Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | HRSV |
| Synonyms | Glycoprotein G, mG, Attachment glycoprotein G |
| Accession | P20896 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | His67-Asn292, with C-terminal 8*His HKVTLTTVTVQTIKNHTEKNISTYLTQVPPERVNSSKQPTTTSPIHTNSATISPNTKSETHHTTAQTKGRITTSTQTNKPSTKSRSKNPPKKPKDDYHFEVFNFVPCSICGNNQLCKSICKTIPSNKPKKKPTIKPTNKPTTKTTNKRDPKTPAKMPKKEIITNPAKKPTLKTTERDTSISQSTVLDTITPKYTIQQQSLHSTTSENTPSSTQIPTASEPSTLNPNGGGSHHHHHHHH |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
| Molecular Weight | 72-95kDa |
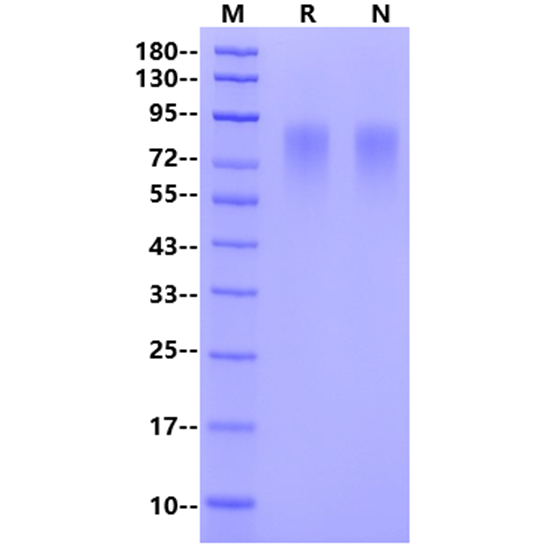
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference | 1、Zlateva K T. et al. (2005). Genetic Variability and Molecular Evolution of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Subgroup B Attachment G Protein. Journal of Virology. 79(14): 9157-9167. |
Background
Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is the most important cause of acute respiratory disease in infants. Two major subgroups (A and B) have been identified based on antigenic differences in the attachment G protein. Antigenic variation between and within the subgroups may contribute to reinfections with these viruses by evading the host immune responses. Furthermore, we have identified 12 positively selected sites in the G protein ectodomain, suggesting that immune-driven selective pressure operates in certain codon positions. HRSV-A and -B strains have similar phylodynamic patterns: both subgroups are characterized by global spatiotemporal strain dynamics, where the high infectiousness of HRSV permits the rapid geographic spread of novel strain variants.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE
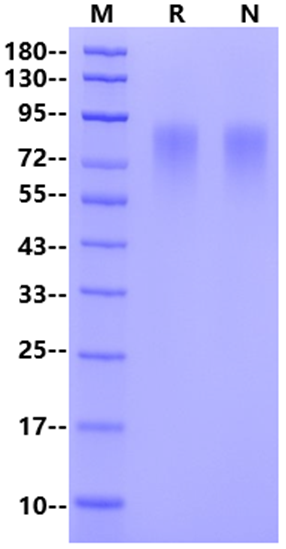
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).