CDK Kinases: The Regulators of the Cell Cycle
Introduction
CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) are a crucial class of protein kinases. Their activity is positively regulated by cyclins and negatively regulated by CDK inhibitors (CKIs). The fluctuations in their activation state can be modulated through transcriptional and post-translational modifications (typically phosphorylation), as well as the rapid turnover of cyclins and CKIs mediated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Phosphorylation or association with CKIs ensures rapid and reversible changes during the process, while ubiquitin-mediated degradation of key components of the cell cycle machinery provides directionality and irreversibility to cell cycle progression.
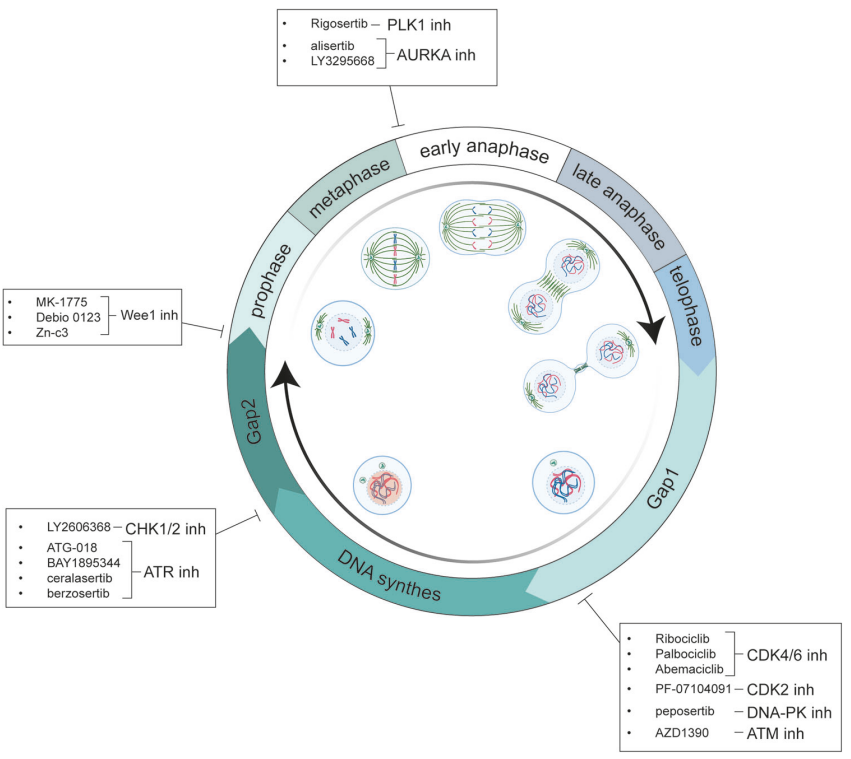
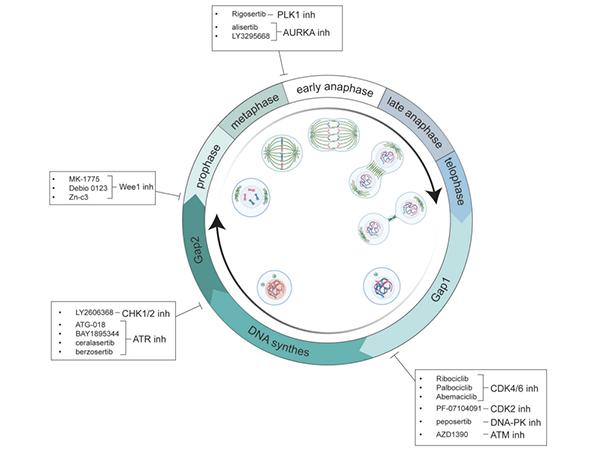
Figure 1. Cell Cycle-Related Kinase Inhibitors in Clinical Trials
Functions
The evolutionary diversification and specialization of the CDK family in mammals have led to the division of CDKs into three cell cycle-related subfamilies (CDK1, CDK4, and CDK5) and six transcriptional subfamilies (CDK7, CDK8, CDK9, CDK11, CDK12, and CDK20). Among the three cell cycle-related subfamilies, only the first two—CDK1 (including CDK1, -2, and -3) and CDK4 (including CDK4 and -6)—are directly involved in cell division. The third subfamily, CDK5, participates in various pathways such as Wnt-dependent signaling or signal transduction in primary cilia, thus only secondarily affecting cell cycle progression.
In addition to cell cycle regulation, CDKs also play significant roles in transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and more. This multifunctional nature makes CDKs pivotal in numerous biological processes.

Figure 2. Phosphorylation Targets of Relevant CDKs Throughout the Cell Cycle
Association with Cancer
Cell division in both unicellular and multicellular eukaryotes is controlled by a complex regulatory system and a balanced network to ensure no errors occur before cells enter and progress through the cell cycle. The cell cycle is divided into mitosis and interphase, each containing multiple subphases. The timely and precise replication and segregation of genomic DNA are achieved by various kinase activities. Dysregulation of these kinase activities can lead to the development of several types of cancer (in the figure, the proximity of cancer types to their respective kinase waves is indicated).
