Optimizing Flow Cytometry Analysis: The Critical Role of Fc Receptor (FcR) Blockers

Fc Receptor (FcR)
Flow cytometry employs fluorescently labeled antibodies to specifically identify and distinguish cells or cell subpopulations, which are subsequently detected and analyzed by flow cytometers. The Fab region of the labeled antibodies facilitates specific recognition, while the highly conserved Fc region of antibodies can also be recognized by certain cells. Proteins that recognize the Fc region of immunoglobulins (Ig) are known as Fc receptors (Fc Receptors).
Fc receptors are expressed on the surface of various immune cells, including monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, myeloid cells, B cells, and NK cells. These receptors play multiple critical roles on the surface of immune cells:
Phagocytosis: Immune cells such as macrophages and neutrophils recognize and engulf antibody-coated microorganisms via Fc receptors, a key innate immune defense mechanism.
Lysosomal Degradation: Following phagocytosis, immune complexes are transported to lysosomes, where enzymes degrade pathogens and other foreign substances, completing the pathogen clearance process.
Cytotoxicity: Natural killer (NK) cells, among others, recognize antibody-labeled cells through Fc receptors and release cytotoxic granules.
Secretion of Cytokines and Chemokines: Activated immune cells secrete cytokines and chemokines, which help regulate immune responses and recruit other immune cells to sites of infection or inflammation.

Figure 1: Functions of Fc Receptors on Immune Cell Surfaces
Fc receptors are classified based on the type of immunoglobulin they bind: FcγR for IgG, FcεR for IgE, FcαR for IgA, FcμR for IgM, and FcδR for IgD. In routine experiments, IgG-type monoclonal antibodies are commonly used, and their Fc receptors (FcγR) can be divided into three subfamilies based on affinity: FcγRI (CD64), FcγRII (CD32), and FcγRIII (CD16).
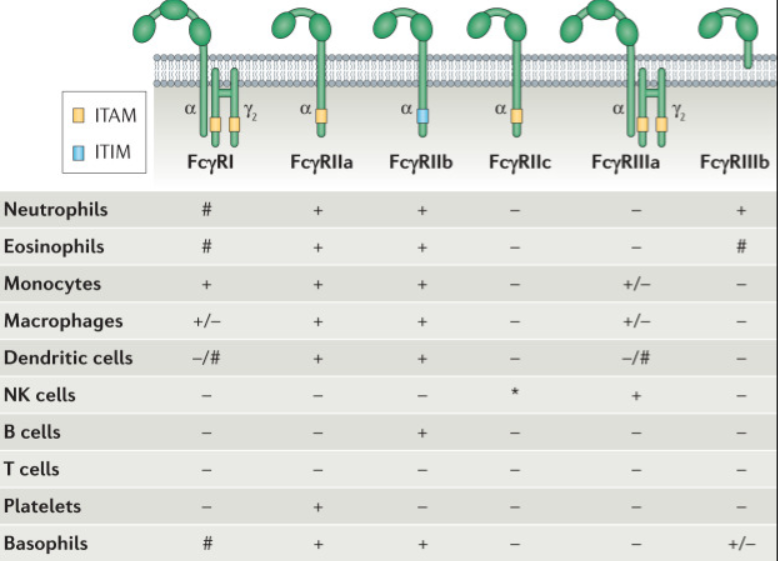

Figure 2: FcγR Family and Expression Patterns
FcR Blocking
In flow cytometry experiments, the expression of multiple FcγRs on cell surfaces can lead to non-specific binding of the antibody Fc region, resulting in high background or even false-positive signals. To accurately identify positive cell populations, blocking reagents can be pre-incubated with cells to occupy binding sites and prevent Fc receptor-antibody interactions, thereby reducing background noise and improving result accuracy.
Common blocking reagents include:
Serum or purified IgG from serum
Anti-CD16/32 antibodies
S-RMab® FcR Blockers
Starter has introduced the Human FcR Blocking Reagent, which exhibits high affinity, alongside the previously
launched Mouse Fc Receptor Blocker, providing comprehensive FcR blocking solutions.
Product Name: Human FcR Blocking Reagent Catalog Number: S0F0002
Blocking Usage: 1.0 µg per 2.5×10^5 cells in a 100 µL volume

Human PBMCs were labeled with rabbit monoclonal IgG isotype control antibodies. After 30 minutes of incubation on ice with PBS (right panel) or Human FcR Blocking Reagent at a 1/100 dilution (1 µg per 2.5×10^5 cells in 100 µL), Fc receptors and non-specific protein interactions were blocked. Results were compared with an unlabeled control group (cells not incubated with primary or secondary antibodies) (blue).
THP-1 cells were labeled with rabbit monoclonal IgG isotype control antibodies. After 30 minutes of incubation on ice with PBS (black) or Human FcR Blocking Reagent at a 1/100 dilution (1 µg per 2.5×10^5 cells in 100 µL) (red), Fc receptors and non-specific protein interactions were blocked. Results were compared with an unlabeled control group (cells not incubated with primary or secondary antibodies) (blue).
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B0599 | Mouse FcR Blocking Reagent | Host : Rat | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0002 | Human FcR Blocking Reagent (Mouse anti-human CD16/32 & human antibody against CD64) | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $120 |





