Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV): The Dark Horse Igniting a Billion-Dollar Battle in the Pharmaceutical Industry

The Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), also known as Human Herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3), is a ubiquitous double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily. VZV is notable for its unique mode of infection and clinical manifestations, capable of causing two distinct diseases: varicella (chickenpox) and herpes zoster (shingles).
VZV is an enveloped DNA virus with a structure consisting, from the outside inward, of a lipid envelope, tegument, nucleocapsid, and double-stranded DNA. The virus exhibits a brick-like morphology with an icosahedral capsid. Glycoprotein E (gE) is the most abundantly expressed glycoprotein in VZV, possessing high immunogenicity and playing a critical role in viral infection and cell-to-cell spread.
01. Mechanisms of VZV Infection
Lytic and Latent Infection
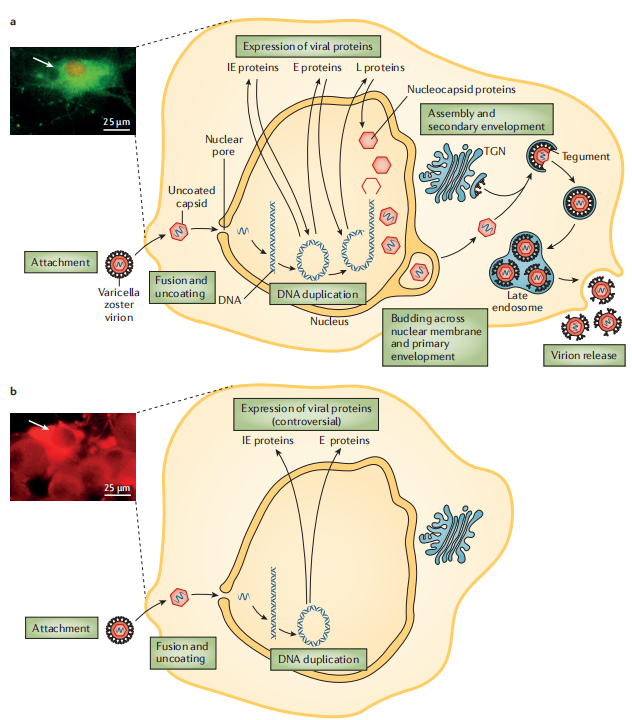
Source: NATURE REVIEWS | DISEASE PRIMERS
The lytic infection of VZV begins with virion attachment, fusion, and uncoating. The viral capsid is then transported to the nucleus, where the viral DNA circularizes. The full repertoire of viral proteins, including immediate-early (IE), early (E), and late (L) proteins, is expressed and transported to the nucleus. New virions are then assembled and released through a two-step budding process. The complete cycle of viral replication results in severe cellular damage and eventual lysis. The acidic environment within endosomes can damage viral particles and reduce their infectivity. Micrographs show VZV infection in guinea pig enteric neurons exhibiting lytic infection. Isolated neurons were cultured in vitro and infected with cell-free VZV to induce infection. Cultures were fixed and immunostained with antibodies against VZV ORF29p (red) and glycoprotein E (green). Neurons were analyzed 48 hours post-infection; following lytic infection, neurons typically die within 48-72 hours. Neurons exhibit abundant cytoplasmic glycoprotein E immunoreactivity, while ORF29p immunoreactivity is almost entirely localized to the nucleus (arrows).
The exact mechanisms of latent infection remain unclear, but viral replication is thought to halt at the circular DNA stage, with limited or no protein expression. Additionally, no viral proteins are detected in the nucleus. Latent infection does not cause observable changes in cell morphology (see micrographs). Micrographs show VZV infection in guinea pig enteric neurons exhibiting latent infection. Isolated neurons were cultured in vitro and infected with cell-free VZV to induce infection. Cultures were fixed and immunostained with antibodies against VZV ORF29p (red) and glycoprotein E (green). Neurons were analyzed 2 weeks post-infection; under latent infection, neurons can survive in vitro as long as the culture is maintained. Note that ORF29p immunoreactivity is confined to the cytoplasm, with no nuclear immunoreactivity (arrows). TGN, trans-Golgi network.
