Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSFs): The Conductor of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation

Introduction
Colony-Stimulating Factors (CSFs) are a class of proteins that play a crucial role in biological systems. Their primary function is to stimulate and regulate the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells, thereby contributing to the process of hematopoiesis. Based on the cell types they target and their specific effects, CSFs are further categorized into various types, including SCF, G-CSF, M-CSF, GM-CSF, EPO, and TPO.
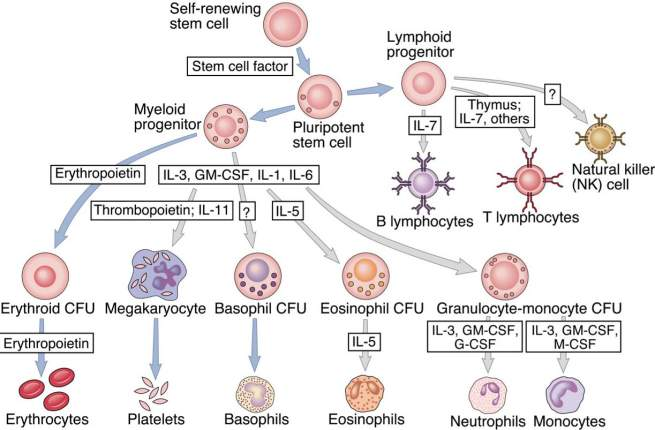
Classification and Functions
The primary function of colony-stimulating factors is to stimulate hematopoietic progenitor cells to form colonies in vitro, thereby mimicking the in vivo hematopoiesis process. By binding to specific receptors on the cell surface, CSFs activate intracellular signaling pathways, promoting cell proliferation and differentiation. These processes are essential for maintaining blood cell homeostasis and combating various diseases.
Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (M-CSF)
Cell Sources: Monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, etc.
Biological Functions:
Stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of monocytes and macrophages.
Prolongs the survival of monocytes and macrophages and enhances their functionality.
M-CSF, Human

Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Murine M-NFS-60 cells, The EC50 for this effect is less than 5ng/ml.


Anti-His antibody Immobilized on CM5 Chip captured M-CSFR His Tag, Cynomolgus (Cat. No. UA010204), can bind M-CSF, Human (Cat. No. UA040042) with an affinity constant of 0.3μM as determined in SPR assay.
M-CSF, Mouse

Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Murine M-NFS-60 cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 2ng/ml.

Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF)
Cell Sources: Activated T cells, monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, etc.
Biological Functions:
Stimulates the growth and differentiation of bone marrow progenitor cells.
Promotes the differentiation of bone marrow progenitor cells into granulocytes and monocytes.
GM-CSF, Human

Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 0.5ng/ml.
GM-CSF, Mouse
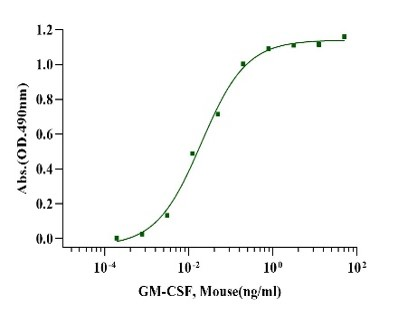
Measured in a cell proliferation assay FDC-P1 cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 0.02ng/ml.

Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF)
Cell Sources: Activated T cells, monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, etc.
Biological Functions:
Stimulates the differentiation and maturation of granulocyte progenitor cells.
Enhances the phagocytic and cytotoxic functions of mature granulocytes and prolongs their survival.
G-CSF, Human
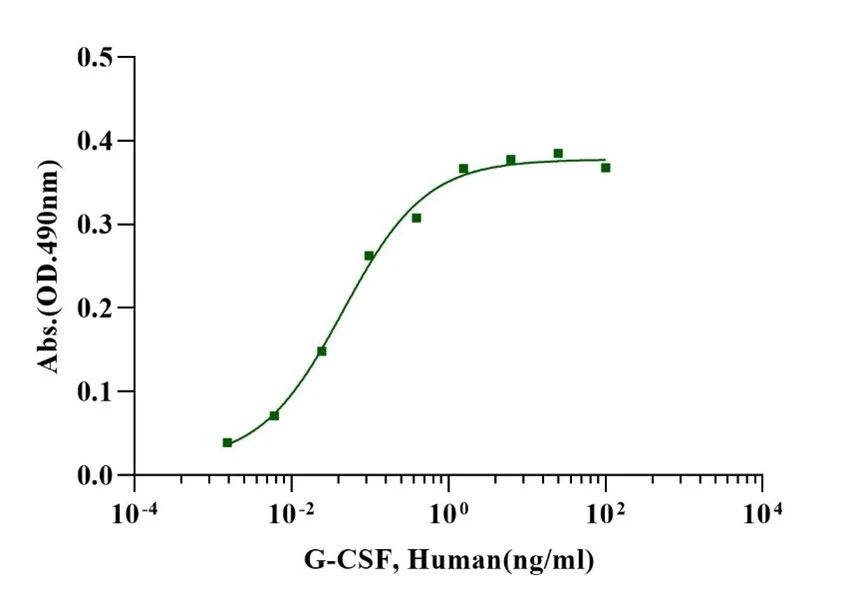
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Murine M-NFS-60 cells, The EC50 for this effect is less than 0.1ng/ml.

