Starter Introduces New Product: Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody for Aβ42/40

Background
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a gradual decline from mild cognitive impairment to severe dementia, significantly impairing patients' daily functioning and cognitive abilities. Globally, the number of AD patients has reached 55 million and is projected to rise to 139 million by 2050. In China, the prevalence of AD and other dementias approached 17 million in 2021. The FDA approval of Aβ-targeting drugs such as Aducanumab and Lecanemab marks a new era in Aβ-directed therapies, with several other candidates currently in clinical trials. These drugs work by clearing cerebral Aβ plaques to delay cognitive decline, complemented by biomarker-based early and precise diagnosis.
On December 31, 2024, China's National Health Commission and 14 other departments jointly issued the National Action Plan for Addressing Senile Dementia (2024–2030), promoting nationwide dementia screening and early intervention, fueling sustained demand for AD diagnostics.
Aβ
Amyloid-β (Aβ), a 4 kDa fragment derived from the sequential cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase (BACE1) and γ-secretase, is a hallmark pathological feature of AD. Its aberrant accumulation triggers neurofibrillary tangles, oxidative stress, microglial activation, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal loss—pathological changes spatiotemporally correlated with AD-related cognitive decline.
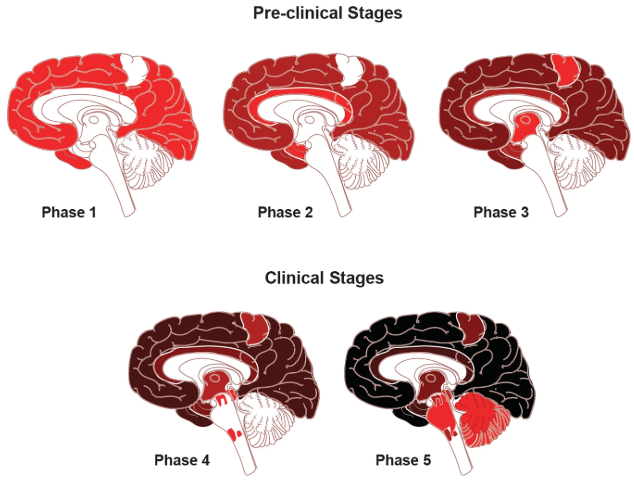
Figure 1. Classical neuropathological staging of Aβ.
Aβ Production and Aggregation
Aβ generation involves two proteolytic pathways of APP:
Non-amyloidogenic pathway (neuroprotective):
APP is cleaved by α-secretase (ADAM family) within the Aβ sequence (e.g., between Aβ16–17), precluding Aβ formation. This yields soluble sAPPα and membrane-bound C83, further processed by γ-secretase into P3 peptide and APP intracellular domain (AICD).
Amyloidogenic pathway (pathological):
APP is first cleaved by BACE1, producing sAPPβ and C99. γ-Secretase (comprising Presenilin 1/2, Nicastrin, PEN2, and APH-1) then cleaves C99’s transmembrane domain (typically at Aβ40 or Aβ42 C-terminus), releasing Aβ40 or Aβ42. Aβ42, with two additional hydrophobic residues (Ile41, Ala42), readily aggregates into neurotoxic oligomers and plaques. Aβ40, though more abundant, exhibits lower aggregation propensity and is a secondary pathological form.
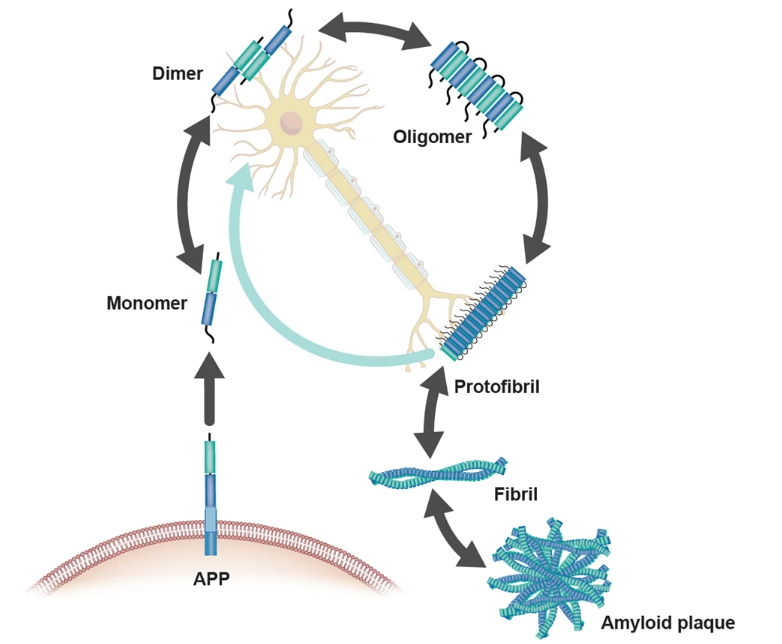
Figure 2. Pathways of Aβ generation.
