CEACAM6: A Rising Star in the Field of Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment
CEACAM6
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6), with its unique biological characteristics, close association with tumors, and potential in drug development, has become the focus of attention for researchers and pharmaceutical companies. It is expected to bring new breakthroughs in tumor diagnosis and treatment.
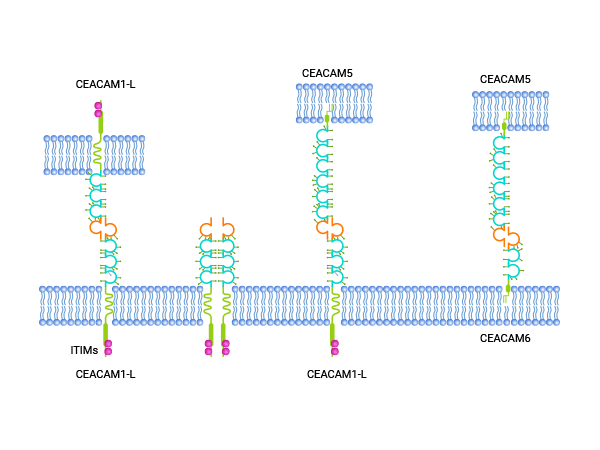
The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family is like a treasure trove, and CEACAM6 is a highly promising "pearl" within it. This family is divided into two major categories: carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAM) and pregnancy-specific glycoproteins (PSG). The CEACAM family has numerous members, including at least 12 proteins. Proteins such as CEACAM1, CEACAM5, and CEACAM7 have already become important drug targets, and CEACAM6 also demonstrates extraordinary value in tumor research. CEACAM6 is located at q13.2 of chromosome 19 and is anchored to the cell membrane through glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). The protein encoded by it contains 344 amino acid residues. It has a unique structure, possessing an N-terminal immunoglobulin variable region (IgV), a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic region. It can interact through homophilic or heterophilic affinities and work in concert with multiple receptors, playing an important role in the "communication" between cells.
The Abnormal Expression of CEACAM6 in Tumors
In normal cells, CEACAM6 is like a low-key "guardian" and is expressed at low levels in normal epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells, etc. However, on the "stage" of tumors, it seems to transform into an "accomplice" and is highly expressed in many malignant tumors. It can be found actively involved in tumors of the digestive system, such as cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, and gastric cancer, as well as tumors in the breast, reproductive system, lungs, and other parts.
It participates in several key links of tumor occurrence and development, promoting the proliferation of tumor cells, making cancer cells grow rampantly like out-of-control wild grass; enhancing the migration and invasion abilities of cells, helping cancer cells break through tissue barriers and spread to surrounding tissues; inhibiting the apoptosis of tumor cells, enabling cancer cells to escape the "sanction" of death; and promoting angiogenesis, constructing a "nutritional channel" for the growth and metastasis of tumors. These characteristics make it a 标志性分子 of invasive tumors and also provide potential "targets" for tumor treatment.
The Mechanism of CEACAM6's Involvement in the Tumor Process
When delving deeper into the mechanism of CEACAM6's action in tumors, it can be found that it is involved in a complex cellular signaling network. It is closely linked to the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. When CEACAM6 is overexpressed, it will trigger the remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and activate the tumor microenvironment (TME). During this process, the activity of Src is enhanced, which activates autocrine and insulin-like growth factor IGF-1R, and then regulates the PI3K/Akt pathway, promoting the survival and migration of tumor cells.
At the same time, after CEACAM6 aggregates on the cell surface, it binds to caveolin-1 (Cav1), phosphorylates FAK, and increases the cell's resistance to anoikis. In addition, the TGF-β signaling pathway also interacts with CEACAM6. After TGF-β binds to its receptor, it can not only increase the expression of CEACAM6 but also activate other signaling pathways to jointly drive the development of tumors. This series of complex molecular mechanisms poses challenges for tumor treatment and also points out the direction.
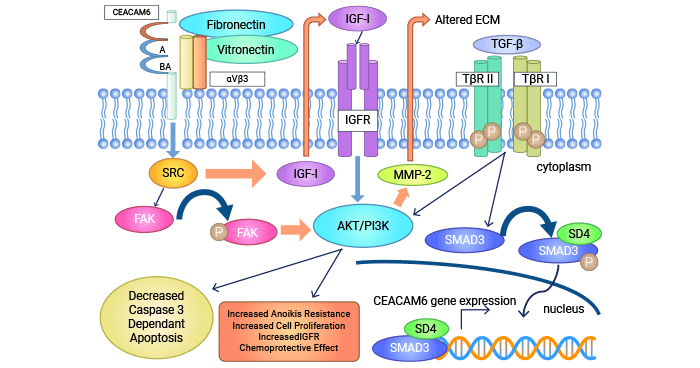
The Key Role of CEACAM6 in Multiple Cancers
CEACAM6 plays a crucial role in multiple cancers. In cholangiocarcinoma, the high expression of CEACAM6 is closely related to lymph node metastasis and tumor staging. It is an important indicator of poor prognosis for patients and is also associated with gemcitabine resistance. Interfering with its expression can change the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapy drugs.
