Chemokines and Their Receptors: This Article Provides Comprehensive Insights!
Introduction
Chemokines and their receptors are integral components of cellular signaling networks, playing a pivotal role in maintaining normal physiological processes and the body's immune defense mechanisms. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the concept and classification of chemokines, as well as their interactions with receptors, with a focus on their biological functions in cell migration, immune responses, and inflammatory processes.
Concept and Classification
Chemokines are a class of signaling molecules that guide cells to move in specific directions. They can be categorized into various types, including chemokine families, growth factors, and extracellular matrix molecules, each playing a unique role in cellular signaling. Among these, the chemokine family is a primary focus of research due to its critical role in cell migration.
The biological effects of chemokines are primarily mediated through their binding to corresponding receptors. These receptors typically belong to the seven-transmembrane protein family, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The binding of chemokines to their receptors activates a series of intracellular signaling pathways, thereby influencing cell migration, proliferation, and survival.
The chemokine family is divided into four subfamilies: CXC, CC, (X)C, and CX3C. The functions of inflammatory chemokines may vary significantly across species. For details, see the table below:
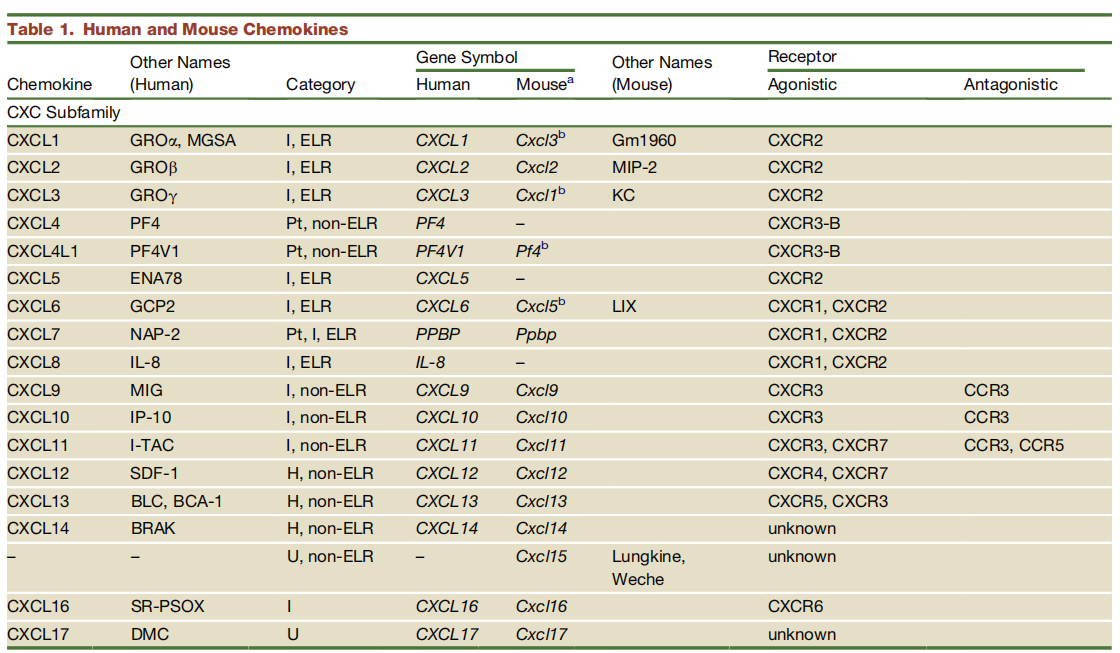
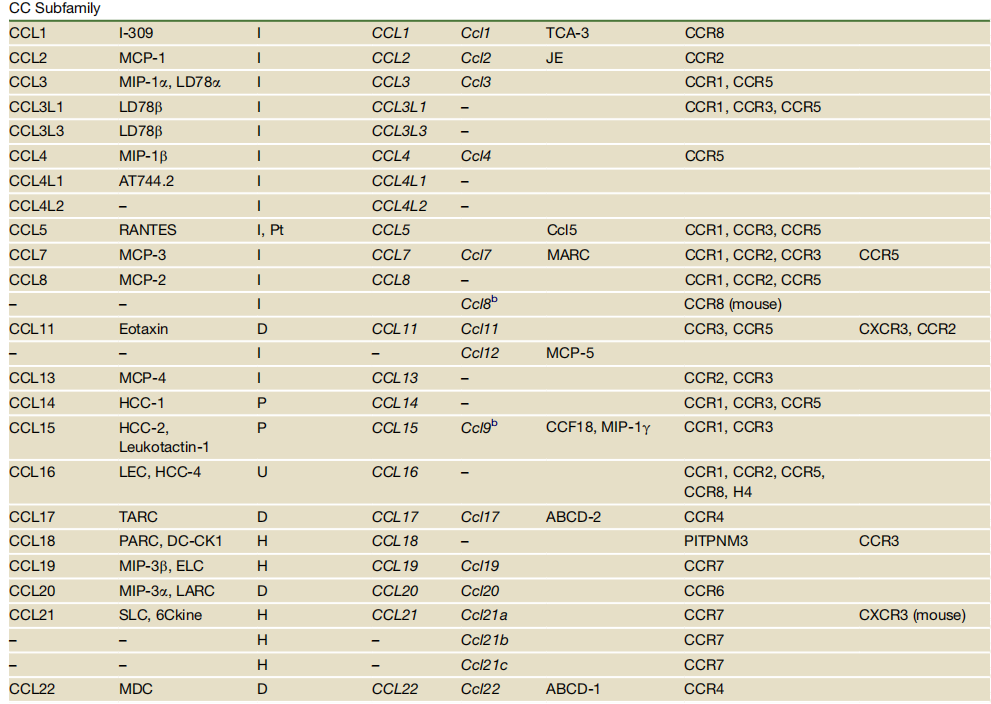
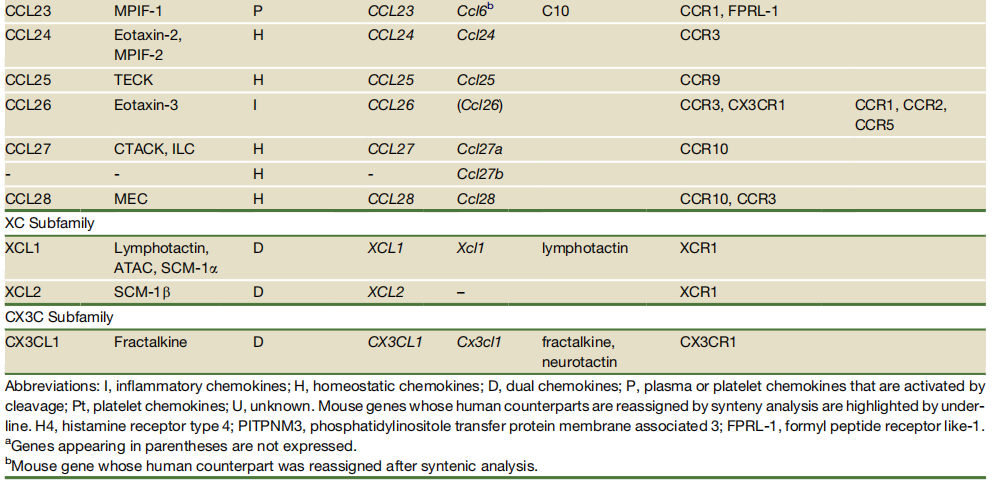
Source: DOI 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.05.008
Chemokine Receptors
To date, 18 chemokine receptors with standard Gai-dependent chemotactic activity have been identified in humans and mice. Additionally, five atypical (non-chemotactic, recycling, or scavenging) chemokine receptors have been described. Notably, inflammatory chemokine receptors often have a large number of chemokine ligands, and some ligands are shared by multiple receptors. For details on chemokine receptors, see the table below:
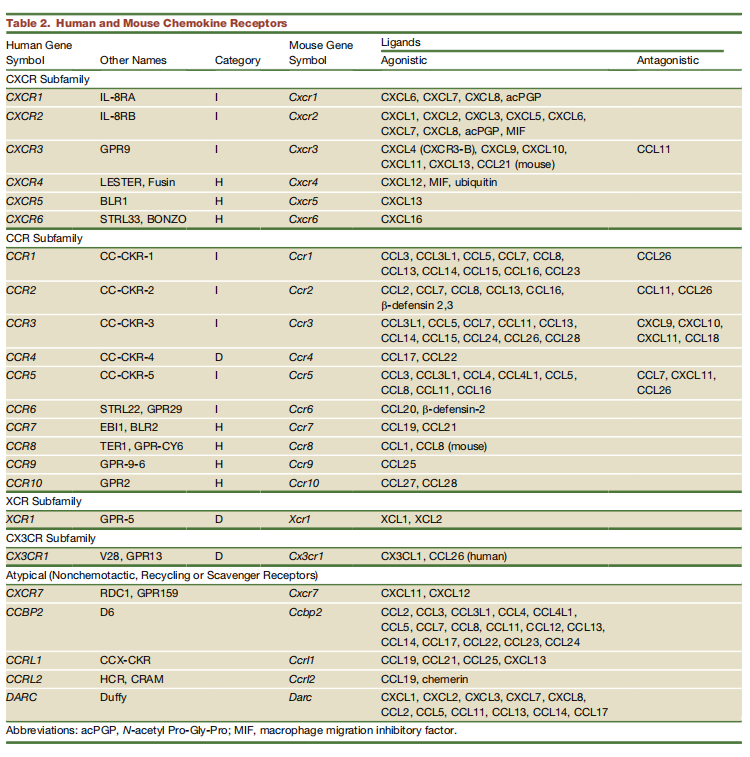
Source: Nomiyama et al., 2011
Biological Functions
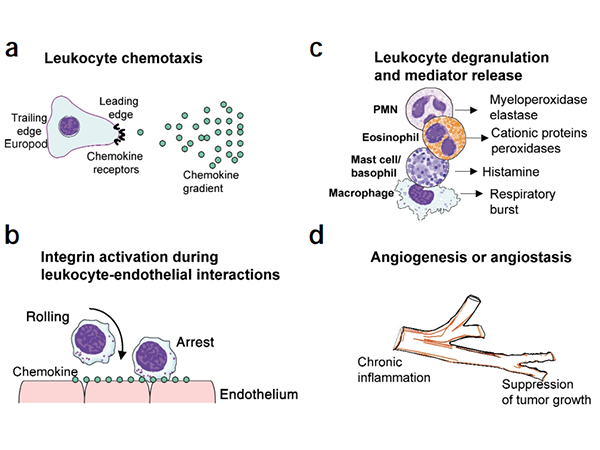
Chemokines play a critical role in cell migration. By binding to cell surface receptors, chemokines guide cells to move in specific directions, participating in physiological processes such as tissue repair and immune cell navigation.
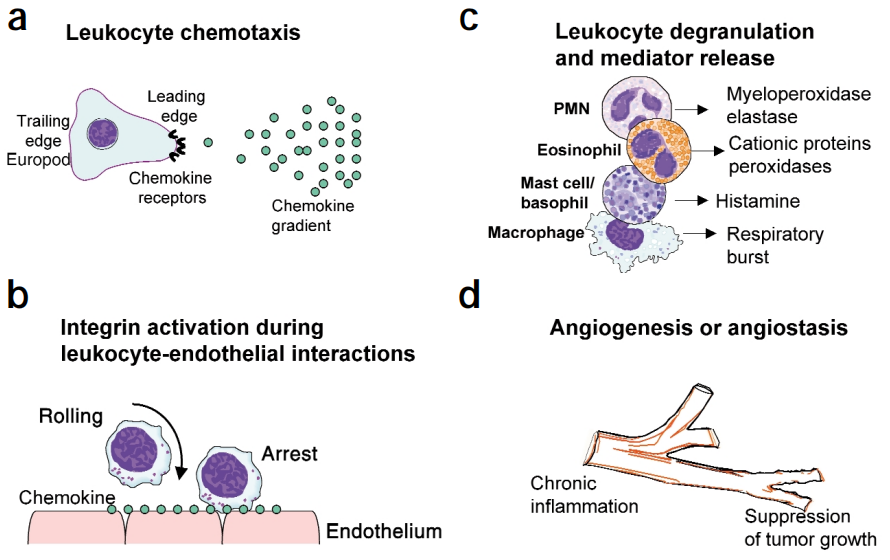
Source: http://immunol.nature.com
Chemoattractants provide directional cues for leukocyte movement by forming gradients that migrating cells can sense. Migrating cells undergo profound transformations, leading to the redistribution of chemokine receptors, integrins, cytoskeletal proteins, and intracellular regulatory molecules. The signaling mechanisms of chemoattractant receptors in cell movement are not yet fully understood but involve tyrosine kinases, lipid kinases, second messengers, and members of the Rho family of small GTPases.