Aβ aggregates dynamically interconvert between monomers, dimers, oligomers, protofibrils, fibrils, and insoluble amyloid plaques, with properties dictated by size, conformation, and solubility. Monomeric Aβ (e.g., Aβ1–40, Aβ1–42) nucleates aggregation, forming soluble neurotoxic oligomers (dimers, trimers, polymers) that impair synapses. Oligomers progressively mature into protofibrils and ultimately insoluble fibrils/plaques, regulated by mechanisms like lipid phase separation. Aβ subtypes (e.g., N-truncated variants) and pathological conditions (e.g., pH, metal ions) critically modulate aggregation kinetics and toxicity.
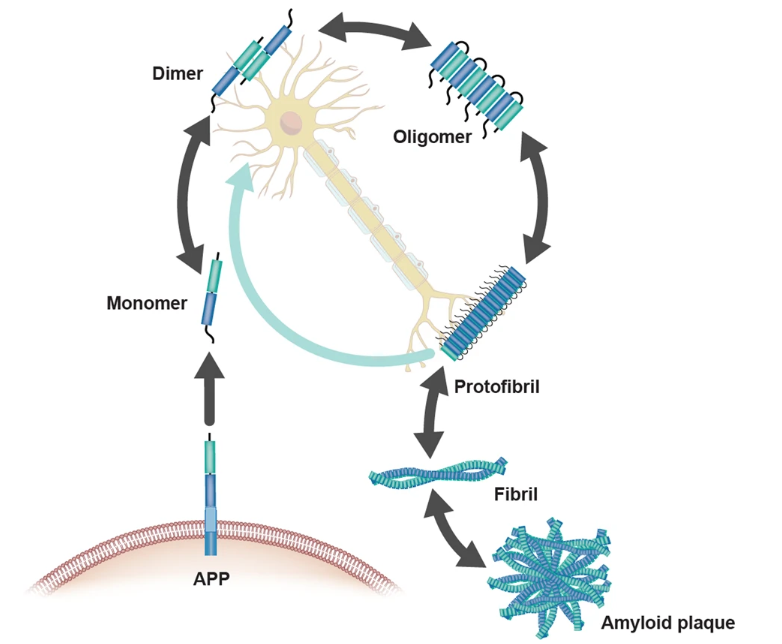
Figure 3. Aβ aggregation states.
AD Biomarkers
A 20-year longitudinal cohort study by Prof. Jianping Jia’s team revealed that Aβ dysregulation emerges earliest, with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Aβ changes detectable 18 years pre-diagnosis, followed by significant Aβ42/40 ratio alterations 14 years pre-diagnosis. Phosphorylated tau (p-tau181) and NFL levels rise subsequently.
Vasilios C. Constantinides demonstrated that the CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio outperforms standalone Aβ42 in distinguishing AD pathology (AUC = 0.939 vs. 0.831; p < 0.001), exhibiting superior sensitivity/specificity. Reclassification using BIOMARKAPD/ABSI criteria confirmed its diagnostic robustness.
Shogyoku Bun’s study employing the HISCL platform showed plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio excelled in identifying amyloid-PET positivity (AUC = 0.949), with high accuracy even in the "gray zone" of early amyloidosis. It outperformed other plasma biomarkers (e.g., p-tau181, GFAP, NfL) across cohorts.
