CEACAM5: A New Target for Tumor Immunotherapy
Characteristics of CEACAM5
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5) has been used as a tumor marker for colorectal cancer to assist in tumor research. In recent years, with the deepening of research, CEACAM5 has started to be used as a tumor target for the development of new drugs. A number of studies have shown that it not only plays a crucial role in the occurrence and development of various tumors, but also serves as a highly potential tumor marker and therapeutic target, bringing new hope for the conquest of cancer.
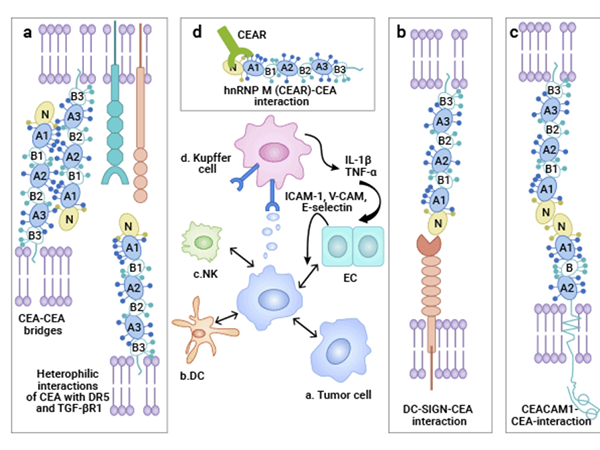
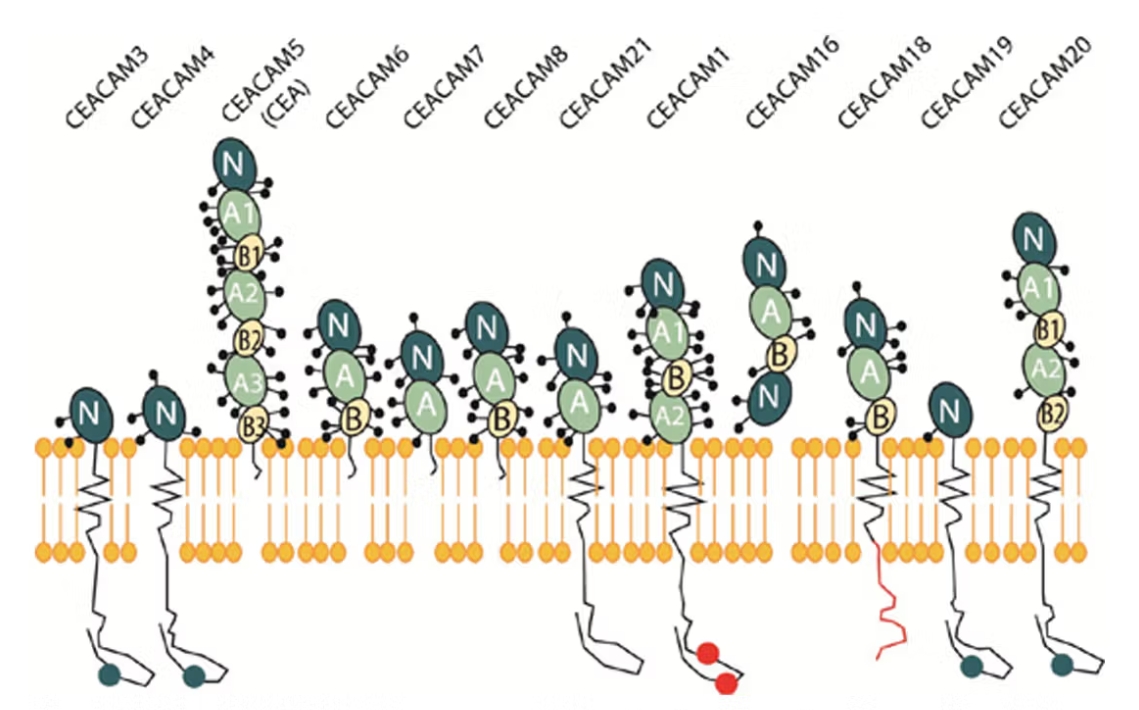
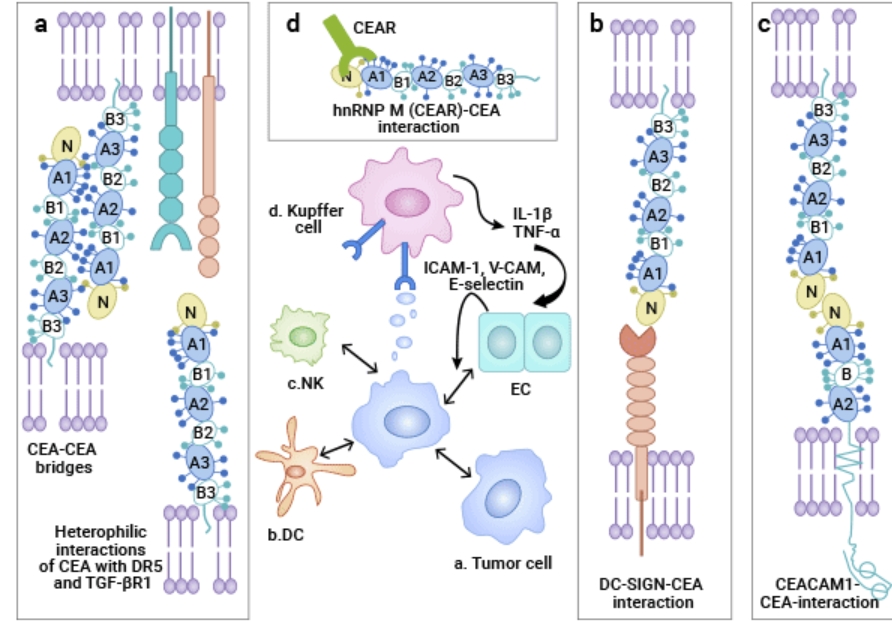
CEACAM5 belongs to the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-related cell adhesion molecule family. Its protein product has a unique structure, consisting of seven characteristic extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) chains and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol chain, presenting a domain structure of N - A1 - B1 - A2 - B2 - A3 - B3. Under normal physiological conditions, CEACAM5 is widely distributed on the surfaces of various cells such as endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and immune cells. It undertakes the important responsibility of cell adhesion, maintaining the normal connections between cells and the homeostasis of tissues. However, in the tumor microenvironment, its role changes dramatically. In many solid tumors, such as colorectal cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, gastric cancer, breast cancer, as well as various cancer tissues like mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary gland, pancreatic tumors, and gallbladder tumors, CEACAM5 is often abnormally overexpressed, which is closely related to tumor invasion, metastasis, and poor prognosis.
The Mechanism of CEACAM5 Promoting Tumor Development