In pancreatic cancer, the overexpression of CEACAM6 endows cancer cells with the ability to resist anoikis, promotes tumor metastasis, and also leads to resistance to gemcitabine. In breast cancer, it promotes angiogenesis, affects disease progression and endocrine therapy resistance, and its expression level can be used as an indicator to predict the treatment effect of breast cancer. In colon cancer, the expression of CEACAM6 increases with the progression of the disease, inhibits the infiltration of immune cells, and affects the tumor microenvironment. In gastric cancer, it enhances the migration and invasion abilities of cancer cells, inhibits apoptosis, and participates in the occurrence and development of tumors. In various cancers such as lung cancer, thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma, leukemia, and multiple myeloma, CEACAM6 also plays an important role and affects the course of tumors.
The Progress of Drug Development Targeting CEACAM6
Given the key role of CEACAM6 in tumors, the development of drugs targeting it is in full swing. Currently, several drugs targeting CEACAM6 are at different stages of development. Sulesomab (manufactured by Immunomedics) has been approved for marketing and is used for the diagnosis of osteomyelitis. Drugs such as L-DOS-47, NEO-201, and EBC-129 are in phase 2 clinical trials, phase 1/2 clinical trials, and phase 1 clinical trials respectively, and are being studied for multiple cancers such as pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. There are also drugs like PM-4008, DNP-002, BAY-1834942, etc., which are in the preclinical research stage, as well as ICT-109 that is currently in the process of drug discovery. The development of these drugs brings new hope for tumor treatment and is expected to provide more precise and effective treatment options for patients.
Future Prospects
With the continuous deepening of research on CEACAM6, its value in the field of tumor diagnosis and treatment will be further highlighted. In the future, it may not only serve as an important biomarker for tumor diagnosis and prognosis evaluation but also potentially become a key target for tumor treatment.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA010474 | FITC-Labeled CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : FITC | |||
| UA010475 | FITC-Labeled CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : FITC | |||
| UA010740 | Biotinylated CEACAM-6/CD66c Fc&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010697 | Biotinylated CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010694 | Biotinylated CEACAM-6/CD66c His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010746 | Biotinylated CEACAM-5/CD66e His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010836 | Biotinylated CEACAM-1/CD66a His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010375 | CEACAM-8/CD66b His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $504 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010336 | CEACAM-6/CD66c His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010288 | CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010358 | CEACAM-3/CD66d His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $620 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010344 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $504 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010389 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010274 | CEACAM-6/CD66c Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010368 | CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010277 | CEACAM-3/CD66d Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $620 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010334 | CEACAM-6/CD66c His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010376 | CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010325 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $540 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0A1010 | Human CD66b, His tag | Host : Human | Inquiry |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0521 | CD66b Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-766-55) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0499 | CD66a/CEACAM1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-678-53) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0411 | CEACAM6 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-720-54) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2091 | CEA(CD66e) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | $880 |
| S0B2091P | CEA(CD66e) Recombinant Rabbit mAb,PBS Only (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| S0A6001 | Human CEA, His Tag | Host : Human | $100 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3056 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-61) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
| S0B3055 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
| S0B3054 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-41) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
Reference
[1] Witzens-Harig, Mathias, et al. "Tumor cells in multiple myeloma patients inhibit myeloma-reactive T cells through carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-6." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 121.22 (2013): 4493-4503.
[2] Zhang, Feng, et al. "ING5 inhibits cancer aggressiveness via preventing EMT and is a potential prognostic biomarker for lung cancer." Oncotarget 6.18 ( 2015): 16239.
[3] Strickland, Laura A., et al. "Preclinical evaluation of carcinoembryonic cell adhesion molecule (CEACAM) 6 as potential therapy target for pancreatic adenocarcinoma." The Journal of Pathology: A Journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland 218.3 (2009): 380-390.
[4] Riley, Christopher J., et al. "Design and activity of a murine and humanized anti-CEACAM6 single-chain variable fragment in the treatment of pancreatic cancer." Cancer research 69.5 (2009): 1933-1940.




