Exploring TNFSF: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Future Medicine?

Introduction
The Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily (TNFSF) represents a class of proteins with extensive and significant biological roles. These proteins are primarily expressed by immune cells and, through binding to their corresponding receptors, regulate a variety of cellular functions, including immune responses, inflammatory reactions, cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and embryogenesis. TNFSF plays a crucial role in maintaining organismal homeostasis and responding to external stimuli.
01. Composition and Structure of TNFSF
TNFSF is a family of type II transmembrane proteins, all of which contain a TNF Homology Domain (THD) at their C-terminus. This domain is critical for the binding of TNFSF members to their receptors, facilitating the formation of trimeric complexes that effectively activate intracellular signaling pathways. The extracellular C-terminal region of TNFSF members contains approximately 150 amino acids of homologous sequences, which fold into a spring-roll-like spatial structure, providing the basis for receptor binding.
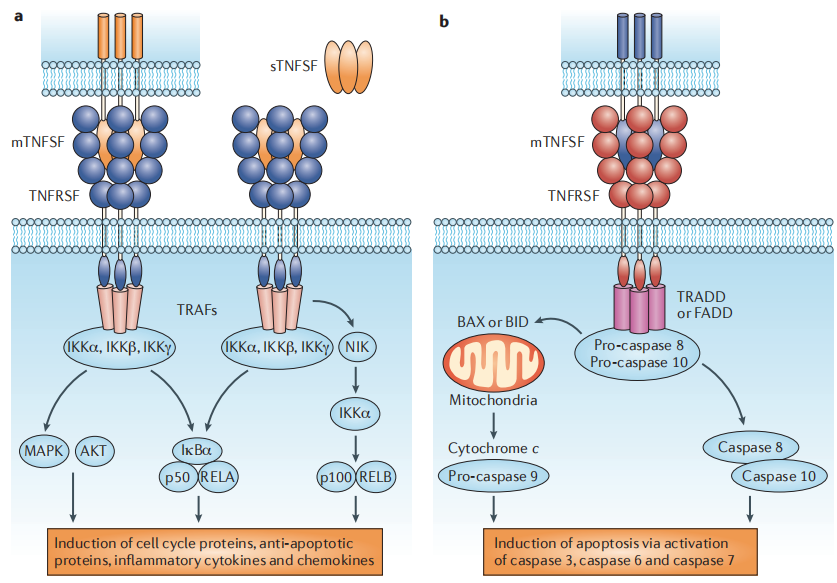
Figure 1: Pro-inflammatory and Death-Inducing Activities of TNFSF Members. Source: NATURE REVIEWS | DRUG DISCOVERY
TNFSF molecules possess a typical TNF homology domain and primarily function as non-covalently bound homotrimers. TNF Receptor Superfamily (TNFRSF) molecules contain varying numbers of cysteine-rich domains in their ligand-binding extracellular regions. Soluble or membrane-expressed TNFSF molecules (sTNFSF and mTNFSF, respectively) can promote survival or inflammatory signaling by organizing TNFRSF monomers (e.g., TNFR2, CD40, OX40, BAFFR, and RANK) into trimeric or oligomeric structures, allowing the recruitment of adaptor molecules known as TNF Receptor-Associated Factors (TRAFs), thereby activating serine/threonine kinase-dependent pathways.
TNFSF molecules can also promote apoptotic cell death by organizing death domain-containing TNFRSF monomers (e.g., TNFR1, FAS, and TRAILR) into trimeric or oligomeric structures, recruiting adaptor molecules with death effector domains (e.g., TRADD and FADD), and activating caspases. Abbreviations: BAX, BCL-2-associated X protein; BID, BH3-interacting domain death agonist; IκBα, inhibitor of κB; IKKα, IκB kinase α; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; p50, NF-κB subunit p50; p100, NF-κB precursor protein p100; RELA, transcription factor p65.
To date, 19 TNFSF ligands have been identified, including TNF-α, TNF-β (also known as LT-α), CD40L, FasL, TRAIL, and RANKL. These ligands share high structural similarity but exhibit functional diversity, regulating various biological processes through interactions with different receptors.
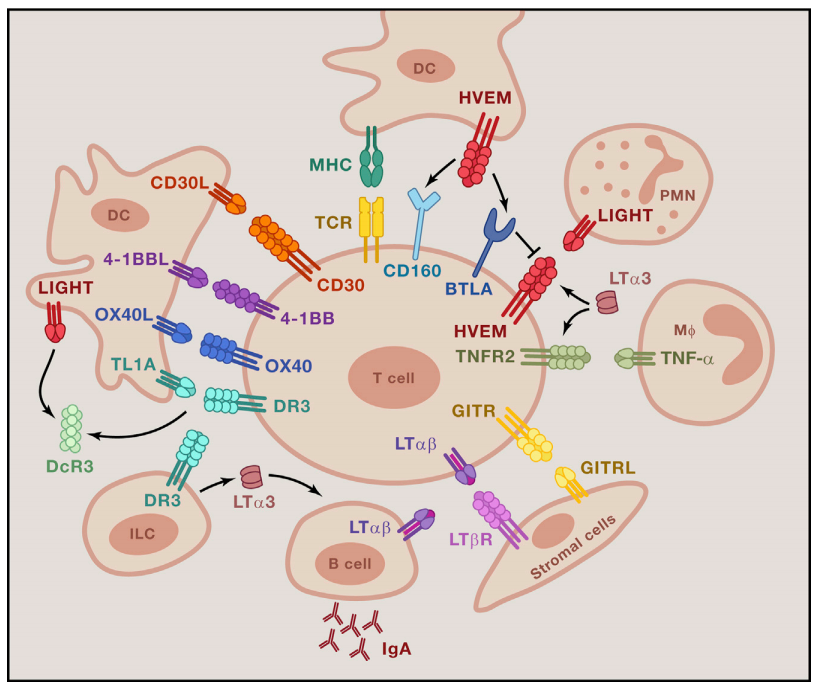
Figure 2: Intercellular Networks of Co-stimulatory TNFRSF Formation. Source: Immunity
Many co-stimulatory TNFRSF members are expressed in activated T lymphocytes, while their specific ligands are expressed in professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), neutrophils, macrophages, or stromal cells. The membrane-anchored expression pattern limits signaling to cell-cell contacts, although some ligands or receptors are released in soluble forms, allowing systemic effects.