In the process of tumor occurrence and development, CEACAM5 plays multiple "villainous" roles. On the one hand, it exerts an anti-adhesion effect, helping tumor cells to break through the connection constraints between cells, creating conditions for tumor invasion and distant metastasis. On the other hand, the overexpression of CEACAM5 will promote the degradation of the extracellular matrix, disrupting the stability of the extracellular environment and making tumor cells more prone to migration. At the same time, it can also activate the integrin signaling pathway, involving key elements such as integrin-linked kinase (ILK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and protein kinase B (AKT), continuously transmitting survival and proliferation signals to tumor cells, further driving the deterioration of tumors.
In addition, CEACAM5 also has a unique influencing mechanism in platelet activation. The soluble carcinoembryonic antigen (sCEA) released after its decomposition by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C/D (PI-PLC/D) can activate the c-Src kinase/mitogen-activated protein-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAP-ERK) kinase signaling pathway, thereby promoting a series of behaviors of vascular endothelial cells, such as adhesion, spreading, proliferation, and migration, which has an important impact on tumor microvascularization.
The Value of CEACAM5 in Tumor Clinical Research
From the perspective of clinical research, CEACAM5 has demonstrated great value in the diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and treatment of various tumors.
n the field of colorectal cancer, although CEACAM5 has certain limitations when used alone as a detection indicator, combined detection with markers like caudal type homeobox 2 (CDX2) can significantly improve the accuracy of evaluating the disease progression and prognosis of patients.
