Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
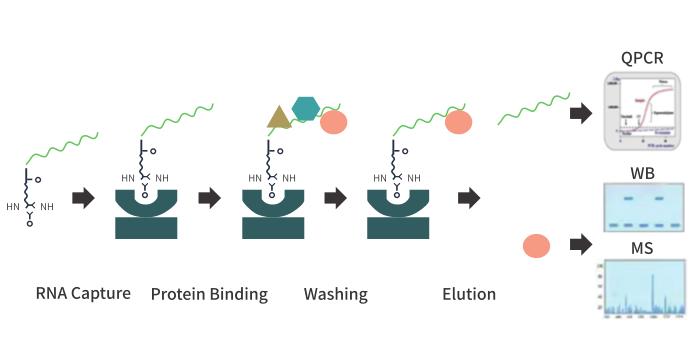
| Usage | A: RNA binds to protein (optional) 1. Sample lysis (1) Cell samples (1) cracking liquid preparation: take 990 ul IP lysis buffer, add 10 ul Protease inhibitor (100 x), blending; ② 2xl07 cell samples were collected and washed with 2mL PBS. After centrifugation, the supernatant was discarded to collect cell precipitation, and 1/4 cell samples were reserved for RNA extraction and purification in Input group (stored in nuclease-free EP tube at -80°C). ③ Add the lysis solution to the remaining cell precipitate and resuspend it, and blow and mix 10 times with a pipetting gun to make the cells fully lysed. The cells were incubated in an ice bath for 30min, vortexed every 5min, 10s/ time. Cracking after the completion of the use of ultrasonic cell disruptor ice bath ultrasonic 5 min, 20% power, ultrasonic 3 s, intermittent 3 s; ⑤ Centrifuged at 12000rpm for 10min at 4℃, the supernatant was taken, and then IP Lysis Buffer was added to the supernatant to a volume of 1mL, mixed, and divided into three parts according to 450uL (control group), 450uL (experimental group), and 100uL (Input). The Input samples were stored at -80°C for later use. (2) animal tissues ① lysis preparation: 990uL IP lysis buffer was added to 10uL Protease inhibitor(100×) and then mixed. ② Fresh or low-temperature tissues (about 0.3g) were placed in a pre-cooled mortar after sterilization, and rapidly ground to powder by adding liquid nitrogen. About 1/4 of the tissue samples were collected for RNA extraction in the subsequent Input group (stored in EP tube without nuclease and stored at -80°C). ③ Add 800uL lysate to the remaining sample of mortar, grind it on ice for 5-10min until the sample is fine and homogenized, and transfer it to a new EP tube. Then add the remaining 200uL lysate to the mortar to collect the remaining sample, and transfer it to the EP tube as well. (4) samples containing homogenate of 30 min EP tube fully crack on the ice, once every 5 min vortex, 10 s/time; (5) pyrolysis with ultrasonic cell disruption instrument ice bath after the completion of ultrasonic 8 to 10 min, 20% power, ultrasonic 3 s, intermittent 3 s; ⑥ Centrifuged at 12000rpm for 10min at 4℃, the supernatant was taken, and then IP Lysis Buffer was added to the supernatant to a volume of 1mL, mixed, and divided into three parts according to 450uL (control group), 450uL (experimental group), and 100uL (Input). The Input samples were stored at -80°C for later use. B: the combination of RNA and RNA (optional) 1, the prey of RNA 1) prey RNA extracted from sample (unknown) prey RNA; (2) the direct synthesis of prey RNA (prey RNA known); (3) by PCR amplification, recycling, agarose gel in vitro transcription and a series of steps for prey RNA (prey RNA is known). Note: If prey RNA is known, it is necessary to determine the obtained RNA in advance. Three ways to be reserved for prey RNA 1/4 as Input for subsequent test for reference. 2, magnetic beads bind to RNA Preparation: (1) Magnetic Beads take 2 1.5 mL without nuclease EP mark tube in the control group and experimental group, remove the kit in Nucleic Acid - Compatible Streptavidin Magnetic Beads, after thoroughly incorporated, taking 40 join the EP tube ul Magnetic Beads; 2. 2 EP tube in the magnetic rack, let stand for 1 min, abandon protection and liquid; ③ The magnetic beads were washed with 200uL Wash Buffer I, and the beads were resuspended by vortexing the EP tube. After low-speed centrifugation, the beads were placed on the magnetic frame, left for 1min, and Wash Buffer I was absorbed and discarded. (4) to join in washing complete magnetic beads 300 ul 1 x RNA binding buffer, the vortex shock EP heavy suspension magnetic beads; (5) to add 150 into the experimental group EP tube pmol biotin labeled probe experiment, EP tube to the control group to join 150 pmol biotin labeling on the control of the probe, and pipetting gun gently blowing mixture; ⑥ Place on a silent mixer and incubate for 2 hours at room temperature with rotation. 3, RNA-magnetic bead complexes bind to proteins A: RNA-bead complex bound to protein (optional) ① Two EP tubes that had completed RNA-magnetic bead incubation were placed on a magnetic frame, and the supernatant was discarded. (2) with 200 ul for Wash Buffer I washing magnetic beads, vortex tube shock EP heavy suspension magnetic beads, microcentrifuge after low-speed centrifugal on magnetic rack, let stand for 1 min, abandon absorption for Wash Buffer, the steps to implement three times; (3) according to the following table in order to wash finish adding volume of corresponding reagent EP tube;
