Tumor Pathology Targets: MLH1 and NaPi2b (SLC34A2) Analysis

MutL Homolog 1 Target
MLH1 (MutL Homolog 1) protein is a DNA repair enzyme found in human cells and belongs to the MutL protein family. The MLH1 protein plays a critical role in the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) process, which identifies and repairs mismatched base pairs generated during DNA replication. The function of MLH1 is essential for maintaining genomic stability and preventing cancer development.
Structural Features
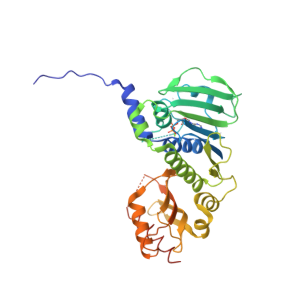
Three-Dimensional Structures of MLH1
The MLH1 protein belongs to the MutL protein family and contains multiple functional domains. It typically forms a heterodimer with the PMS2 protein, which is the active form for DNA mismatch repair. The N-terminal domain contains an ATP-binding domain that binds and hydrolyzes ATP, providing energy for protein activity. The C-terminal domain interacts with other mismatch repair proteins, playing a crucial role in the assembly and function of the mismatch repair complex.
Main Functions
-
DNA Mismatch Repair: During DNA replication, DNA polymerase occasionally introduces incorrect bases, leading to base mismatches or insertion-deletion loops. The MLH1-PMS2 heterodimer recognizes these mismatches and collaborates with other mismatch repair proteins (e.g., the MSH2-MSH6 complex) to excise and repair the incorrect bases, thereby maintaining genomic stability and integrity.
-
DNA Damage Response: In addition to mismatch repair, MLH1 is involved in the cellular response to DNA damage. When DNA is damaged, MLH1 can activate cell cycle checkpoints, causing cell cycle arrest to allow time for DNA repair. If the damage is irreparable, MLH1 may also initiate apoptosis to eliminate damaged cells and prevent carcinogenesis.
Role in Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Hereditary Colorectal Cancer and Lynch Syndrome Screening
Lynch syndrome (LS) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder caused by functional defects in mismatch repair genes (MMR), such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, and is closely associated with hereditary colorectal cancer. Loss of MLH1 protein function is a significant cause of Lynch syndrome. Immunohistochemical (IHC) detection of MLH1 protein expression in tumor tissues can indicate Lynch syndrome if MLH1 expression is absent.
Diagnosis and Prognostic Assessment of Sporadic Colorectal Cancer
In sporadic colorectal cancer, some patients exhibit abnormal MLH1 protein expression. Detecting MLH1 expression helps differentiate molecular subtypes of sporadic colorectal cancer. For example, hypermethylation of the MLH1 gene promoter region can silence MLH1 expression, leading to distinct tumor biology and clinicopathological features. MLH1 expression status is also associated with prognosis in sporadic colorectal cancer. Generally, patients with MLH1-deficient sporadic colorectal cancer may have a better prognosis and respond differently to certain chemotherapeutic agents compared to those with normal MLH1 expression. Thus, MLH1 expression detection provides critical information for treatment selection and prognosis evaluation.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is another common tumor associated with Lynch syndrome. Approximately 20-30% of Lynch syndrome patients develop endometrial cancer. Detecting MLH1 expression in endometrial cancer tissues aids in screening for Lynch syndrome-related cases. For patients with MLH1-deficient endometrial cancer, further evaluation for Lynch syndrome is necessary to provide genetic counseling and cancer prevention for the patient and their family. MLH1 expression detection also assists in the differential diagnosis of endometrial cancer. For instance, Lynch syndrome-related endometrial cancer often exhibits unique histological and molecular features compared to sporadic cases, and MLH1 expression status helps distinguish between these types, guiding treatment and follow-up.
