CD79B: An Emerging Target for the Diagnosis and Treatment of B-Cell-Related Diseases
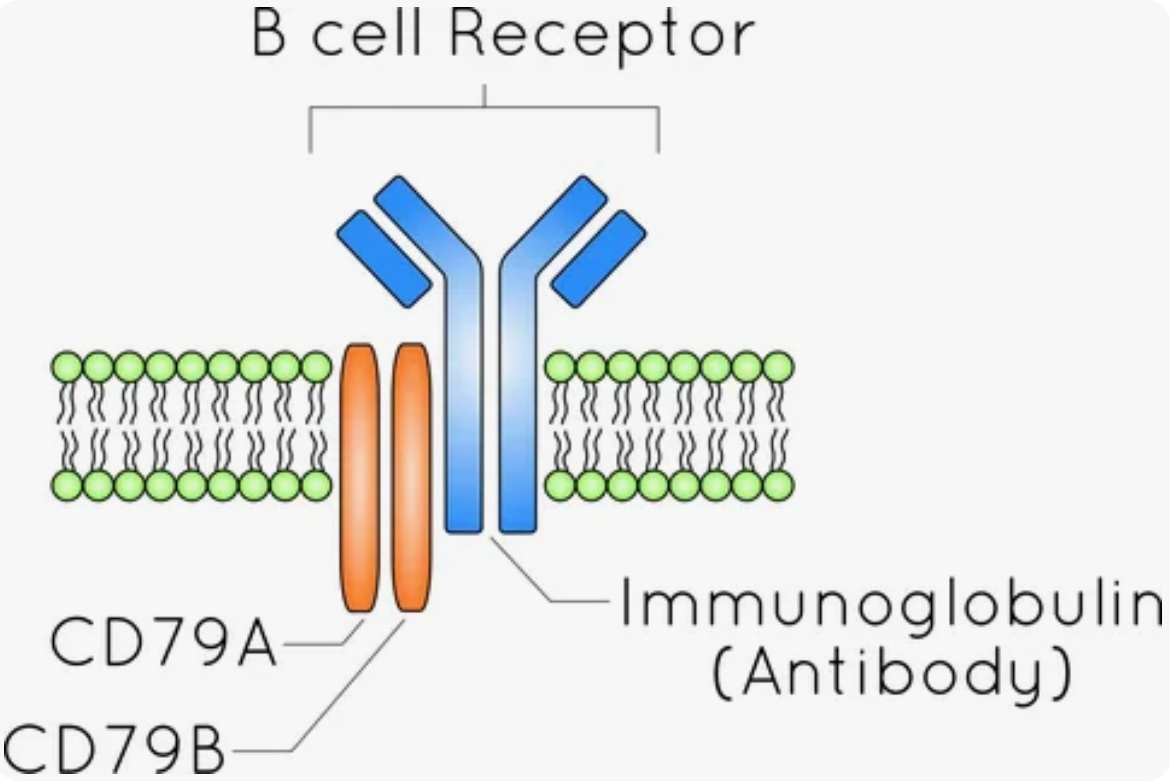
CD79B, as an important component of the B-cell receptor (BCR), is expressed on the surface of almost all B cells. It plays a vital role in the expression of BCR and its transportation to the cell membrane. CD79B is highly expressed on B cells in various B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and has a mechanism of action for extensively killing B-cell tumors.
The Structural and Functional Basis of CD79B
CD79 is a transmembrane protein. Two different peptide chains, CD79a (Iga) and CD79B (Igβ), form a heterodimer on the surface of B cells through disulfide bonds. This heterodimer combines with the B-cell receptor (BCR) to form a complex. In this complex, CD79B, as a key member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) complex on the surface of B cells, is expressed from the pre-B cell stage to the mature B cell stage of B cell development.
