The Pivotal Role of Vimentin-High Macrophages in Immunosuppression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Vimentin, a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein widely expressed in mesenchymal cells, plays pivotal roles in cytoskeletal organization, cell shape maintenance, migration, signal transduction, and stress responses. It anchors to the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria through lateral or terminal attachments, regulating directional cell movement, orientation alignment, lamellipodia formation, and maintaining Golgi apparatus polarity at the leading edge of migrating cells. Furthermore, vimentin protects SCRIB protein from proteasomal degradation via cell-contact dependent mechanisms and facilitates its localization to intermediate filament structures.
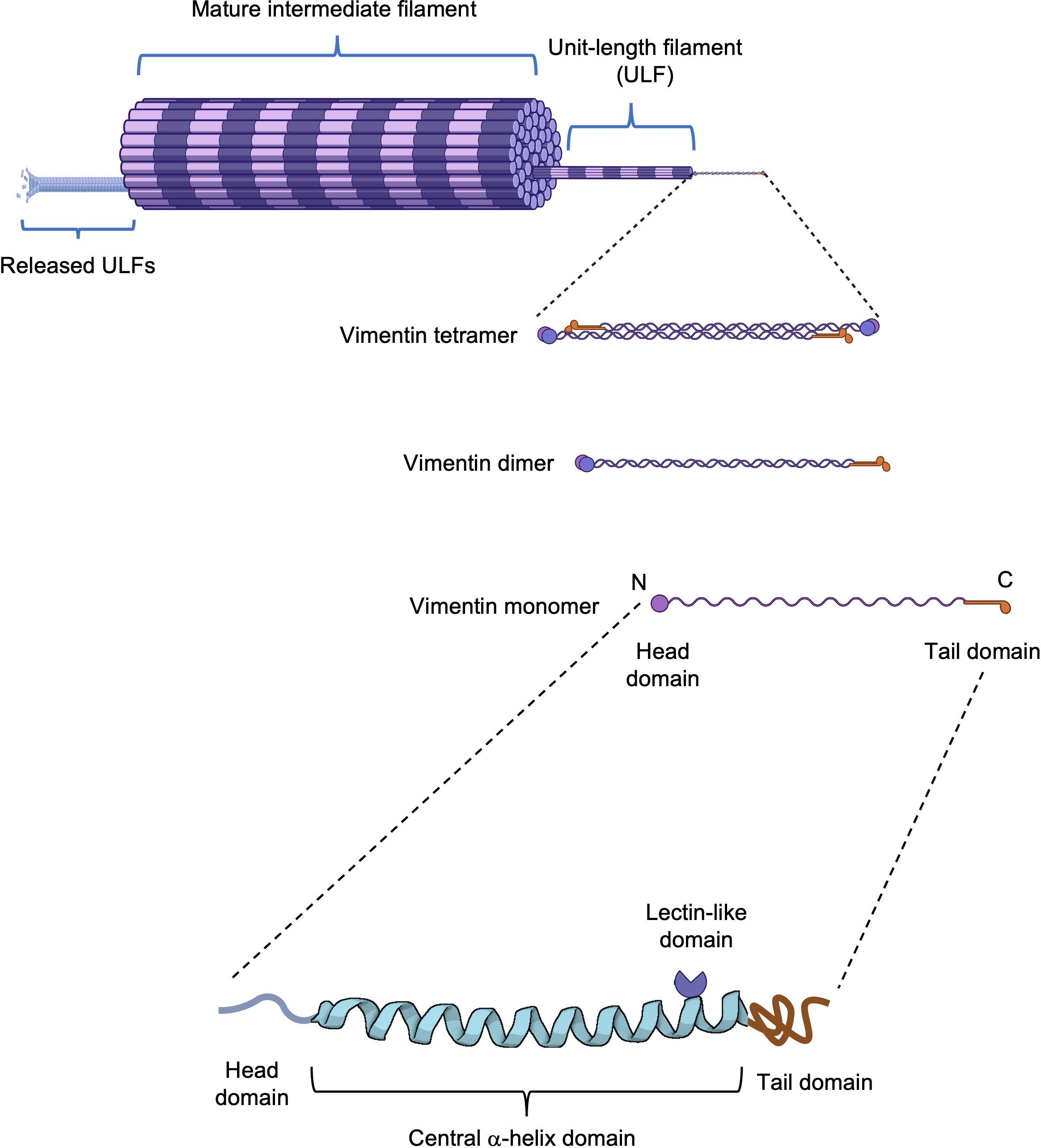
Structural Organization of Vimentin.The schematic representation illustrates vimentin filament assembly from monomer to mature filament. The vimentin monomer consists of a central α-helical domain flanked by unstructured head and tail domains. Notably, the central domain contains a rod II region with lectin-like properties.
