A New Breakthrough in Immunoglobulin Detection: Precise Quantification of IgG, IgA, and IgM Within One Hour.

Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are produced by B cells and play a vital role in humoral immunity. They are widely distributed in blood, tissue fluids, and mucosal surfaces, where they recognize and bind antigens, activate complement, and participate in immune responses. Among the various immunoglobulins, IgG, IgA, and IgM are the most critical types.
IgG: The "Long-Term Guardian" of the Immune System
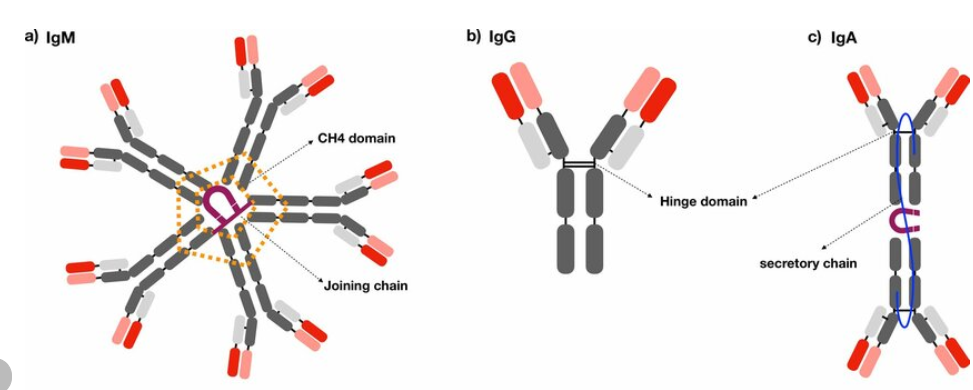
IgG is the most abundant immunoglobulin in serum, accounting for 75%-80% of the total. It has a small molecular weight, a long half-life (approximately 21 days), and can cross the placenta, providing passive immune protection to fetuses and newborns.
Functions:
-
IgG is the primary antibody during the late stages of infection, capable of neutralizing pathogens and toxins, activating complement, and promoting phagocytosis.
Clinical Significance:
-
Infection Diagnosis: Elevated IgG levels can indicate recovery from infection or the presence of chronic infections.
-
Autoimmune Disease Detection: Abnormal increases in IgG levels are used to aid in the diagnosis of diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Vaccine Efficacy Evaluation: Elevated IgG antibody levels are a key indicator of vaccine effectiveness.
IgA: The "Frontline Defender" of Mucosal Immunity
IgA is predominantly found on mucosal surfaces, such as the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital tracts. It exists in two forms: serum IgA and secretory IgA (sIgA). sIgA has a dimeric structure and is resistant to protease degradation.
Functions:
-
IgA is the primary antibody in mucosal immunity, preventing pathogen adhesion to mucosal surfaces and blocking infection.
Clinical Significance:
-
Mucosal Immunity Research: IgA plays a crucial role in mucosal immune defense, and studying its function aids in the development of vaccines against mucosal infections.
-
Immunodeficiency Diagnosis: IgA deficiency is a common primary immunodeficiency, and measuring IgA levels can aid in diagnosis.
-
Inflammatory Disease Monitoring: Changes in IgA levels are used to assess disease activity in chronic inflammatory conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
IgM: The "Vanguard" of Immune Response
IgM is the largest immunoglobulin, typically existing as a pentamer. It is the first antibody type synthesized during an immune response and exhibits strong antigen-binding and complement-activating capabilities.
Functions:
-
IgM is the primary antibody during the early stages of infection, rapidly recognizing and binding pathogens, activating complement, and enhancing immune responses.
Clinical Significance:
-
Early Infection Diagnosis: The presence of IgM typically indicates recent infection, aiding in the early diagnosis of bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections.
-
Autoimmune Disease Research: IgM antibodies play a significant role in diseases such as cryoglobulinemia, and studying their mechanisms can lead to new therapeutic approaches.
-
Neonatal Infection Screening: Elevated IgM levels in newborns can be used to screen for congenital infections, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus.
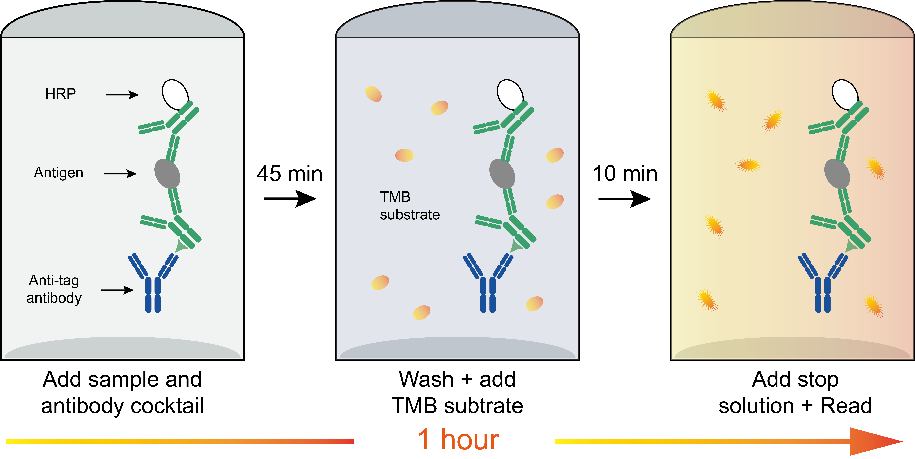
OneStep ELISA Kit
STARTER's OneStep ELISA Kit utilizes a tag antibody capture technology, enabling the completion of experiments within one hour. The plate is pre-coated with tag antibodies, which can sensitively capture the sandwich complex. When paired with highly specific recombinant monoclonal antibodies, the antibody-analyte sandwich complex is formed in solution in a single step, allowing for easy and accurate protein quantification.