In patients with lung adenocarcinoma, the high expression of CEACAM5 is closely related to a decrease in survival rate, and together with clinical stage and lymph node metastasis, it becomes a key risk factor affecting prognosis.
In the research of gastric cancer, the expression level of CEACAM5 gradually increases with the progression of the disease. It can not only be used to predict the risk of gastric cancer occurrence but also serves as an independent prognostic indicator. The higher the expression, the shorter the survival period of patients is usually.
In the aspect of breast cancer, the level of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) labeled by CEACAM5 mRNA in the peripheral blood before surgery is significantly increased in patients with metastatic breast cancer, making it a potential biomarker for predicting the distant metastasis of breast cancer.
The Progress of Drug Development Targeting CEACAM5
Fortunately, based on the key role of CEACAM5 in tumors, the development of drugs targeting it is in full swing. Up to now, 15 related drugs are at different stages of development, covering various types such as monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy, trispecific antibodies, and vaccines. Among them, Tusamitamab ravtansine developed by Sanofi has shown excellent performance in the study of treating patients with CEACAM5-positive advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. The overall response rate of combination therapy reaches 40%, and the disease control rate is as high as 88%. Currently, it has entered the third phase of clinical trials and is just one step away from being launched on the market. Other drugs are also steadily advancing in their respective clinical stages, continuously exploring more possibilities of CEACAM5 as a therapeutic target.
Future Prospects
With the continuous deepening of research and the continuous progress of technology, CEACAM5 is expected to become a powerful weapon in the field of tumor diagnosis and treatment. In the future, it may not only assist in tumor diagnosis and prognosis assessment more accurately, but also lead a new direction for personalized tumor treatment. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies are also closely collaborating to continuously optimize the drug development strategy targeting CEACAM5.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA010474 | FITC-Labeled CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : FITC | |||
| UA010475 | FITC-Labeled CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : FITC | |||
| UA010740 | Biotinylated CEACAM-6/CD66c Fc&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010697 | Biotinylated CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010694 | Biotinylated CEACAM-6/CD66c His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010746 | Biotinylated CEACAM-5/CD66e His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010836 | Biotinylated CEACAM-1/CD66a His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $490 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010375 | CEACAM-8/CD66b His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $504 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010336 | CEACAM-6/CD66c His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010288 | CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010358 | CEACAM-3/CD66d His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $620 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010344 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $504 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010389 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010274 | CEACAM-6/CD66c Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010368 | CEACAM-5/CD66e Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010277 | CEACAM-3/CD66d Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $620 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010334 | CEACAM-6/CD66c His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010376 | CEACAM-5/CD66e His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $520 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010325 | CEACAM-1/CD66a His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $540 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0A1010 | Human CD66b, His tag | Host : Human | Inquiry |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0521 | CD66b Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-766-55) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0499 | CD66a/CEACAM1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-678-53) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0411 | CEACAM6 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-720-54) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2091 | CEA(CD66e) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | $880 |
| S0B2091P | CEA(CD66e) Recombinant Rabbit mAb,PBS Only (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| S0A6001 | Human CEA, His Tag | Host : Human | $100 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3056 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-61) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
| S0B3055 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-54) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
| S0B3054 | CEA Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-098-41) | Host : Rabbit | $80 |
Reference
[1] Beauchemin, Nicole, and Azadeh Arabzadeh. "Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs) in cancer progression and metastasis." Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 32 (2013): 643-671.
[2] Wan, Wen, et al. "Platelet Carcinoembryonic Antigen Cell Adhesion Molecule 5 (CEACAM5) as a Possible Novel Diagnostic Tool for Evaluation of Acute Coronary Syndrome." Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research 25 (2019): 9864.
[3] Xiao, Yitai, et al. "Identification of a CEACAM5 targeted nanobody for positron emission tomography imaging and near-infrared fluorescence imaging of colorectal cancer." European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2023): 1-14.




