Literature Review: sTREM2 for AD Tau Phosphorylation and Cognitive Deficits
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline, memory loss, and language impairment, typically occurring in the elderly but also affecting younger individuals. Patients may exhibit symptoms such as memory deterioration, cognitive impairment, language disorders, and behavioral abnormalities. The etiology of AD is not fully understood, but studies suggest that it is associated with genetic, age-related, and lifestyle factors. The pathological hallmarks of AD include extracellular aggregates composed of amyloid-beta (Aβ) and intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) formed by hyperphosphorylated tau. Research indicates that microglia may play a complex role in the development and progression of AD by sensing neuronal activity and modulating neuronal function through cell-cell signaling pathways.
TREM2 (Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid cells 2) belongs to the TREM family and is a transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily, expressed exclusively in myeloid cells, such as microglia in the central nervous system (CNS). Studies have shown that rare variants of TREM2 can increase the risk of AD by 2-3 times, although its role in tau pathology requires further investigation.
On October 21, 2023, a research team led by Professor Zhang Zhentao from Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University published a study titled “Soluble TREM2 ameliorates tau phosphorylation and cognitive deficits through activating transgelin-2 in Alzheimer’s disease” in Nature Communications. The study identified transgelin-2 (TG2), an actin-binding protein expressed on neurons, as the receptor for sTREM2. The interaction between sTREM2 and TG2 mediates crosstalk between microglia and neurons, and sTREM2 and its active peptides may serve as potential therapeutic interventions for tauopathies, including AD.
Main Results:
1. In vitro studies show that sTREM2 inhibits tau hyperphosphorylation by suppressing GSK3β
The research team constructed a stable HEK293 cell line overexpressing GFP-Tau and treated the cells with Fc vehicle, heat-inactivated sTREM2, or sTREM2 (40 nM). Results showed that sTREM2 reduced tau phosphorylation at S202, S396, T181, and S404 residues. Further investigation focused on the most significantly affected sites, S202 and S396, revealing that the inhibitory effect of sTREM2 on tau phosphorylation was dose-dependent.
These four tau phosphorylation sites are known targets of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β). The team assessed GSK3β activity in the presence of sTREM2 and found that sTREM2 significantly reduced the phosphorylation of GSK3β at Y216 in a concentration-dependent manner, indicating that sTREM2 induces a decrease in GSK3β activity.

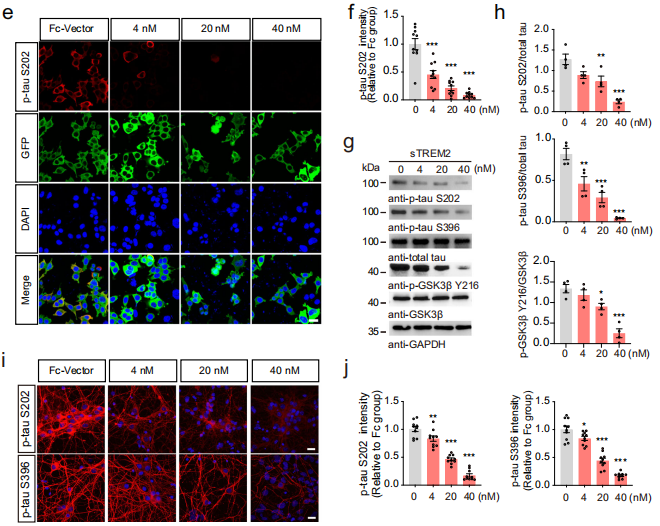
Figure: sTREM2 inhibits tau hyperphosphorylation in vitro
2. sTREM2 interacts with TG2 and inhibits tau phosphorylation via TG2 activation
The research team used Fc-tagged recombinant sTREM2 for affinity purification experiments, extracting interacting proteins from SH-SY5Y cell membranes. Western blotting and mass spectrometry identified TG2 as a candidate receptor interacting with sTREM2. Further experiments confirmed the binding of sTREM2 and TG2 on neuronal cell membranes. In brain sections from AD patients and tau P301S mice, TG2 and sTREM2 co-localized with neuronal and glial markers. The interaction between sTREM2 and TG2 on the cell surface was demonstrated, and TG2 knockdown reduced sTREM2 binding to neurons.
