Exploring the Potential of CD45 in Immunotherapy
05 Aug 2025
by AntBio
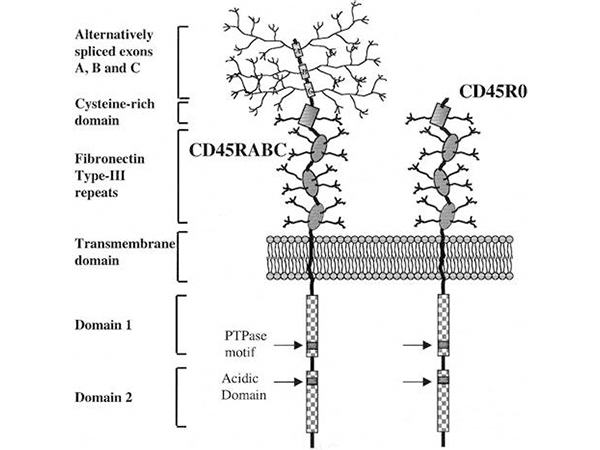
CD45, also known as Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor C (PTPRC), is expressed on all leukocytes and is thus also referred to as Leukocyte Common Antigen (LCA). It is a large glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 180–220 kDa, accounting for 5–10% of the total surface glycoproteins on T cells and B cells.
CD45 is composed of a cytoplasmic domain, a transmembrane domain, and an extracellular portion. The cytoplasmic domain contains two phosphatase domains, which are responsible for enzymatic activity and substrate recruitment, respectively. CD45 also exists in multiple splice variants, such as CD45RA, CD45RO, CD45RB, and CD45RABC. These variants are differentially expressed in various cell types and play a role in fine-tuning immune cell signaling through their expression in different cell types and activation states.
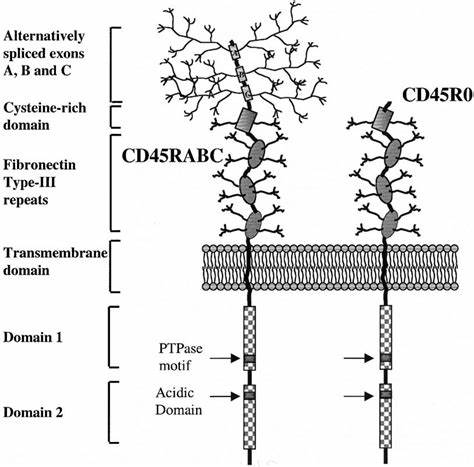
Figure 1: Structure of CD45
Biological Functions of CD45
Dysregulation of CD45 is associated with various immune disorders, including diseases related to T cell and B cell dysregulation, hematological malignancies, and autoimmune diseases. CD45 is a critical regulator of immune cell signaling pathways:
-
In T cells and B cells, CD45 modulates the activity of Src family kinases, thereby influencing signaling through the T cell receptor (TCR) and B cell receptor (BCR). The absence of CD45 leads to developmental defects in T and B cells and a reduction in the number of mature T and B cells.
-
In natural killer (NK) cells and mast cells, CD45 regulates signaling through Fcγ receptors and NK cell receptors, affecting cell activation and cytokine production.
