Unveiling IL-31: Why Has It Become a Hotspot in Canine Atopic Dermatitis Research?

Introduction
Atopic Dermatitis (AD) is a common and complex chronic inflammatory skin disease, particularly prevalent in canines. This dermatological condition not only significantly impacts the quality of life of affected dogs but also poses considerable challenges for pet owners. In recent years, with the deepening understanding of the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, Interleukin-31 (IL-31) has emerged as a critical pruritogenic cytokine, garnering increasing attention from researchers.
IL-31, a cytokine discovered in 2004, belongs to the IL-6 cytokine family. It is produced by type 2 helper T (Th2) cells and is a single-chain molecule with a four-helix structure. The IL-31 gene is located at 12q24.31 and encodes a polypeptide chain of 164 amino acids, with the mature IL-31 molecule consisting of 141 amino acids. The IL-31 receptor is a heterodimer composed of the IL-31 receptor A (IL-31RA) and oncostatin M receptor (OSMR) subunits, belonging to the type I cytokine receptor gp130 subfamily.
Since the approval of lokivetmab (Cytopoint, Zoetis; Parsippany, NJ, USA) in 2016 for the treatment of canine AD, this cytokine has taken center stage in veterinary dermatology. Lokivetmab is a caninized therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets and neutralizes canine IL-31. It exhibits rapid and effective antipruritic effects, benefiting ≤88% of atopic dogs and preventing atopic flares for over a year in 28% of cases.
01. Mechanisms of IL-31 in Atopic Dermatitis
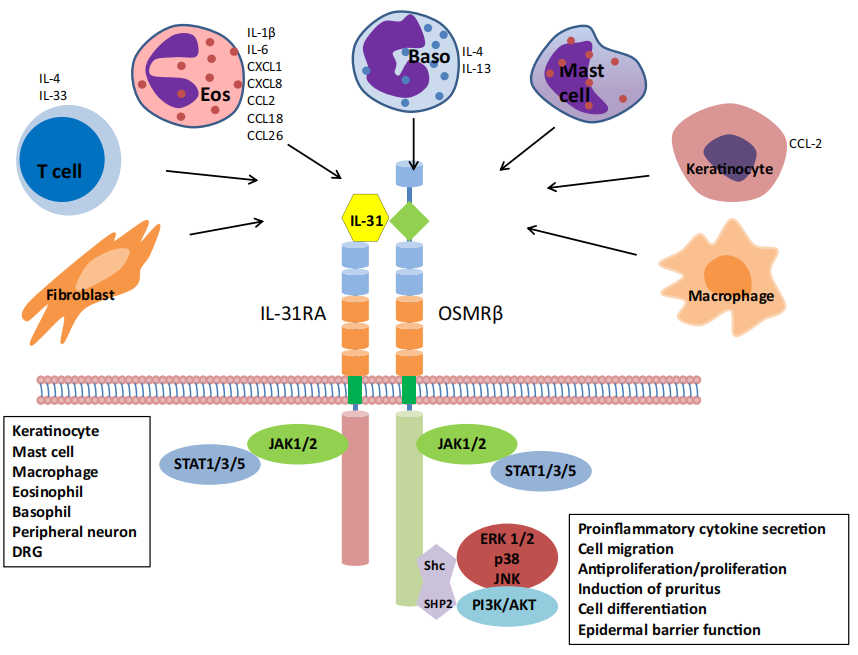
Figure 1: Cellular Sources of IL-31, Related Cytokines, and Signaling Pathways.
Left panel: Cells expressing IL-31R. Right panel: Biological effects of IL-31.
The role of IL-31 in atopic dermatitis is complex and multifaceted. It is widely involved in various physiological functions, particularly those related to the skin and immune system. IL-31 is highly correlated with chronic pruritus in atopic dermatitis and exerts its effects through the following mechanisms:
-
Signaling Pathways: IL-31 binds to the IL-31RA subunit on the surface of pruriceptive sensory nerve fibers, activating the OSMRβ subunit. This triggers signaling pathways such as JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and MAPK-JNK/p38, upregulating the expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), enhancing neuronal excitability, and promoting the development of late-phase and chronic pruritus.