Chemokines stimulate leukocyte degranulation or the release of inflammatory mediators. For example, CCL2 (MCP-1) effectively stimulates basophils to release histamine, while CXCL8 stimulates neutrophil granule exocytosis. Chemokines can also stimulate respiratory bursts, leading to the production of reactive oxygen intermediates.
Some chemokines can stimulate angiogenesis or vascular homeostasis. ELR+ CXC chemokines and CCL2 have angiogenic properties, while CXCR3 ligands, such as CXCL10 and CCL21 (SLC), exhibit angiostatic properties. The biological relevance of the angiogenic or angiostatic properties of chemokines may be related to tumor suppression or inflammatory responses, where angiogenesis is a critical requirement. These diverse properties of chemokines are integrated into various biological responses. For instance, tumor rejection involves the recruitment of leukocytes from the blood, tumor chemotaxis, and vasoconstriction, while allergic inflammation includes leukocyte recruitment and the release of inflammatory mediators.
Chemokines and Disease
Chemokines and their receptors play significant roles in the development and progression of various diseases, such as inflammatory diseases, cancers, and autoimmune disorders. In-depth research on chemokines and their receptors holds promise for identifying new therapeutic targets and strategies for these diseases.
The primary motivation for studying chemokines in diseases is that their expression can be readily documented in conditions associated with leukocyte infiltration. The major chemokine receptors expressed on leukocyte subsets and their associated chemokines are summarized below:
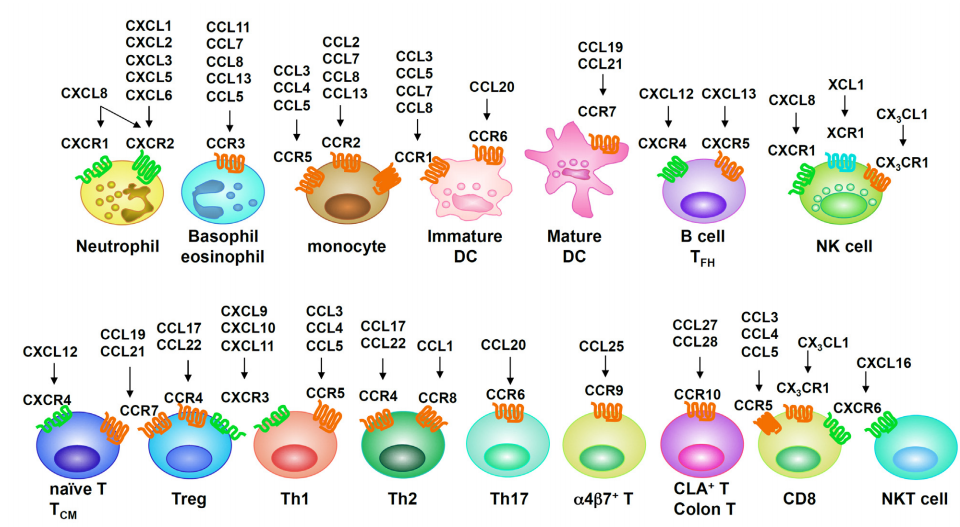
Source: Inflammation and Regeneration Vol.31 No.1 January 2011
Chemokines and Disease: Corresponding Animal Models
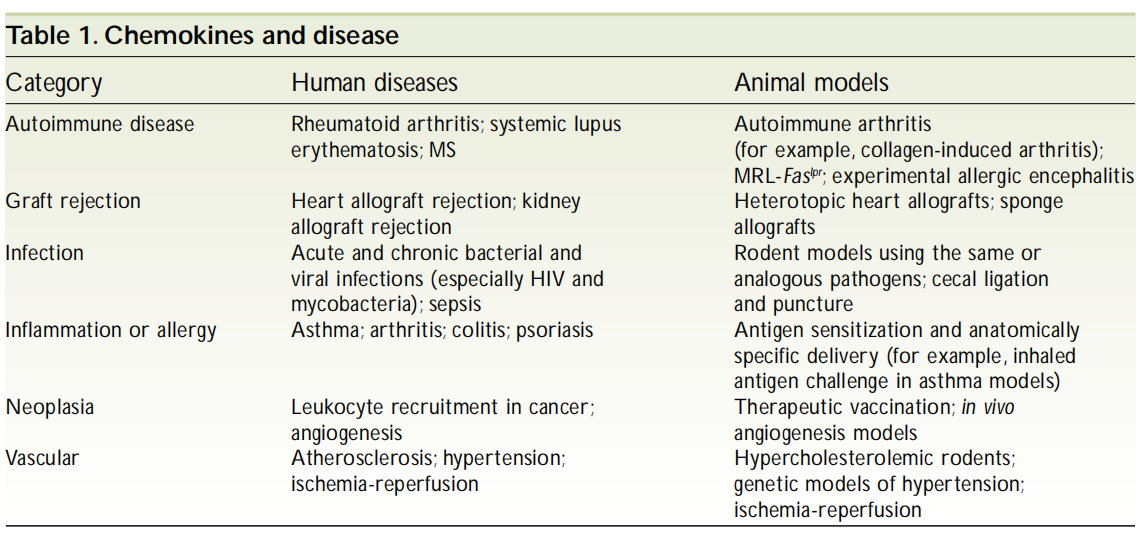
Source: http://immunol.nature.com
Conclusion
Chemokines and their receptors hold an irreplaceable position in cellular signaling, significantly influencing both normal physiological processes and disease development. In-depth research in this field will help elucidate the mechanisms of cellular signaling and provide new insights and approaches for disease treatment.
Research in the field of chemokines continues to advance, with the potential to discover new chemokines, receptors, and their mechanisms of action. Furthermore, by investigating the role of chemokines in diseases, new therapeutic strategies for related conditions may be developed.
1. Craig Gerard, et al. Chemokines and disease.nature immunology. 2001;108-115.
2. Murphy PM, et al. Chemokines and the molecular basis of cancer metastasis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;345(11):833-835.
3. Baggiolini M, et al. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. Journal of Immunology. 1994; 153(8): 3751-3758.
4. Kouji Matsushima, et al. Chemokines: Chemokines in inflammatory and immune diseases. Inflammation and Regeneration Vol. 2011;31:11-22.
5. Rossi D, Zlotnik A. The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annual Review of Immunology. 2000;18:217-242.