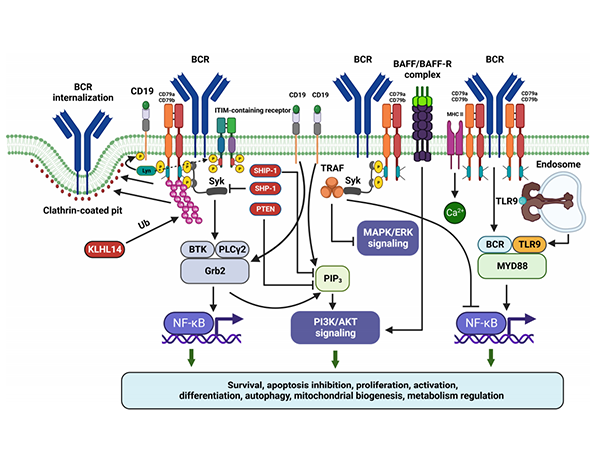
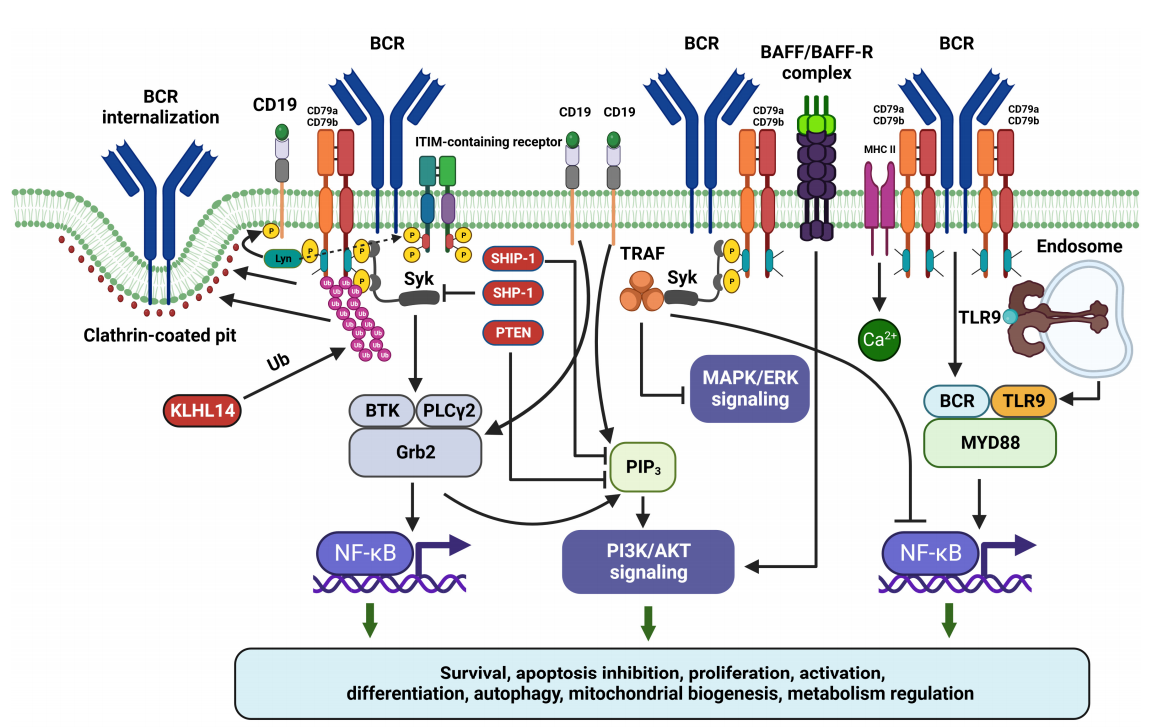
The N-terminal tyrosine kinase domain of CD79B is a crucial region for its function. After the BCR recognizes an antigen, CD79B can recruit and activate downstream signaling molecules such as Syk, and then initiate a series of signaling pathways, such as PI3K-AKT, ERK, and NF-κB. These signaling pathways play a central regulatory role in the development, proliferation, differentiation, immune response, and antibody production of B cells, ensuring that B cells can perform their immune functions normally.