-
Neuro-Immune Interactions: IL-31 not only mediates pruritus but also activates immune cells (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils) to release inflammatory mediators, exacerbating skin inflammation. This neuro-immune interplay plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis.
02. Advances in IL-31 Research in Canine Atopic Dermatitis
Anti-IL-31 monoclonal antibodies, such as lokivetmab, inhibit IL-31-mediated pruritus in vivo. Lokivetmab, a caninized monoclonal antibody, has provided a novel therapeutic option for canine atopic dermatitis. Compared to traditional glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants, lokivetmab offers superior safety and tolerability. It not only rapidly alleviates pruritus but also reduces skin inflammation and erythema. In clinical practice, lokivetmab is often used in combination with other medications to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes.
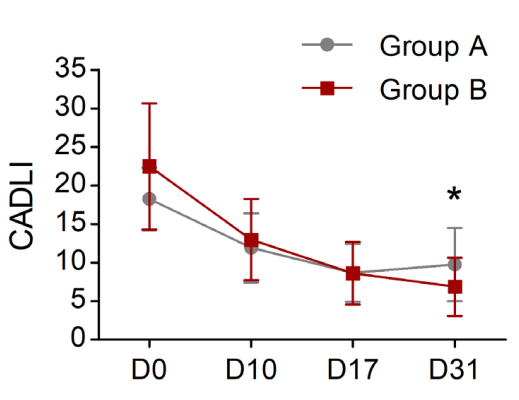
Mean and Standard Deviation (SD) of Canine Atopic Dermatitis Lesion Index (CADLI) Scores Assessed by Investigators at Day 0 (D0), Day 17 (D17), and Day 31 (D31) After Treatment with Lokivetmab Alone or in Combination with Weekly Topical Therapy (*, P<0.05).
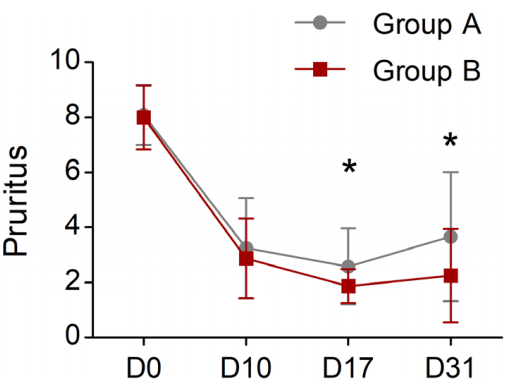
Mean and Standard Deviation (SD) of Pruritus Severity Assessed by Owners Using a Pruritus Visual Analog Scale (pVAS) at Day 0 (D0), Day 17 (D17), and Day 31 (D31) After Treatment with Lokivetmab Alone or in Combination with Weekly Topical Therapy (*, P<0.05).
Beyond its use in atopic dermatitis, lokivetmab has shown potential therapeutic value for other allergic skin conditions, such as cutaneous mastocytosis. With further research and clinical experience, lokivetmab is expected to find broader applications in dermatology.
Future Perspectives
As a key pruritogenic cytokine, IL-31 plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of canine atopic dermatitis. By elucidating the mechanisms of IL-31 and its associated signaling pathways, we can gain a deeper understanding of atopic dermatitis and develop more targeted therapies. Future research may lead to the development of additional IL-31-targeted treatments, offering comprehensive and effective solutions for managing canine atopic dermatitis.