Key Discovery: Vimentin-High (VIM+) Macrophages Activate Treg-Mediated Immunosuppression via IL-1β Secretion
A groundbreaking study by Professor Hongyang Wang and Lei Chen's team at Fudan University, published in September 2024 in Nature Cancer (Impact Factor: 23.5) under the title "Spatial single-cell protein landscape reveals vimentin-high macrophages as immune-suppressive in the microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma," has provided crucial insights into HCC progression. The research comprehensively mapped the spatial single-cell protein landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), systematically analyzed the spatial heterogeneity among HCC tumors, established a prognostically relevant spatial classification (Spatial Pattern) for HCC, and through integrated multi-omics approaches combined with in vitro experiments, revealed that spatial interactions between vimentin-high macrophages and regulatory T cells (Tregs) promote HCC progression.
The study employed single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomic analysis to uncover distinct gene expression signatures of VIM+ macrophages and demonstrated a strong transcriptional correlation between VIM+ macrophages and Treg populations, suggesting potential immunosuppressive interactions. Ligand-receptor analysis further identified interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) as key mediators in the regulatory axis between VIM+ macrophages and Tregs. Subsequent experimental validation involved flow cytometry-based isolation of VIM+ versus VIM-low macrophage subsets, which revealed significantly elevated IL-1β expression in VIM+ macrophages compared to other macrophage subtypes. Through co-culture experiments, the researchers demonstrated that VIM+ macrophages potently stimulated IL-10 secretion by Tregs, an effect that was markedly attenuated by IL-1β neutralization, thereby confirming the critical role of IL-1β in this immunosuppressive pathway. These findings establish VIM+ macrophages as pivotal regulators of tumor immunosuppression in HCC through their IL-1β-mediated activation of Tregs, providing novel mechanistic insights into the tumor microenvironment and identifying potential therapeutic targets for HCC immunotherapy.
S-RMab®
Vimentin Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-029-120, catalog number:S0B2254) antibody serves as a powerful tool for vimentin research
Experimental Validation:
Western Blot Analysis
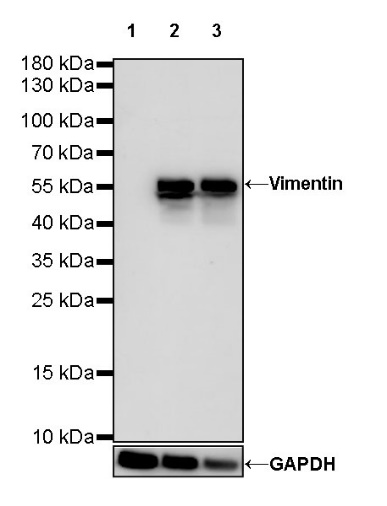
WB result of Vimentin Rabbit mAb
Primary antibody: Vimentin Rabbit mAb at 1/500 dilution
Lane 1: Daudi whole cell lysate 20 µg
Lane 2: HeLa whole cell lysate 20 µg
Lane 3: A549 whole cell lysate 20 µg
Negative control: Daudi whole cell lysate
Secondary antibody: Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, (H+L), HRP conjugated at 1/10000 dilution
Predicted MW: 54 kDa
Observed MW: 57 kDa
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
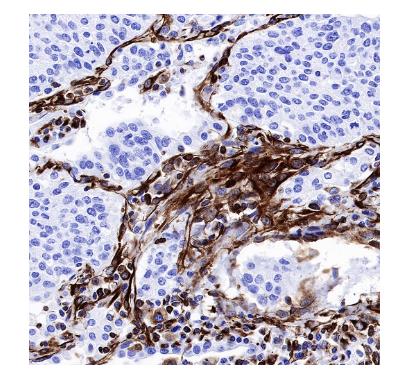
S-RMab®antibody series empowers advanced life science research and pathological investigations with high specificity and reproducibility.
Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
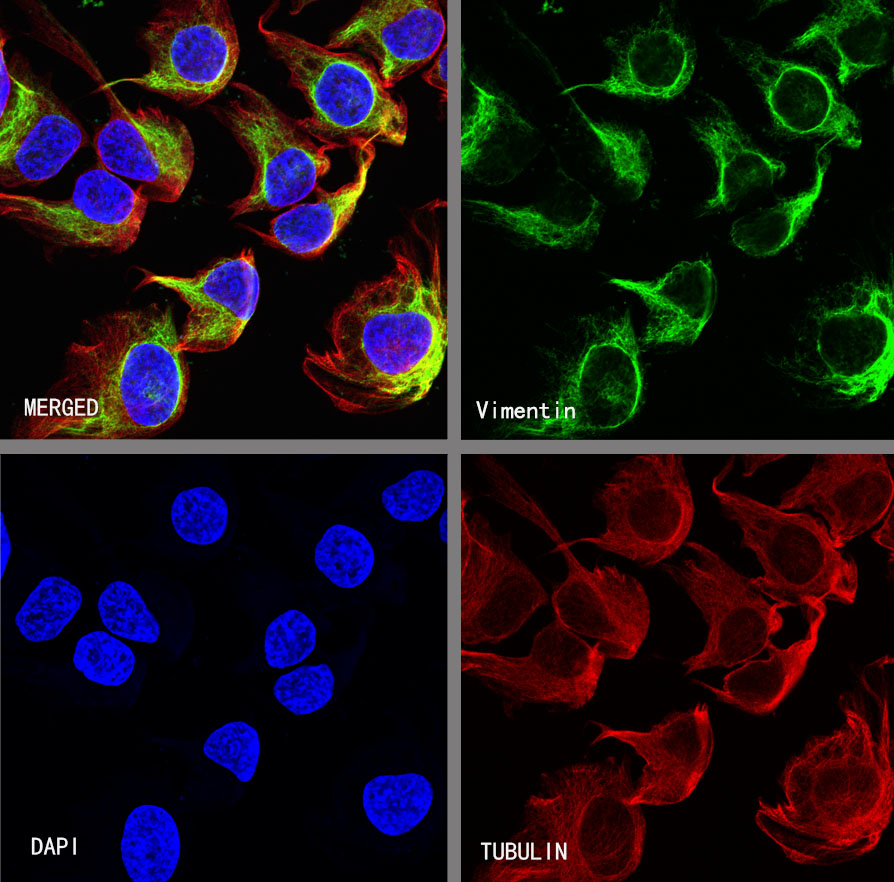
ICC shows positive staining in HeLa cells. Anti-Vimentin antibody was used at 1/250 dilution (Green) and incubated overnight at 4°C. Goat polyclonal Antibody to Rabbit IgG - H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488) was used as secondary antibody at 1/1000 dilution. The cells were fixed with 4% PFA and permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Triton X-100. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (Blue).Counterstain with tubulin (Red).
Click on the product catalog numbers below to access detailed information on our official website.