Product Introduction
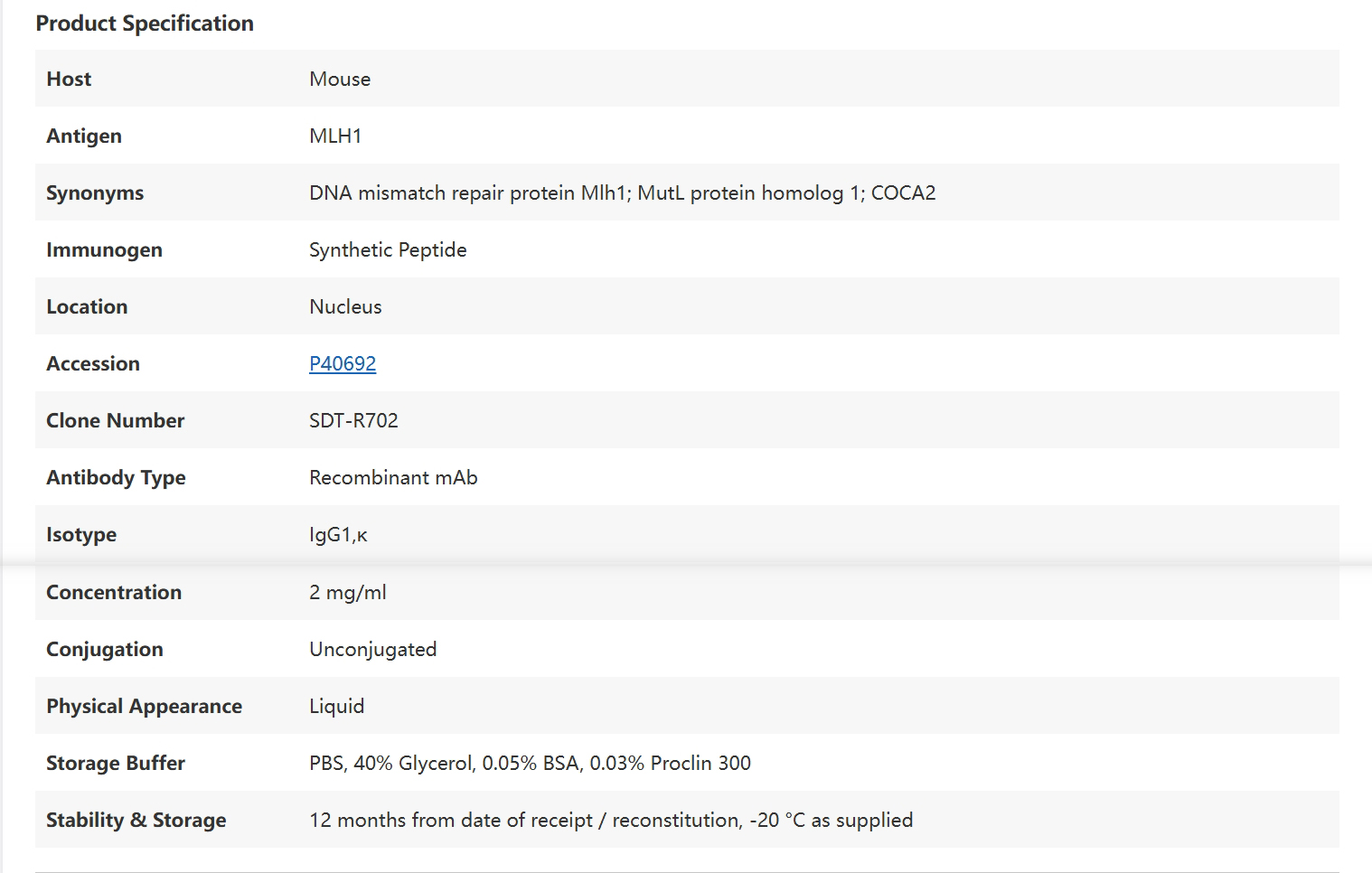
MLH1 Recombinant Mouse mAb (SDT-R702) Catalog Number: S0B2363
Data Presentation
Positive staining
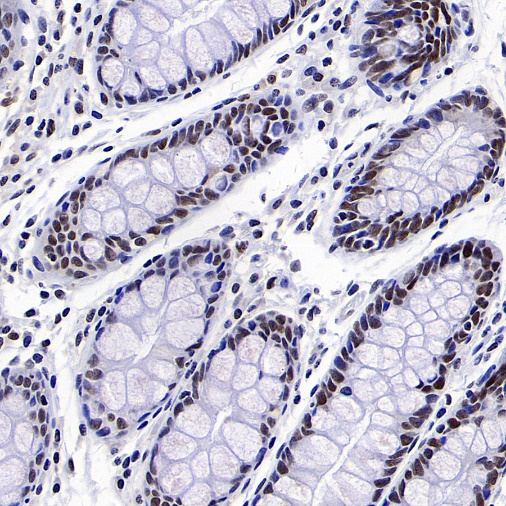
IHC shows positive staining in paraffin-embedded human colon
Positive staining
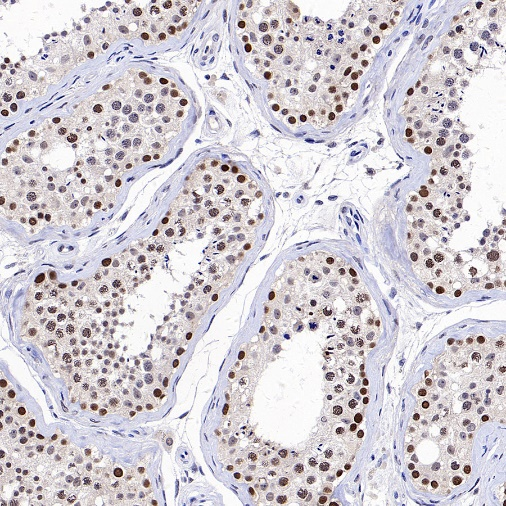
IHC shows positive staining in paraffin-embedded human testis
Negative staining
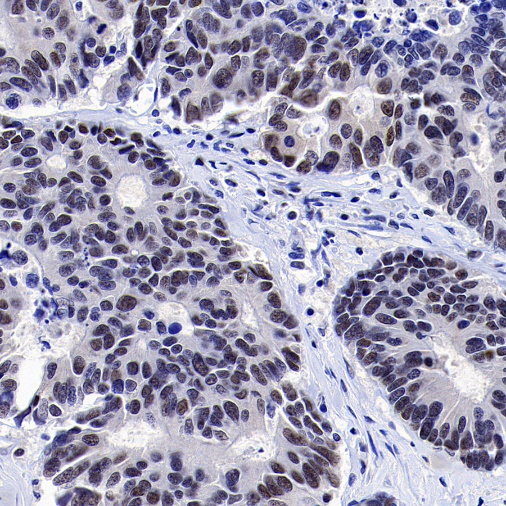
IHC shows negative staining in paraffin-embedded human colon cancer
Negative staining
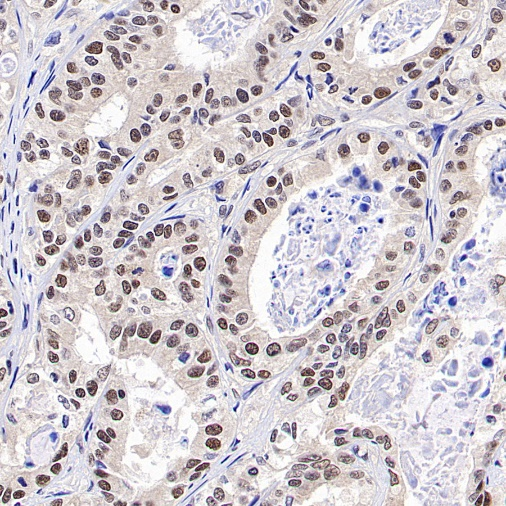
IHC shows negative staining in paraffin-embedded human pancreatic cancer
Tissue Expression Atlas:
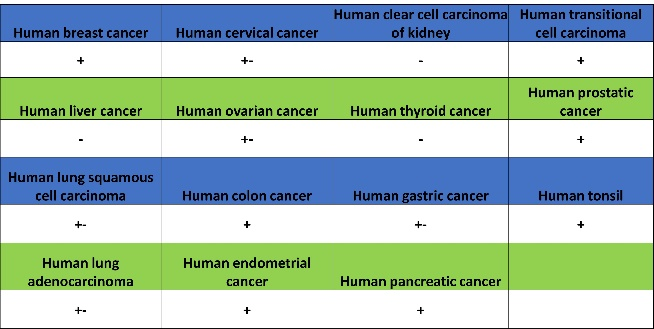
Expression of MLH1 in tumor tissue
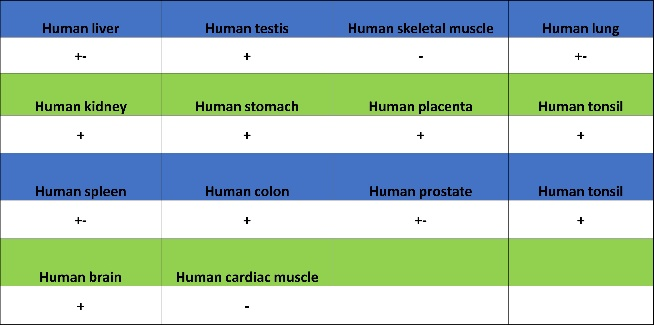
Expression of MLH1 in human tissue.
NaPi2b/SLC34A2 Target
NaPi2b, also known as SLC34A2, is a sodium-dependent phosphate transporter. It belongs to the SLC34 family, which is responsible for phosphate transport across cell membranes.