Product Data Sharing
Product Name: IL-31 Protein, Canine
Catalog Number: UA040130
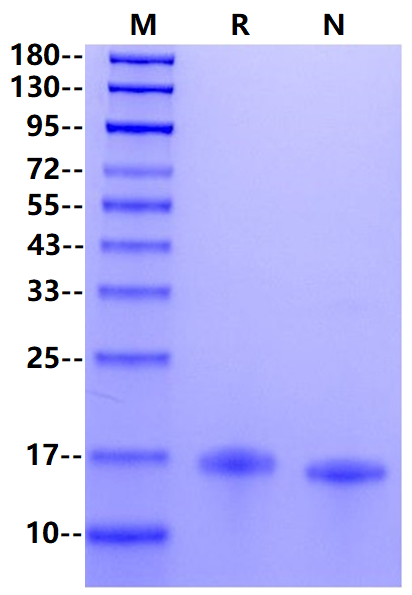
>95% by SDS-PAGE
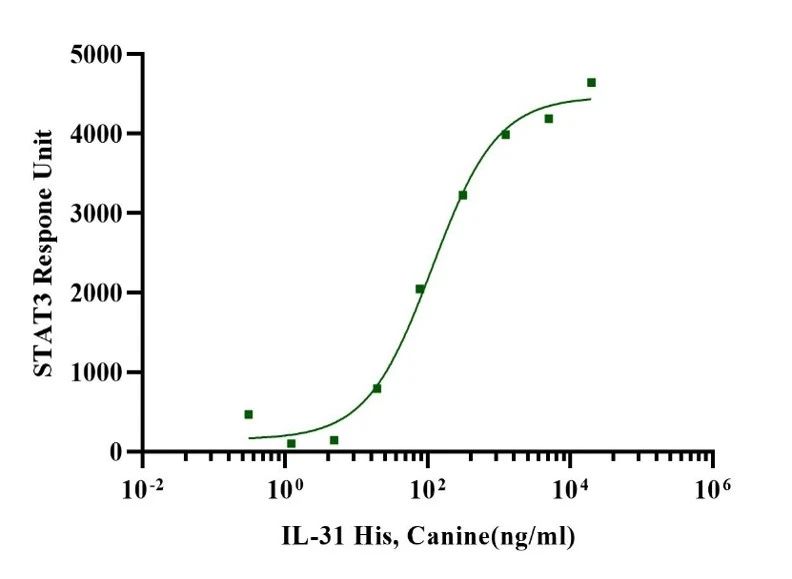
EC50 for this effect is 80- 200ng/mL
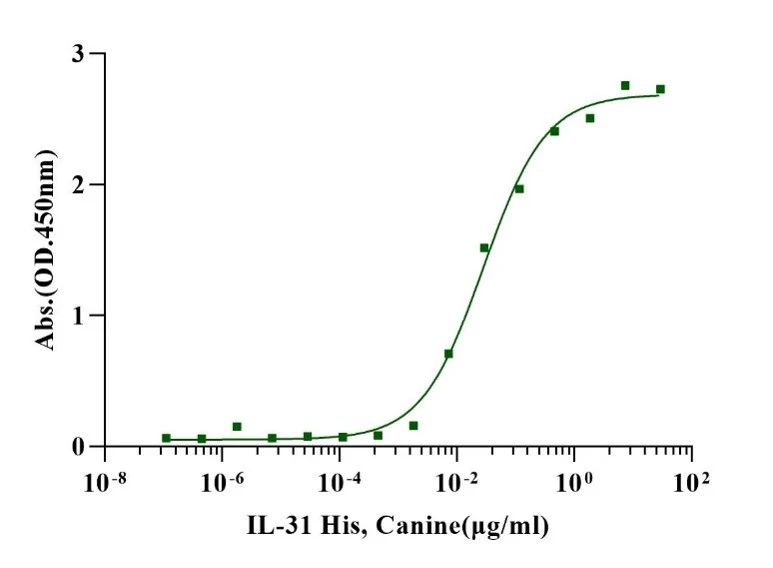
When Recombinant Canine IL31 His Tag is immobilized 2.5µg/mL (100µL/well), Recombinant Canine OSMR Fc Chimera binds with an EC50 of 0.02-0.04μg/ml.
