CD48: A Key Molecule in the Immune Regulation Network
In recent years, the research on CD48 has gradually deepened, and its unique position in immune regulation and its close relationship with various diseases have begun to emerge, attracting extensive attention from the scientific community.
The Structural and Expression Characteristics of CD48
CD48, also known as BLAST-1 or SLAMF2, is a member of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored immunoglobulin superfamily. Its encoding gene is located on human chromosome 1q21-23, and the final product is a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of approximately 45kD. It is worth noting that CD48 can exist in a soluble form in human serum and plasma, but the specific mechanism by which its solubility is generated remains an unsolved mystery. In terms of protein structure, CD48 contains a signal peptide, an immunoglobulin variable region (IgV), a constant region 2 (IgC2), and a C-terminal GPI-anchored protein. Among them, the conserved cysteine residues in the IgC2 domain can form disulfide bonds. CD48 is firmly anchored to the cell membrane via a GPI linkage, which enables it to effectively bind to relevant signaling molecules and thus exert its biological functions.

At the cellular expression level, CD48 is widely distributed on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, monocytes, and basophils, playing an important role in cell adhesion and activation pathways. Moreover, when the body is under inflammatory conditions, such as exposure to cytokines like interferon-α (IFN-α), interferon-β (IFN-β), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ), the expression level of CD48 on the surface of human peripheral blood monocytes will significantly increase. This characteristic implies that CD48 may play a crucial role in inflammation-related immune responses.
The Ligands of CD48 and Immune Regulation
CD48 has multiple ligands, among which the more prominent ones include CD2, CD244, and FimH. When CD48 binds to these ligands, it will trigger a series of intracellular changes, such as the rearrangement of signaling factors in lipid rafts, the activation of Lck kinase activity, and the promotion of tyrosine phosphorylation, thereby exerting different functions in immune regulation.
Specifically, the ligand CD2 is mainly expressed on T cells and NK cells, while CD244 is expressed on the surface of NK cells, some memory CD8+ T cells, monocytes, and granulocytes, etc. In terms of immune cell interactions, CD48 can promote the communication between immune cells by binding to CD2 and CD244, but it has a relatively higher affinity for CD244. In addition, CD48 can also bind to the lectin FimH on Escherichia coli, assisting macrophages and mast cells in the recognition and phagocytosis of bacteria. However, since CD58 is a high-affinity ligand for CD2 in the human body, the interaction between CD48 and its ligands is affected by the expression levels of CD244, CD2, and CD58, as well as the affinity of each receptor-ligand interaction.
The Counter-Receptor of CD48 and Signal Regulation
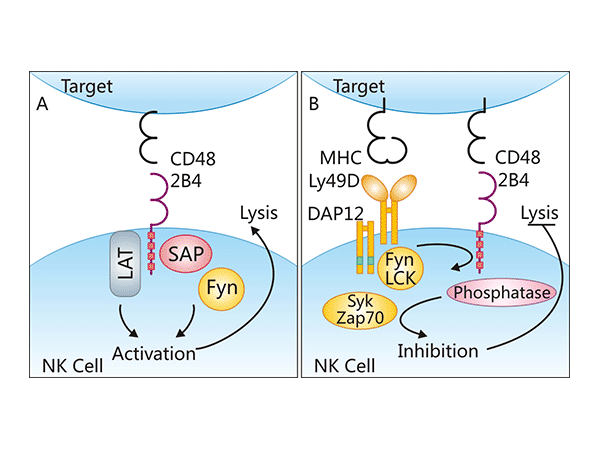
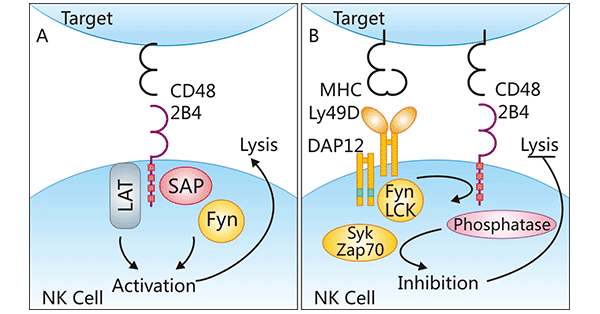
In human NK cells, CD48 acts as the counter-receptor (i.e., ligand) of CD244, an important activator of NK cells, playing a key role in the process of cell-cell interaction. Studies have found that the binding of CD48 and CD244 exhibits complex characteristics in signal transduction, which can both promote the downstream signaling pathway and potentially inhibit it.