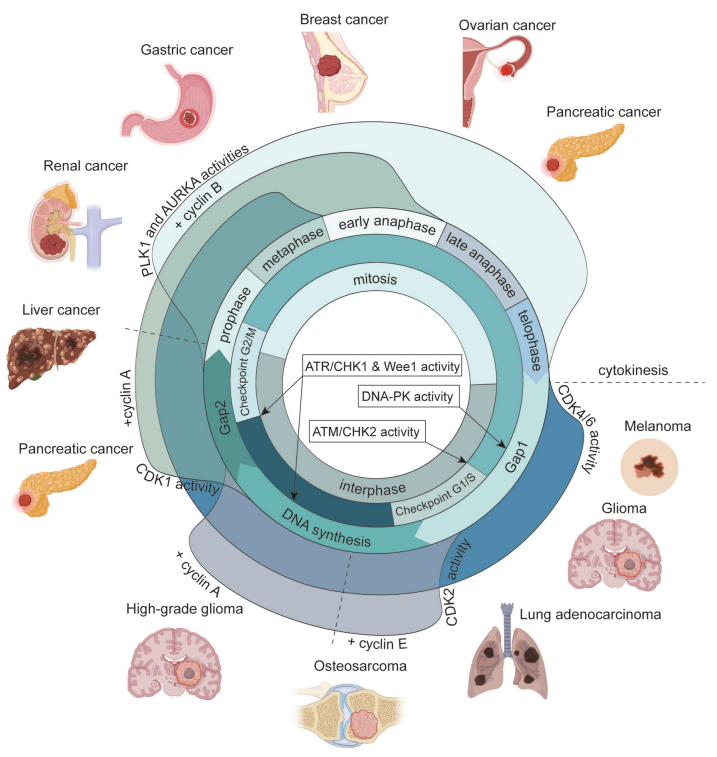
Figure 3. Cell Cycle-Related Kinase Activities and Their Associated Tumors
The increased dependence of cancer cells on cell cycle regulatory pathways provides opportunities for targeting pathways or processes that are essential in cancer cells but dispensable in healthy cells. However, the complexity of the cell cycle control network suggests that different cancers should be targeted through different pathways or processes. Therefore, to enhance the effectiveness of anticancer drugs targeting cell cycle control mechanisms, it is necessary to understand the dynamics of normal versus cancer cells in the context of specific cancer-related mutations. This understanding can guide drug design, therapeutic combinations, and patient selection. The table below lists existing therapeutic approaches and highlights opportunities for developing novel and combination therapies.

Figure 4. Drugs Targeting Cell Cycle Regulators as Cancer Therapeutics
Beyond their applications in cancer, CDKs have shown significant potential in research on other diseases. For example, in neurodegenerative diseases, CDKs may serve as new therapeutic targets for conditions such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Additionally, the roles of CDKs in cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders are increasingly being recognized. Thus, the CDK kinase family has become an important target for drug development.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA080223 | CDK6/Cyclin D1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080224 | CDK6/Cyclin D2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080156 | CDK6/Cyclin D3 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080225 | CDK7 Protein | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080226 | CDK7/Cyclin H/MAT1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080227 | CDK8 Protein | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080228 | CDK8/Cyclin C/MED12 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080229 | CDK9 Protein | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080230 | CDK9/Cyclin K Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080231 | CDK9/Cyclin T1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080232 | CDK9/Cyclin T2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080053 | CDK12/Cyclin K Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080205 | CDK12/Cyclin T1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080054 | CDK13/Cyclin K Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080206 | CDK13/Cyclin T1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080207 | CDK15/Cyclin Y Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080208 | CDK16/Cyclin Y Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080209 | CDK17/Cyclin Y Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080210 | CDK18/Cyclin Y Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080211 | CDK19/Cyclin C/MED12 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080051 | CDK1/CycE1 Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080203 | CDK1/Cyclin A2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080154 | CDK1/Cyclin A2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080204 | CDK1/Cyclin E2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080212 | CDK2 Protein | Host : Human | $320 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080055 | CDK2/CycE1 Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080213 | CDK2/Cyclin A2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080214 | CDK2/Cyclin D1 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080216 | CDK2/Cyclin E2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080215 | CDK3 Protein | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080057 | CDK3/CycE1 Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080217 | CDK3/Cyclin E2 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080218 | CDK4 Protein | Host : Human | $484 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080157 | CDK4/Cyclin D2 Protein | Host : Human | $960 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080155 | CDK4/Cyclin D3 Protein | Host : Human | $960 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080219 | CDK5 Protein | Host : Human | $576 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080220 | CDK5/p25 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080221 | CDK5/p35 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080222 | CDK6 Protein | Host : Human | $756 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA080050 | CDK1/CycB1 Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