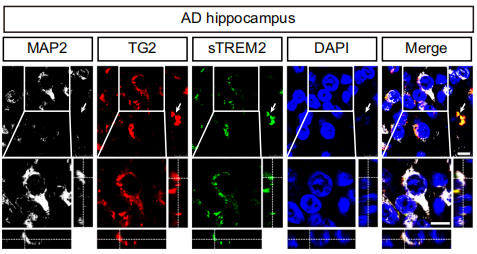
Figure: Co-localization staining of MAP2, TG2, and sTREM2 in the hippocampus of AD patients and tau P301S mice
To further investigate whether TG2 is involved in sTREM2-mediated regulation of tau phosphorylation, the team treated HEK293-tau cells with the TG2 agonist TSG12, which significantly reduced p-tau levels at S202 and S396 and inhibited GSK3β activation. Similar results were observed in primary neurons, indicating that TG2 agonists mimic sTREM2 in inhibiting tau phosphorylation. Using shRNA to knockdown TG2 in HEK293-tau cells or primary neurons from tau P301S mice, the team found that the effects of sTREM2 on tau phosphorylation and GSK3β activation were abolished in the absence of TG2. These results demonstrate that TG2 is essential for sTREM2-mediated inhibition of tau phosphorylation. Subsequent studies revealed that sTREM2 activates the TG2-Rho-ROCK pathway to inhibit tau phosphorylation by inducing RhoA phosphorylation at S188, thereby inactivating the RhoA-ROCK pathway.

Figure: Schematic diagram of the potential mechanism by which sTREM2 regulates tau phosphorylation
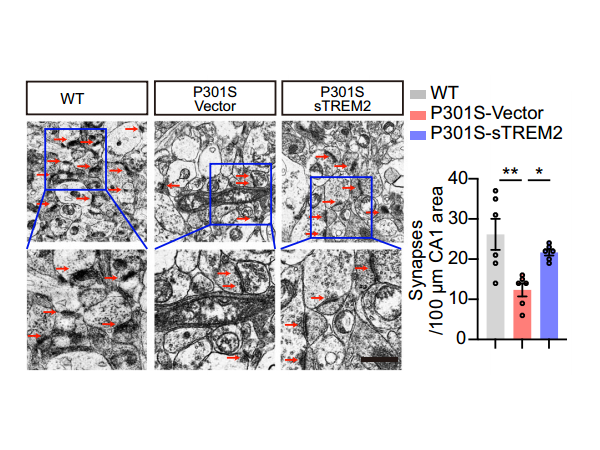
3. sTREM2 alleviates tau hyperphosphorylation and memory loss in tau P301S mice
The research team injected AAVs encoding EGFP-sTREM2 or EGFP vector into the hippocampus of 3-month-old tau P301S mice and observed strong expression of EGFP and EGFP-sTREM2 in the hippocampus at 7 months. Compared to control mice, tau P301S mice injected with AAV-sTREM2 showed significant improvement in tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus. sTREM2 also inhibited GSK3β activation in tau P301S mice. Electron microscopy revealed that sTREM2 protected against synaptic loss in the hippocampus of tau P301S mice. Behavioral tests showed that tau P301S mice injected with AAV-EGFP-sTREM2 exhibited better memory in the water maze test and enhanced long-term potentiation (LTP) of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSCs). These results indicate that sTREM2 reverses tau pathology, synaptic dysfunction, and cognitive impairment in tau P301S mice.