Stages of VZV Infection
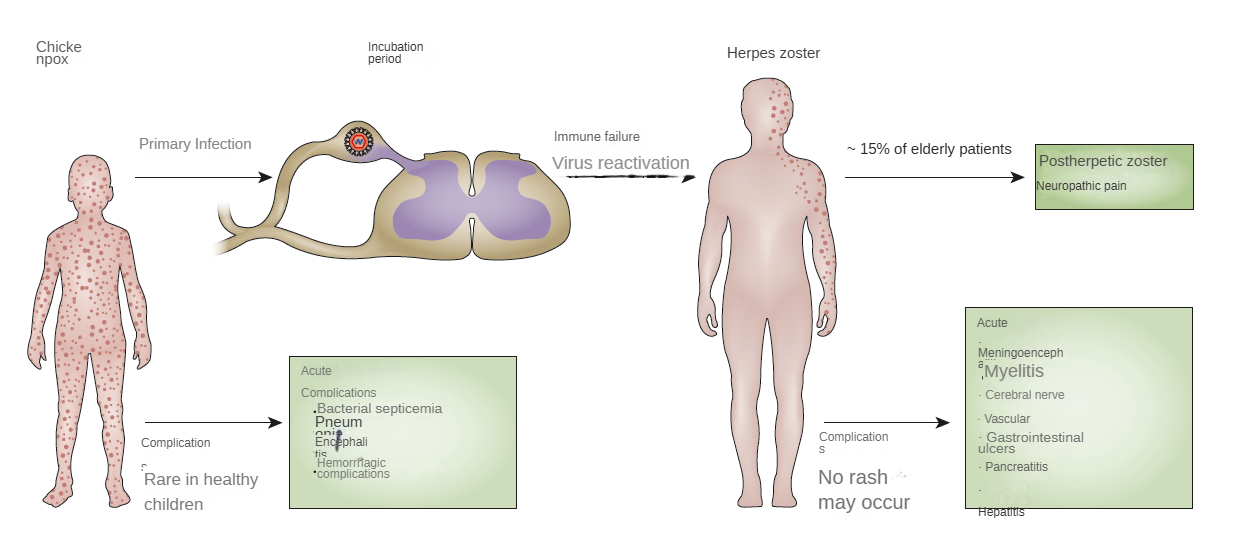
Source: NATURE REVIEWS | DISEASE PRIMERS
Primary infection with VZV in susceptible individuals results in varicella, which is typically benign in healthy children as their immune systems can control the infection. VZV establishes latency in ganglion cells, and reactivation of the virus leads to herpes zoster, characterized by viral replication and spread to the skin areas innervated by these neurons. Aging and immunocompromised status are risk factors for complications of VZV infection. However, some complications, such as postherpetic neuralgia, can occur even in the absence of these risk factors.
02. The Billion-Dollar Market Potential of VZV Vaccines
The market size for VZV vaccines has been steadily increasing in recent years.
Varicella Vaccine:
According to a report by Yi Hai Business Intelligence, the market size for varicella vaccines in China reached approximately 5 billion yuan in 2021. The average vaccination rate for varicella in China is 61.1%, with even lower rates in central and western regions (40.8%). Compared to developed countries such as Germany, Italy, and the United States, where vaccination rates exceed 80%, there is significant room for improvement. The varicella vaccine market is dominated by a few key players, including Changchun BCHT Biotechnology, Shanghai Institute of Biological Products, Rongsheng Biological, Changchun Qiyan, and Sinovac Biotech. Among these, Changchun BCHT Biotechnology's live attenuated varicella vaccine holds a leading market position, with the highest market share and batch issuance.
With the promotion of the "two-dose regimen" and the advancement of immunization programs, the vaccination rate and market size for varicella vaccines are expected to expand further. Additionally, the increasing number of newborns and adjustments to fertility policies across regions will drive sustained growth in demand for varicella vaccines.