6. Charles R. Mackay.Chemokines: immunology’s high impact factors.nature immunology.95-101
7. Albert Zlotnik, et al.The Chemokine Superfamily Revisited.Cell press Immunity 36.2012;5:705-716.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA080160 | Human IKZF1 Protein | Host : Human | $596 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040031 | Tissue Factor Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $1,200 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040132 | TECK/CCL25 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $90 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040131 | TECK/CCL25 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $90 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040025 | RSPO3 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $820 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040230 | RSPO2 C-Flag Protein,Human | Host : Human | Inquiry |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| UA040168 | RANTES/CCL5 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $189 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040022 | R-Spondin 1(21-146) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $696 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040186 | PF-4/CXCL4 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $162 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040189 | NAP-2/CXCL7 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $162 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040164 | MIP-1α/CCL3 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $159 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040133 | MIG/CXCL9 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $156 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040222 | MIG/CXCL9 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $180 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040119 | MIF Protein, Human | Host : Human | $216 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040169 | MDC/CCL22 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $190 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040175 | MCP-1/CCL2 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $200 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040161 | GRO beta/CXCL2 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $178 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040122 | GRO alpha/CXCL1 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $600 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040163 | Eotaxin/CCL11 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $136 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040183 | CXCL4 Protein(C-6His) Protein, Human | Host : Human | $232 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040167 | CXCL14/BRAK Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $178 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040114 | CXCL1 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $162 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040177 | CX3CL1 Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $144 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