Structural Features
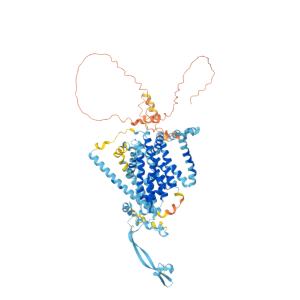
Three-Dimensional Structures of NaPi2b
-
Transmembrane Structure: NaPi2b/SLC34A2 is a glycosylated transmembrane protein with 12 transmembrane domains, with both the N- and C-termini located intracellularly. This structure allows it to embed in the cell membrane, forming a channel or carrier for transmembrane transport.
-
Glycosylation: Glycosylation is critical for the stability, transport function, and interactions of NaPi2b/SLC34A2. Alterations in glycosylation sites may affect protein folding, localization, and activity.
Main Functions
-
Phosphate Absorption: The primary function of NaPi2b is to facilitate cellular phosphate absorption. Phosphate is an essential mineral for cell growth, energy metabolism, and bone health.
-
Sodium Dependence: The transport activity of NaPi2b depends on the presence of sodium ions. It utilizes the electrochemical gradient of sodium ions to drive phosphate into cells.
-
Tissue Distribution and Related Functions: This protein is widely distributed in various tissues and organs, such as the lungs, small intestine, and mammary glands. In the small intestine, it participates in dietary phosphate absorption; in lung tissue, it may be involved in phosphate balance in alveolar surface fluid.
Role in Cancer Diagnosis
-
Ovarian Cancer: NaPi2b is highly expressed in ovarian cancer (particularly serous ovarian cancer), and its expression levels correlate with tumor grade and prognosis. Thus, NaPi2b serves as an auxiliary marker for ovarian cancer diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
-
Lung Adenocarcinoma: Some studies indicate that NaPi2b is also highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma, potentially aiding in diagnosis and classification.