Herpes Zoster Vaccine:
According to a Frost & Sullivan report, the market size for herpes zoster vaccines in China is projected to reach 5.63 billion yuan by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.4%. The herpes zoster vaccine market is currently a duopoly, dominated by GSK's Shingrix and Changchun BCHT Biotechnology's Ganyu. Furthermore, several domestic companies, including Green Cross Biologics, Shanghai Institute of Biological Products, and Mecon Biotech, are actively developing herpes zoster vaccines, which will intensify market competition.
The herpes zoster vaccine market is expected to maintain rapid growth in the coming years. On one hand, the increasing elderly population and growing awareness of vaccination will significantly boost vaccination rates. On the other hand, the accelerated development of herpes zoster vaccines by domestic companies will further expand the market and reshape the competitive landscape.
03. Product Details & Advantages
VZV gE His Tag Protein Catalog Number: UA030069
01. High Purity
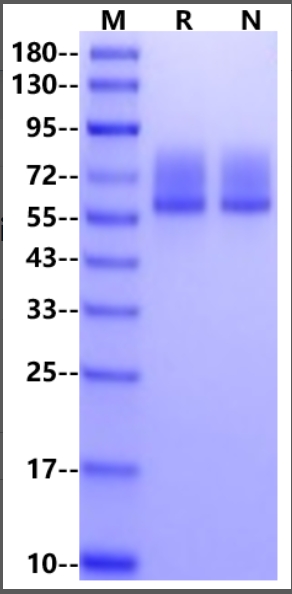
95% by SDS-PAGE & RP-HPLC.
02. High Activity
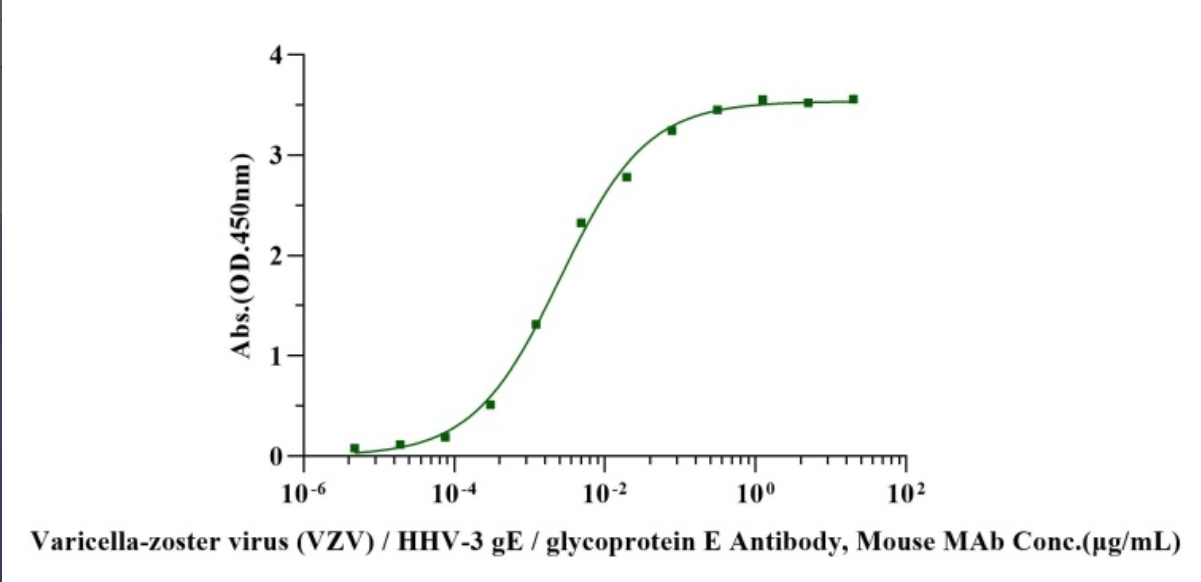
ELISA binding assay confirmed EC50 of 1.98-3.23 ng/mL.
