepatokine, adipokine, and myokine in metabolism and diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014, 5:107
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA040070 | FGF-21 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $560 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040075 | FGF-21 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $136 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040013 | FGF-21 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $480 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040001 | FGF-21 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $360 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040086 | FGF-19 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $156 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040094 | FGF-18 Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $576 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040092 | FGF-18 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040139 | FGF-17 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $136 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040116 | FGF-12 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $124 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040076 | FGF-10 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $576 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040037 | FGF-10 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040097 | FGF-9 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $800 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040087 | FGF-9 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $800 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040049 | FGF-8e Protein, Human | Host : Human | $696 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040074 | FGF-8c Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $696 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040027 | FGF-8b Protein, Human | Host : Human | $696 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040110 | KGF/FGF-7 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $600 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040046 | FGF-4 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040032 | FGF-1/FGF-Acidic Protein, Human | Host : Human | $276 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040089 | FGF-1 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $276 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040170 | FGF-basic (154aa) Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $121 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040197 | FGF-basic Protein, Bovine | Host : Bovine | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040007 | FGF-basic(154aa) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $216 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040145 | FGF-basic(146aa) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $80 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