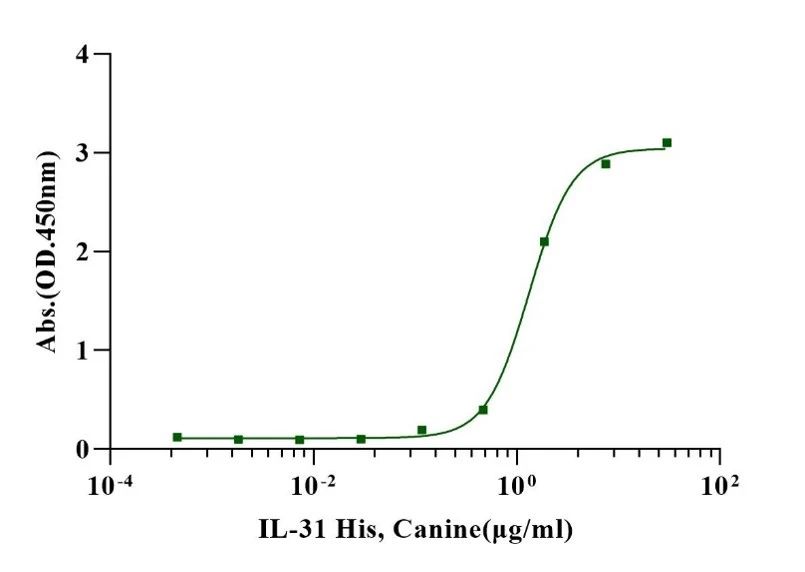
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Recombinant Canine OSMR Fc Chimera is immobilized 2.5µg/mL (100µL/well), Recombinant Canine IL-31 His tag binds with an EC50 of 1.2-1.4μg/ml.
Product Name: Lokivetmab Catalog Number: UA010875
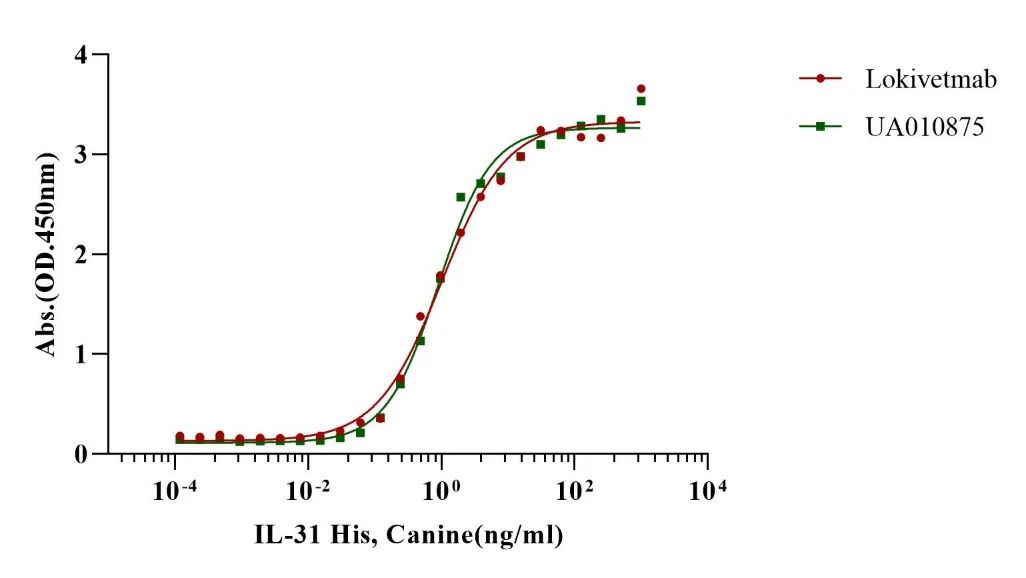
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Lokivetmab(Anti-Canine IL-31Recombinant Antibody) is immobilized 0.5µg/mL (100µL/well), Recombinant Canine IL-31 binds with an EC50 of 0.07-1ng/ml.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA010875 | Lokivetmab | Host : Canine | $116 |
| Expression System : CHO | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| UA040130 | IL-31 Protein, Canine | Host : Canine | $1,440 |
| Expression System : E.coli | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