CD79B and B-Cell Malignancies
The abnormal manifestations of CD79B in various B-cell lymphomas have attracted great attention from researchers. Numerous studies have found that CD79B is often highly expressed in B-cell lymphomas. In some B-cell lymphomas, due to gene mutations or abnormal expression regulation, CD79B continuously activates downstream signaling pathways, enabling B cells to break away from the normal growth regulation mechanism, proliferate abnormally, and survive. This endows lymphoma cells with a growth advantage and allows them to evade apoptosis.
Taking diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) as an example, CD79B is expressed in more than 95% of cases. Research shows that antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting CD79B have more advantages in treatment effects compared with ADCs targeting CD79a, which further highlights the important value of CD79B as a therapeutic target for B-cell lymphomas.
CD79B and Autoimmune Diseases
In addition to its importance in the field of oncology, CD79B also plays a key role in the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases. During the immune response process, CD79B is not only involved in signal transduction but also affects the regulation of cell activation, proliferation, and cell death.
In autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, the immune system is disordered, and B cells are over-activated. Therapeutic methods targeting CD79B have become a new direction for exploring the treatment of such diseases. By interfering with the signaling pathway mediated by CD79B, the abnormal activation state of B cells can be regulated, providing a new strategy for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
The Research and Development Progress of CD79B-Related Drugs
With the in-depth research on CD79B, significant progress has been made in the research and development of drugs targeting this target, and a variety of drugs are at different research and development stages.
Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq, jointly developed by Roche and Genentech, is the first ADC drug targeting CD79B to be approved for marketing. It is used for the treatment of refractory lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and refractory aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma, bringing new treatment options for related patients.
PRV-3279 of Huadong Medicine, as a bispecific antibody, is currently in the Phase II clinical trial stage for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Many drugs under research, such as the CD79B CAR-T therapy for B-cell lymphoma carried out by the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University and SHR-A1912 (ADC targeting CD79B) of Hengrui Medicine, are respectively in the Phase II or Phase I/II clinical research stage, demonstrating the great potential of the CD79B target in the field of drug research and development.
In addition, a variety of drugs, including NBT-508 developed by Xingang Biomedical Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd and JNJ-80948543 of Johnson & Johnson, are in the Phase I clinical research stage. These drugs target diseases such as B-cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia, continuously expanding the boundaries of CD79B-targeted therapy.
As a key molecule in B-cell signal transduction, CD79B provides important clues for understanding the pathogenesis of B-cell-related diseases and also brings new ideas and methods for the precise diagnosis and treatment of diseases. With the continuous in-depth research and the research and launch of more drugs, it is believed that CD79B will play a greater role in future clinical treatments and bring more benefits to patients.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B2021P | CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb,PBS Only (SDT-043-9) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2347P | S-RMab® CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb,PBS Only (SDT-R513) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2347 | S-RMab® CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R513) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2021 | CD79B Recombinant Rabbit mAb(SDT-043-9) | Host : Rabbit | $45 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010240 | CD79B Fc Chimera Protein, Human | Host : Human | $540 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010276 | CD79B His Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $540 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA010901 | Biotinylated CD79B Fc&Avi Tag Protein, Human | Host : Human | $556 |
| Expression System : HEK293 | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |
Reference
[1] Chu PG, Arber DA. CD79: A review. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2001;9(2):97-106.
[2] Dong Y, Pi X, Bartels-Burgahn F, et al. Structural principles of B cell antigen receptor assembly. Nature. 2022;612(7938):156-161.
[3] Visco C, Tanasi I, Quaglia FM, et al. Oncogenic Mutations of MYD88 and CD79B in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Implications for Clinical Practice. Cancers. 2020;12(10):2913.
[4] Tkachenko A, Kupcova K, Havranek O. B-Cell Receptor Signaling and Beyond: The Role of Igα (CD79a)/Igβ (CD79b) in Normal and Malignant B Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(1):10.
[5] Puja Bhattacharyya, et al. Combination of High-Resolution Structures for the B Cell Receptor and Co-Receptors Provides an Understanding of Their Interactions with Therapeutic Antibodies. Cancers (Basel). 2023.