-
Other Cancers: NaPi2b is expressed in other cancers, such as endometrial and thyroid cancers, but its diagnostic value requires further research.
Product Introduction
NaPi2b/SLC34A2 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-1771-79) Catalog Number: S0B2364
Data Presentation
Positive staining
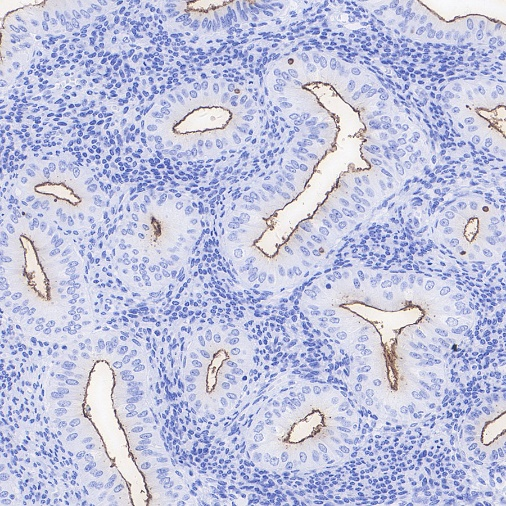
IHC shows positive staining in paraffin-embedded human endometrial cancer
Negative control
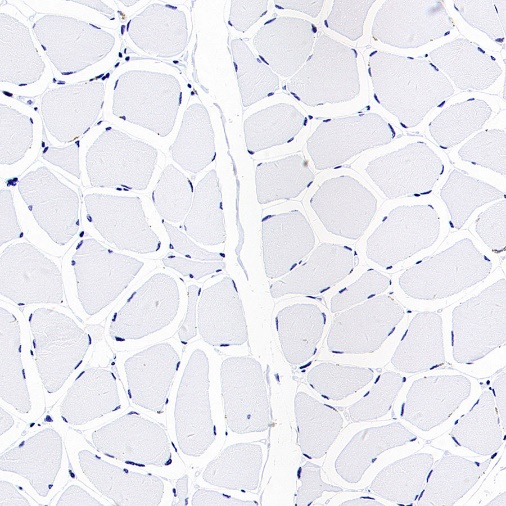
IHC shows negative staining in paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle
Tissue Expression Atlas:
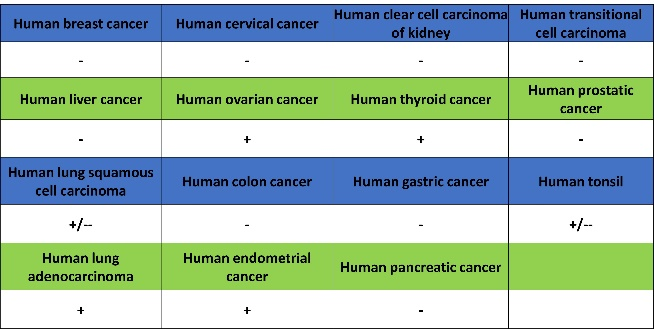
Expression of NaPi2b/SLC34A2 in tumor tissue
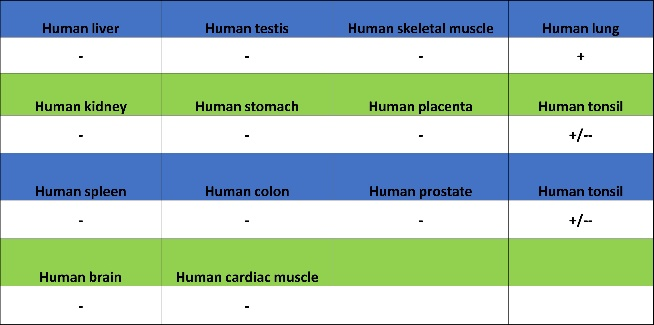
Expression of NaPi2b/SLC34A2 in human tissue