In terms of promoting the signaling pathway, the binding of CD48/CD244 can activate the linker for activation of T cells (LAT), and at the same time induce the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM), and then recruit the adapter protein SAP. After SAP binds to ITSM, it recruits the tyrosine kinase Fyn, and Fyn promotes the phosphorylation of downstream proteins, ultimately achieving the activation of NK cells. However, in terms of inhibiting the downstream signaling pathway, although its regulatory mechanism has not been fully clarified, some studies have speculated that it may be similar to the mode of action of the inhibitory receptor Ly49. Interestingly, the signals generated by the interaction between CD48 and CD244 vary among different species. For example, it induces an activation signal in human NK cells, while it sends an inhibitory signal in mouse NK cells.
The Complex Association between CD48 and Diseases
Numerous studies have shown that CD48 plays an important role in the occurrence and development of various diseases. In the mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease, CD48/CD244 is involved in inhibiting the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and the function of effector CTLs. In the mouse tumor model, CD244 is highly expressed on dysfunctional CD8+ T cells and is associated with the exhaustion of CD8+ T cells. Although the specific mechanism by which CD48 acts in this process has not been fully elucidated, in vitro studies have shown that the binding of CD48 and CD244 can inhibit the production of IFN-β, prolong the survival time of dendritic cells (DCs), and reduce the exhaustion of activated T cells. This indicates that CD48 has an important regulatory effect on the proliferation and effector functions of T cells.
In terms of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, some studies have pointed out that the decreased expression of CD48 on CD8+ T cells may lead to the obstruction of the activation and proliferation of CD8+ T cells, weaken the function of inhibitory T cells, and ultimately contribute to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition, the relationship between the high expression of CD48 and allergic diseases has received increasing attention. Abnormally elevated expression of CD48 has been found in allergic diseases such as intermittent allergic rhinitis (IAR), allergic rhinitis, and asthma. In studies related to the hematopoietic system, some researchers have found that the expression of CD48 is associated with the dysfunction of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. In the field of cancer, although current research is relatively limited, CD48 has been found to have a certain connection with breast cancer, glioma, hepatocellular carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, etc., but the specific mechanism still needs to be further explored.
The Prospects of Clinical Applications of CD48
With the continuous in-depth research on the molecular functions of CD48, its core position in immune regulation has become more and more prominent. Given that CD48 is involved in regulating humoral and cellular immune responses and is closely related to the regulation of the activation of various cells, it is highly likely to become an important biomarker or therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases, allergic diseases, and tumors.
Currently, in clinical research, only one antibody-drug conjugate targeting CD48 (SGN-CD48A) has entered phase I clinical trials for the treatment of multiple myeloma. However, the enthusiasm of the scientific community for exploring CD48 continues to rise, and more and more studies are being carried out around CD48 to explore its potential value in the treatment of allergic diseases, other inflammatory diseases, and tumors. Although the current research on CD48 is still in its preliminary stage, with the continuous progress of research, it is expected to more deeply reveal the key role of CD48 as a receptor or counter-receptor in immune and other physiological and pathological processes, opening up new paths for future disease treatment.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B1051 | CD48 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-1515-9) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0346 | CD48 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R265) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B5018 | Armenian hamster Anti-Mouse CD48 Antibody (S-R654) | Host : Armenian hamster | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B5024 | FITC Armenian hamster Anti-Mouse CD48 Antibody (S-R654) | Host : Armenian hamster | $435 |
| Conjugation : FITC | |||
| UA010577 | CD48 Fc Chimera Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010595 | CD48 His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $500 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010596 | CD48 His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010734 | CD48/SLAMF2 His Tag Protein, Mouse | Host : Mouse | $604 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010747 | Biotinylated CD48/SLAMF2 His&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $560 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Biotin |