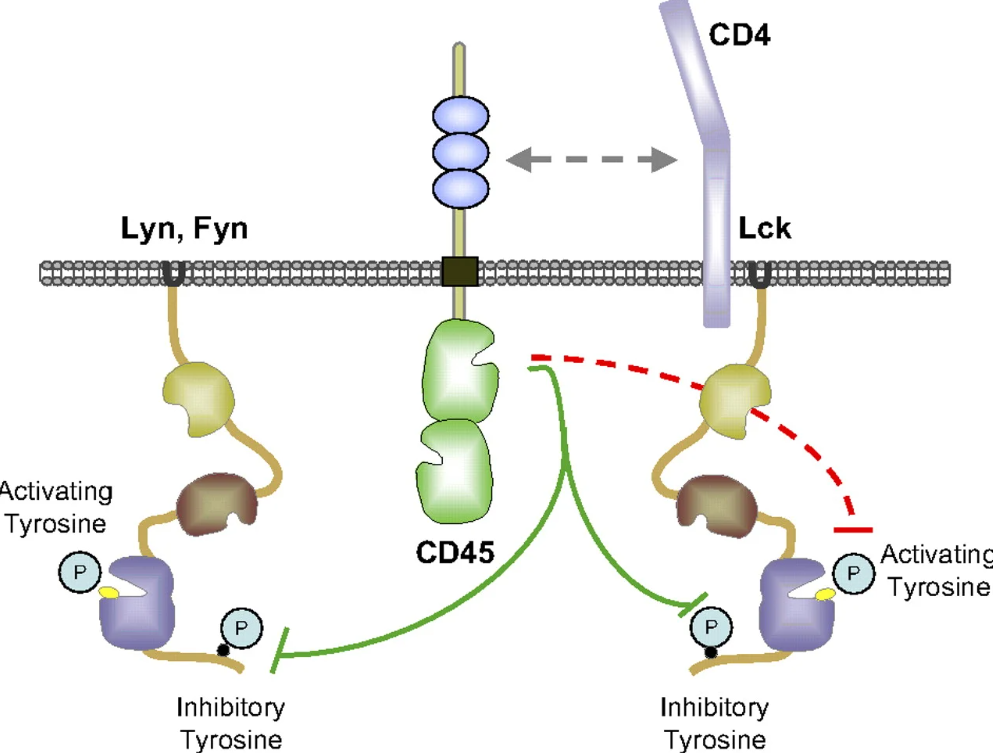
Figure 2: Differential Regulation of Src Family Kinase Phosphorylation by CD45 in T Cells and B Cells
CTC Detection
Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) are defined as tumor cells that spontaneously or due to diagnostic and therapeutic procedures detach from the primary or metastatic site of a solid tumor and enter the peripheral blood circulation. CD45, as a cell surface antigen, is commonly used to distinguish tumor cells from non-tumor cells, particularly in the detection of CTCs. It is frequently employed in the negative enrichment of CTCs: during the isolation of CTCs, adsorption of leukocytes expressing CD45 can increase the probability of capturing CTCs.
In cancer patients, CD45 expression is often detected in nucleated blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Compared to CD45++-CTCs, CD45-CTCs are closely associated with metastasis and poor prognosis. When masked by CD45, CTCs can easily evade immune surveillance and resist T cell killing through intercellular CD45-CD45 homotypic interactions between CTCs and T cells, thereby reducing TCR signaling.
Therapeutic Target
CD45 is expressed in all hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) except for red blood cells and platelets, making it an attractive target for universal hematological malignancy immunotherapy. In the treatment of hematological malignancies, anti-CD45 monoclonal antibodies can effectively deplete lymphocytes, inhibit rejection reactions, and induce immune tolerance. They can also be conjugated with various payloads to exert targeted anti-tumor effects. Additionally, as a protein expressed on the surface of multiple immune cells, CD45 helps reduce immune rejection of neoantigens or allogeneic antigens, making it an excellent target for payload delivery.