G-CSF, Mouse
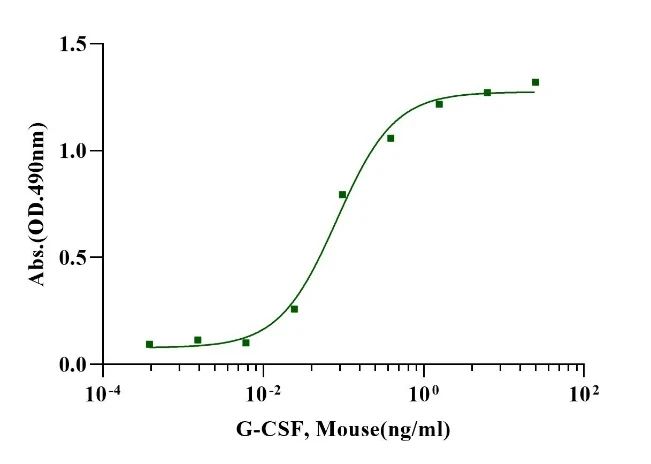
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Murine M-NFS-60 cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 0.05ng/ml.

Stem Cell Factor (SCF, also known as c-Kit Ligand)
Cell Sources: Bone marrow stromal cells.
Biological Functions:
Stimulates the development of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells.
Promotes the proliferation of mast cells.
SCF, Human
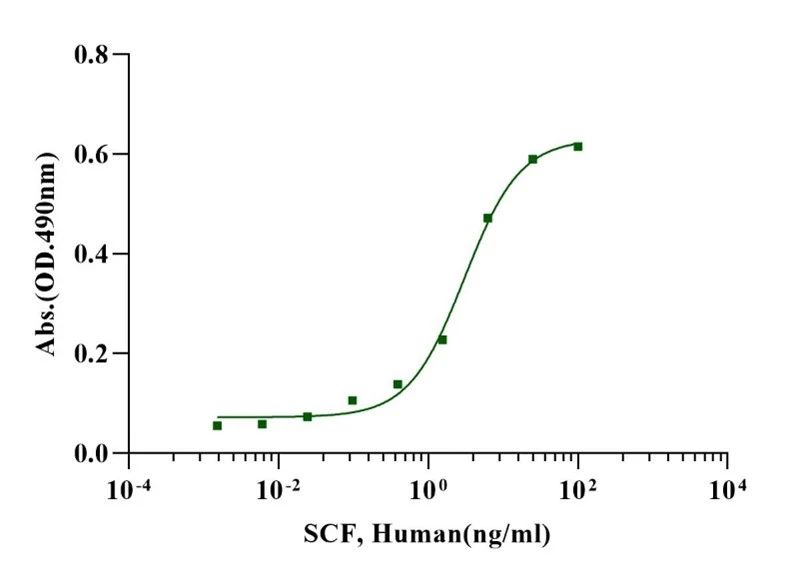
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using human Mo7e cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 3ng/ml.

SCF, Mouse

Measured in a cell proliferation assay using human TF-1 cells, the EC50 for this effect is less than 5ng/ml.
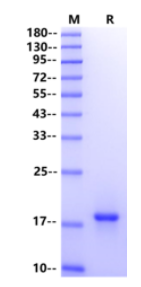
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Cell Sources: Peritubular interstitial cells in the kidney.
Biological Functions: Promotes the differentiation of erythroid progenitors into mature red blood cells.
EPO, Human

EC50 < 0.5ng/ml, measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells
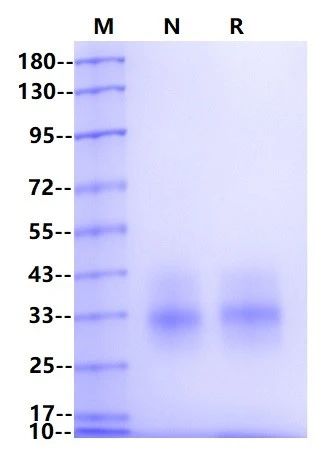
Thrombopoietin (TPO)
Cell Sources: Smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells.
Biological Functions: Stimulates the differentiation and maturation of bone marrow megakaryocytes into platelets.
Future Perspectives
With the deepening of research on colony-stimulating factors, our understanding of their functions and mechanisms of action has significantly advanced. In the future, CSFs are expected to find broader applications in fields such as regenerative medicine and immunotherapy. Additionally, with the development of gene-editing technologies, it may become possible to directly edit the genes encoding CSFs, leading to the development of more effective therapeutic methods and drugs.
In summary, colony-stimulating factors are a class of vital bioactive molecules that play a significant role in maintaining blood cell homeostasis and treating related diseases. As scientific and technological advancements continue, research and applications of CSFs are expected to achieve further breakthroughs and progress.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA040004 | EPO Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,600 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040149 | SCF Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $144.40 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040138 | SCF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $136 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040115 | SCF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $136 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040232 | G-CSF Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $196 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040198 | G-CSF Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $236 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040043 | G-CSF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,160 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040101 | GM-CSF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $156 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040056 | GM-CSF Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $876 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040002 | GM-CSF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $156 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040128 | M-CSF Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $144 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040042 | M-CSF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,000 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040016 | M-CSF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,000 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