03. High Quality
Expressed in eukaryotic HEK293 cells, the protein structure closely resembles the native conformation.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA030043 | Spike Trimer (Omicron/XBB.1.5) His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $730 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030039 | Spike Trimer (Omicron/XBB) His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $730 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030068 | Spike S2(GCN4-IZ) His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2(K986P&V987P) | Host : Human | $446 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030028 | Spike RBD His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2(BA.2/Omicron) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $600 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030036 | Spike RBD His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2(B.1.1.529/Omicron,N terminal) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $600 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030024 | Spike RBD His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 (BA.4 /Omicron) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $600 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030071 | Spike His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2(R682S,R685S,K986P&V987P) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $750 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030070 | SARS-CoV-2 (BA.4&BA.5/Omicron) S, His Tag Protein | Expression System : HEK293 | $520 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030017 | Nucleocapsid NTD His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $720 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030020 | Nucleocapsid His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 (BA.4 /Omicron) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $840 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030019 | Nucleocapsid His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 (BA.2&BA.5/Omicron) | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $1,440 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030016 | Nucleocapsid His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $720 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030015 | Nucleocapsid CTD His Tag Protein, SARS-CoV-2 | Host : SARS-CoV-2 | $720 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030058 | Influenza B HA (B/Florida/4/2006) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $372 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030080 | Human papillomavirus type 18 E7 Protein | Host : Human papillomavirus type 18 | $240 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030079 | Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 Protein | Host : Human papillomavirus type 16 | $240 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030063 | HRSVL (strain Long) Glycoprotein G Protein, His Tag | Host : HRSV | $970 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030038 | HRSVB(Strain 18537)Nucleoprotein ,His tag Protein | Host : HRSV | $560 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030040 | HRSVB (strain 18537) GlycoProtein G Protein, His Tag | Host : HRSV | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030078 | HRSVA (strain A2) pre-fusion glycoProtein F0 Protein, His Tag | Expression System : HEK293 | $720 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030059 | HRSVA (strain A2) post-fusion glycoProtein F0 Protein, His Tag | Host : HRSV | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030041 | HRSVA (strain A2) GlycoProtein G Protein, His Tag | Host : HRSV | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030037 | HRSV(Strain A2)Nucleoprotein,His Tag Protein | Host : HRSV | $560 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030010 | HBV Surface Antigen-preS2 Protein | Host : HBV | $96 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030018 | HBV Surface Antigen-preS1 Protein | Host : HBV | $84 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030047 | H9N2 HA (A/Hong Kong/WF10/99) His Tag Protein | Host : H9N2 | $368 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030042 | H7N9 HA (Shanghai/2/2013) His Tag Protein, Influenza | Host : Influenza | $360 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030061 | H5N1 HA (A/Turkey/1/2005) His Tag Protein | Host : H5N1 | $360 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030048 | H5N1 HA (A/Hong Kong/483/97) His Tag Protein | Host : H5N1 | $360 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030056 | H1N1 NP (A/Puerto Rico/8/1934) His Tag Protein, Influenza | Host : Influenza | $604 |
| Expression System : Hi5(Baculovirus-InsectCells) | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030057 | H1N1 HA1 (A/California/04/2009) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $604 |
| Expression System : Hi5(Baculovirus-InsectCells) | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030046 | H1N1 HA1 (A/California/04/2009) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $368 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030050 | H1N1 HA1 (A/Brisbane/59/07) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $604 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030055 | H1N1 HA1 (A/Brevig Mission/1/1918) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $604 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030045 | H1N1 HA (A/WSN/1933) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $360 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030044 | H1N1 HA (A/Puerto Rico/8/1934) His Tag Protein | Host : Influenza | $360 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030049 | GP120 (group M/subtype B/Isolate MN) His Tag Protein, HIV-1 | Host : HIV | $604 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA030069 | VZVgE His Tag Protein | Expression System : HEK293 | $224 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