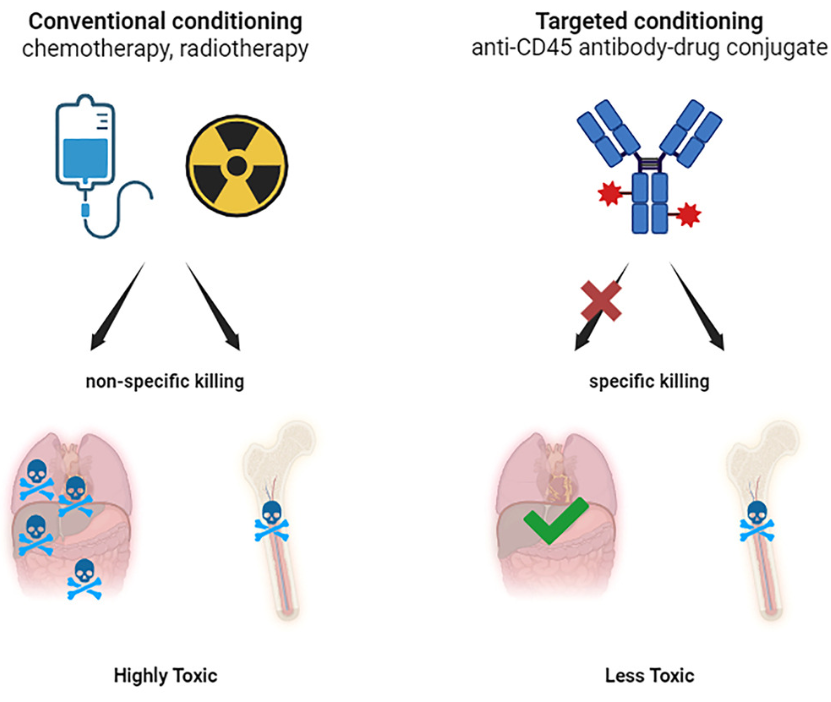
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
CD45-ADCs have the potential to eliminate effector cells and hold significant value for various hematological diseases and conditions requiring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). In preclinical studies, CD117 ADC demonstrated strong activity against human and NHP CD34+ cells; it could deplete hematopoietic stem cells in rhesus monkeys to accommodate graft infusion and exhibited good safety.
Magenta's CD45-ADC, in a single dose, achieved complete myeloablation in mouse models and complete engraftment in fully mismatched allogeneic HSCT models. A single dose of CD45-ADC was well-tolerated, leading to the depletion of lymphocytes and hematopoietic stem cells in non-human primates (NHPs) and achieving donor cell engraftment in NHP transplant models. The CD45-ADC IND study is currently being advanced.
Antibody-Radiation Conjugates (ARCs)
Lomab-B, a targeted radiotherapy developed by Actinium Pharmaceuticals, rapidly and simultaneously depletes blood cancer cells, immune cells, and bone marrow stem cells expressing CD45, thereby increasing the likelihood of patients receiving potentially curative bone marrow transplants (BMT). The drug molecule design of Lomab-B links the anti-CD45 monoclonal antibody apamistamab to the radioactive isotope iodine-131, targeting CD45 on the cell surface to deliver iodine-131, which can destroy cancer cells in AML patients and eliminate cancer cells in cancer patients. The pivotal Phase III SIERRA trial of 131I-CD45 monoclonal antibody Lomab-B (apamistamab) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (r/r AML) patients has been completed: compared to the control group, more patients achieved durable complete remission lasting up to 6 months, with a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P<0.0001).
Bispecific Antibodies
A study proposed Receptor Inhibition by Phosphatase Recruitment (RIPR), a general strategy to directly attenuate signaling from cell surface receptors activated by kinases. This approach forces cell surface receptors containing specific tyrosine phosphorylation motifs (ITAM, ITIM, or ITSM) to form a cis-ligation with the cell surface phosphatase CD45, achieving direct intracellular dephosphorylation of the receptor target and thereby attenuating cell surface receptor signaling. Using this method, RIPR-PD1 was designed to induce the cross-linking of PD-1 with CD45, inhibiting signaling activated by complement and ligands. In mouse tumor models, it demonstrated more significant therapeutic effects than anti-PD-1 antibodies.
Future Perspectives
CD45 holds broad application prospects in immunotherapy, particularly in hematological malignancies and conditions requiring HSCT. With the advancement of research and technology, CD45-based immunotherapeutic strategies are expected to bring hope to more patients.
S-RMab® Monoclonal Antibodies
Starter's CD45 monoclonal antibodies offer higher specificity, sensitivity, and stability, providing more accurate diagnostic results for clinical use.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B0228 | CD45 Mouse mAb (429-1) | Host : Mouse | $100 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0427 | CD45 Mouse mAb (S-839-3) | Host : Mouse | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0626 | CD45RA Recombinant Mouse mAb (S-R377) | Host : Mouse | $45 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B2087 | S-RMab® CD45 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R035) | Host : Rabbit | $880 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