④ After vortexing and mixing, the mixture was stirred and incubated at 4°C overnight. B: RNA-magnetic bead complex binding to RNA (optional) ① Two EP tubes that had completed RNA-magnetic bead incubation were placed on a magnetic frame, and the supernatant was discarded. ② The magnetic beads were washed with 200uL Wash Buffer I, and the beads were resuspended by vortexing the EP tube. After low-speed centrifugation, the beads were placed on the magnetic frame, left for 1min, and Wash Buffer I was absorbed and discarded. (3) to join in washing complete magnetic beads 300 ul 1 x RNA binding buffer, the vortex shock EP heavy suspension magnetic beads; (4), respectively, to join in the control group and experimental group EP tube 20 ug or 200 pmol prey of RNA, and move gently blowing mixed liquid gun, 4 ° C, stir incubation overnight; ⑤ Put the EP tube on the magnetic frame and discard the supernatant; 6 in 200 ul for Wash buffer washing magnetic beads, I heavy suspension magnetic beads, tube vortex EP microcentrifuge after low-speed centrifugal on magnetic rack, let stand for 1 min, abandon absorption for Wash buffer, I collect magnetic beads, the step, 3 times, skip to step 4. 4, washing of RNA-binding protein complexes 1) will be completed in 3 a protein - RNA - magnetic beads incubation EP tube into the magnetic rack, absorbing supernatant; ② Wash the magnetic beads with 200uL Wash Buffer I, resuspend the magnetic beads by vortexing EP tube, centrifuge at low speed and put them on the magnetic stand for 1min. Wash Buffer I was absorbed and discarded to collect the magnetic beads. (3) with 200 ul for Wash Buffer II washing magnetic beads, heavy suspension magnetic beads, tube vortex EP microcentrifuge after low-speed centrifugal on magnetic rack, let stand for 1 min, abandon absorption for Wash Buffer II, collect magnetic beads, the steps to implement three times; (4) to join in washing finished EP tube 200 ul for Wash Buffer II, after blending number assigned to the corresponding volume tube (if there are two or more downstream experiment, it needs to be in charge of magnetic beads, the control group and experimental group are to set up, there are several kinds of downstream experiment, each tag several tube, Suggestions according to the WB/volume: silver stain qPCR: Mass spectrometry is allocated = 3:5:2); ⑤ The EP tube that separated the magnetic beads was put into the micro-centrifuge for low-speed centrifugation, and then placed on the magnetic frame for 1min. Wash Buffer II was aspirated and discarded to collect the magnetic beads. 5, protein elution (downstream for WB or silver stain, choose to do) ① 100uL Elution Buffer was added to each of the two EP tubes after washing, then the elution buffer was mixed and boiled for 10 min. (2) after the microcentrifuge low-speed centrifugal on magnetic rack, let stand for 1 min, from the qing to the new tag good EP tube; ③ Add 10uL 6×Loading Buffer to two new EP tubes. Step 1 Add 10uL 6×Loading Buffer to 100uL Input reserved after adding lysate, mix well, and store at -20°C. 6, RNA extraction (downstream as QPCR, choose to do) ① Add 500uL Trizol to each EP tube after washing. Step 1 Add 500uL Trizol to EP tube with 1/4 cells reserved, vortex and mix, leave for 5min, add 100uL chloroform, vortex and mix, centrifuged at 4 ° C at 14000rpm for 10min; ② Take the upper aqueous phase (about 250uL) into a new EP tube, add 50uL solution I and 500uL isopropanol, vortex and mix, and precipitate RNA at -80°C overnight; (3) take out overnight to precipitate EP tube in 4 ° C, 4 ° C, 14000 RPM centrifuge for 10 min, abandon the supernatant; (4) with 1 ml of 75% ethanol, vortex blending, 4 ° C let stand for 5 min, 4 ° C 14000 RPM centrifuge for 10 min, abandon supernatant, the steps to implement three times; ⑤ Open the lid at room temperature for 3-5min, add appropriate amount (10-20uL)DEPC water to dissolve RNA. 7, mass spectrometry (downstream for mass spectrometry, choose to do: if the samples of mass spectrometry for protein liquid, can be directly from the sampling in step 5, need not operation this step) ① Add 200uL precooled 1×PBS washing magnetic beads to the washed EP tube, separate by magnetic force, and abandon the washing solution. This step is carried out for a total of 3 times; ② - 20 ° C save mass spectrum identification. |
||||||||
| Synonym | RNA Pull Down Kit | ||||||||
| Description |
I. Experimental principle RNA pull-down is a technique for studying the binding of RNA to protein/RNA in cells. RNA is first labeled (such as biotin labeling), and then incubated with cell lysates to form RNA-RNA/protein complexes, and then the bound RNA or protein can be detected. After elution of the complex, real-time quantitative PCR (RNA pull down QPCR) or high-throughput sequencing (RNA pull down seq) were used to identify whether the target RNN interacted with certain RNA molecules. Western blot (pull down-WB) assay and mass spectrometry (pull down -MS) technology was used to detect whether the target RNA interacted with certain proteins. |
||||||||
| General Notes | It is used mainly in animals. | ||||||||
| Storage Temp. | Store at -20 & 4 ° C (see component storage information for details); Valid for 1 year. |