02. TNFSF and Disease
The TNFSF family encompasses numerous members, each potentially involved in multiple functions and diseases. Moreover, due to the overlapping or similar functions of different members, their roles in diseases may be interrelated.
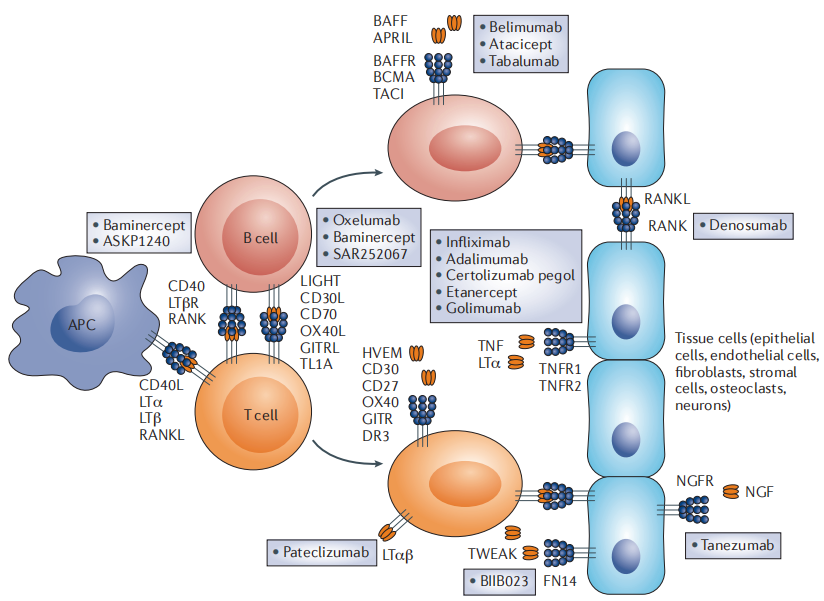
Figure 3: TNFSF Family and Human Diseases. Source: Frontiers in Immunology
TNFSF members play pivotal roles in cancer, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders. TNF-α is aberrantly expressed in various cancers, promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis while inhibiting apoptosis. TRAIL has garnered attention for its ability to selectively induce tumor cell apoptosis, making it a novel target for cancer therapy. Additionally, overexpression of CD40L is associated with autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, driving excessive immune responses and tissue damage. Dysregulation of the RANKL/RANK signaling pathway is also linked to osteoporosis.
Future Perspectives
As research on TNFSF advances, an increasing number of TNFSF members are being identified as important drug targets. Therapeutics targeting TNFSF members have demonstrated promising efficacy and safety in treating various diseases. For example, Denosumab, a biosimilar targeting RANKL, has been accepted for clinical trial registration review by the National Medical Products Administration for osteoporosis treatment. Denosumab specifically binds RANKL, inhibiting osteoclast formation and activity, thereby increasing bone density and reducing fracture risk. Additionally, inhibitors targeting TNF-α, CD40L, and other TNFSF members have shown favorable outcomes in clinical trials. For instance, TNF-α inhibitors are widely used in treating rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other inflammatory conditions.
TNFSF represents a diverse and functionally rich group within the cytokine family, playing a critical role in maintaining organismal homeostasis and immune responses. A deeper understanding of the biological properties and mechanisms of TNFSF members is essential for developing novel therapeutic strategies and improving outcomes for related diseases.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA040039 | TRAIL/Apo2L Protein, Human | Host : Human | $400 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040256 | TRAIL Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $144 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040273 | TNF-β Protein, Human | Host : Human | $188 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040059 | TNF-α(80-235aa) Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $2,400 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040134 | TNF-α Protein, Rhesus Macaque | Host : Rhesus macaque | $136 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040217 | TNF-α Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $164 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040173 | TNF-α Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $242 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040083 | TNF-α Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $2,400 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040062 | TNF-α Protein, Human | Host : Human | $92 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040005 | TNF-α Protein, Human | Host : Human | $184 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040188 | TNF-α Protein, Bovine | Host : Bovine | $396 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010623 | Biotinylated TNFSF11/RANKL Avi&Fc Protein, Human | Host : Human | $1,530 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| UA010453 | TNFSF11/RANKL Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $864 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040184 | TL1A/TNFSF15 Protein,Human | Host : Human | $112 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010778 | OX40 Ligand/TNFSF4 His Tag Protein, Cynomolgus | Host : Cynomolgus | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040274 | LIGHT/TNFSF14 His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $190 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040275 | Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 Protein, Human | Host : Human | $270 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA011012 | Fas Ligand/TNFSF6 His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $200 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010378 | CD30 Ligand mFc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010611 | CD27 Ligand/TNFSF7 Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $556.80 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040088 | AITRL Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $600 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040214 | AITRL Protein, Human | Host : Human | $180 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010859 | 4-1BB Ligand/TNFSF9 His Tag Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $604 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010904 | 4-1BB ligand/TNFSF9 Fc Chimera Protein, Rat | Host : Rat | $240 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010783 | 4-1BB ligand/TNFSF9 Fc Chimera Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $336 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA011048 | 4-1BB Ligand/TNFSF9 Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $256 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