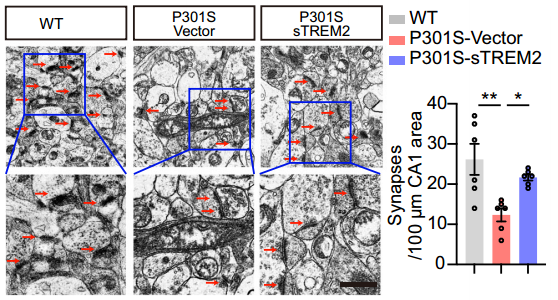
Figure: Electron microscopy results of hippocampal synapses
4. TG2 plays a crucial role in mediating the beneficial effects of sTREM2
The research team successfully downregulated TG2 expression in tau P301S mice by injecting AAV-EGFP-shRNA-TG2 into the hippocampus. Results showed that the inhibitory effects of sTREM2 on tau phosphorylation were dependent on TG2, and sTREM2 acted through the RhoA-ROCK-GSK3β pathway. Electron microscopy revealed that sTREM2 protected against synaptic loss in the hippocampus of control mice, but this protective effect was lost in mice with TG2 inhibition. Additionally, TG2 knockdown weakened the protective effect of sTREM2 on synaptic density, emphasizing the key role of TG2 in mediating the beneficial effects of sTREM2.
5. sTREM2 active peptides inhibit tau pathology in tau P301S mice
The research team synthesized four short peptides based on sTREM2(77-105), among which Peptide 1 (amino acids 77-89) significantly inhibited tau phosphorylation, similar to sTREM2. To further evaluate the effect of Peptide 1 on tau hyperphosphorylation in tau P301S mice, the team injected FITC-labeled Peptide 1 intraperitoneally into mice and confirmed its brain permeability, with detectable levels in various brain regions. Peptide 1 interacted with TG2 on neurons. Subsequently, 3-month-old tau P301S mice were intraperitoneally injected with Tat-sTREM2(77-89) or Tat-sTREM2(89-77) for four consecutive months. The results showed that Peptide 1 significantly inhibited tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus, as well as the activation of Gsk3β and RhoA, and attenuated synaptic loss. In behavioral tests, mice treated with Peptide 1 exhibited better learning and memory functions. Electrophysiological studies also found that synaptic function was higher in mice injected with Peptide 1 than in those injected with the reverse peptide. Overall, the active peptide of sTREM2 holds promise for improving tau pathology, synaptic dysfunction, and cognitive deficits in tau P301S mice.
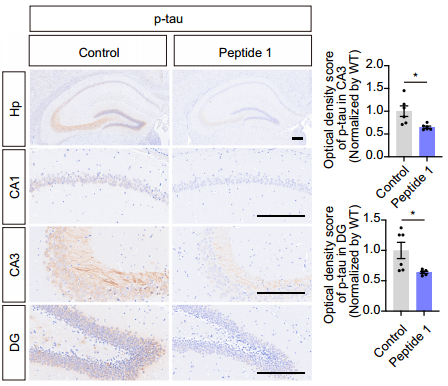
Figure: Immunohistochemical staining and quantification in the mouse hippocampus
Conclusion:
In summary, the research team discovered that microglia secrete sTREM2, which may play a protective role in tauopathies. They designed a peptide to mimic the protective effects of sTREM2, which holds promise as a potential therapeutic intervention for Alzheimer's disease.
References
Zhang X, Tang L, Yang J, Meng L, Chen J, Zhou L, Wang J, Xiong M, Zhang Z. Soluble TREM2 ameliorates tau phosphorylation and cognitive deficits through activating transgelin-2 in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 21;14(1):6670. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42505-x. PMID: 37865646; PMCID: PMC10590452.
Although the antibody stripping buffer solves the problem of heat repair in frozen sections, multiple rounds of stripping may still result in section detachment. Use blank sections to test the tolerance of multiple antibody stripping to determine the final number of staining targets.
|
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Specification |
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 4-Color IHC Kit(Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 5-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit and Mouse Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 6-Color IHC Kit (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Absin 7-Color IHC Kit (plus) (Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody) |
20T |
|
|
Antibody eluent (for mIHC) |
30ml |
AntBio provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us