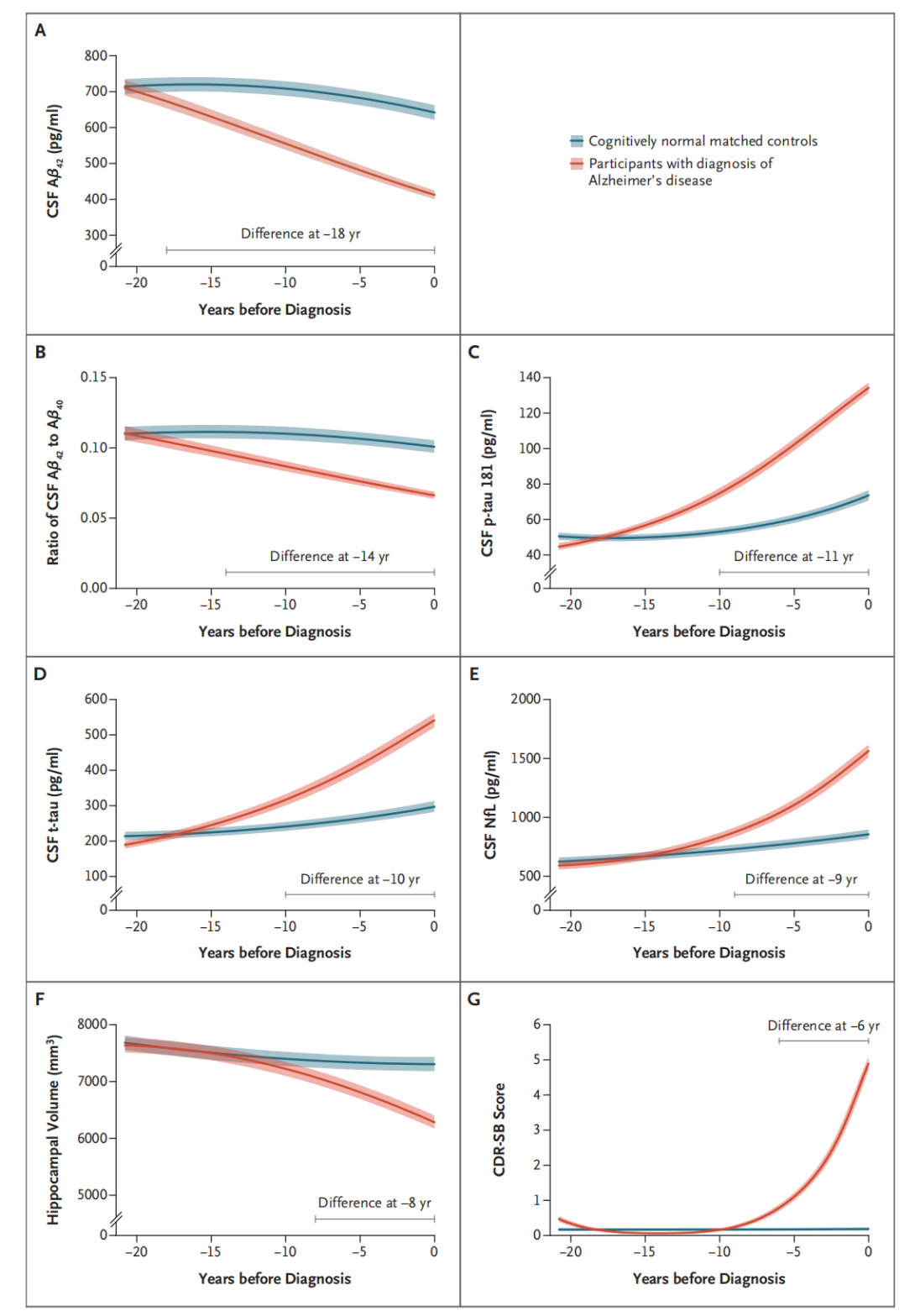
Figure 4. Temporal trajectories of AD biomarkers.
The Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio is pivotal for early and accurate AD diagnosis. With advancing detection technologies and standardization, large-scale Aβ screening may enable preemptive intervention, improving patient outcomes.
S-RMab® Monoclonal Antibodies
Starter launches high-sensitivity recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies against Aβ42 and Aβ40, empowering AD diagnostics.
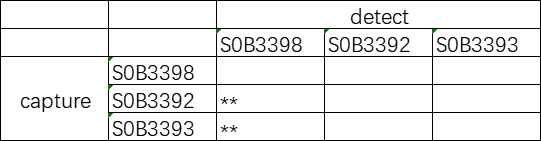
Recommended pairings for Aβ40 detection:
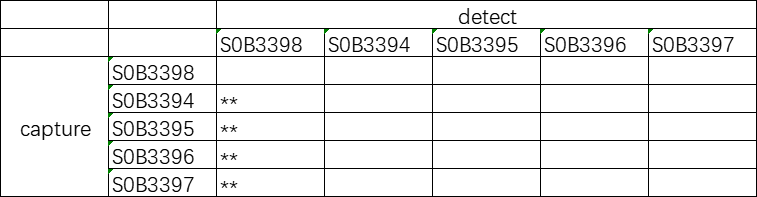
Recommended pairings for Aβ42 detection:
Click on the product catalog numbers below to access detailed information on our official website.




