Bispecific Antibody Combined with Radiotherapy Breaks Through Tumor Therapy Bottlenecks!
In the field of tumor therapy, converting immunologically "cold tumors" into "hot tumors" and activating systemic anti-tumor immunity to overcome metastatic lesions has long been a core challenge in both scientific research and clinical practice. A 2025 study published in Advanced Science titled "Bispecific Antibody Targeting VEGF/TGF‐β Synergizes with Local Radiotherapy: Turning Tumors from Cold to Inflamed and Amplifying Abscopal Effects" proposes an innovative solution: the bispecific antibody Y332D, which targets VEGF/TGF-β, acts synergistically with local radiotherapy (RT). This combination not only remodels the tumor microenvironment (TME) but also significantly enhances the abscopal effect, providing a new strategy for the treatment of solid tumors and metastatic lesions. Absin's Mouse CXCL10/IP-10 ELISA Kit (Catalog No.: abs520013) provided accurate data support for verifying the immunological mechanism in this study.
1. Research Background: The "Double-Edged Sword" of Radiotherapy and the Breakthrough Idea of Bispecific Antibodies
Local radiotherapy is a first-line treatment for solid tumors. Its core value lies not only in directly inducing double-strand breaks in tumor cell DNA but also in remodeling the TME through immune priming effects: activating the cGAS-STING pathway, inducing immunogenic cell death (ICD), promoting antigen presentation, and T cell infiltration. Theoretically, this can convert "cold tumors" into "hot tumors."
However, radiotherapy has a significant "side effect"—it induces high expression of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) and TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-β) in the TME:
• VEGF: Promotes abnormal angiogenesis, leading to tumor hypoxia and acidosis, which inhibits the function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) and the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs);
• TGF-β: Induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and accumulation of immunosuppressive cells (e.g., Tregs, M2-type macrophages). This impairs the immune activation effect of radiotherapy and even enhances tumor radioresistance and metastatic potential.
Based on this, the research team proposed a core hypothesis: Simultaneously blocking the VEGF and TGF-β signaling pathways may reverse the negative effects of radiotherapy while amplifying its immune activation.
2. Core Research Results: The Synergistic "Triple Effects" of Y332D + Radiotherapy
The research team verified the synergistic anti-tumor effect of Y332D and radiotherapy in multiple mouse models, including 4T1 breast cancer, CT26 colorectal cancer, H22 liver cancer, and GL261 glioblastoma. The core results can be summarized as "triple effects":
2.1 Reverse the Negative Effects of Radiotherapy and Enhance Tumor Radiosensitivity
Radiotherapy significantly upregulates the expression of VEGF and TGF-β in tumor tissues and mouse plasma, while Y332D achieves dual blocking to:

• Inhibit TGF-β-mediated DNA damage repair (DDR): Reduce the formation of γ-H2AX foci and decrease tumor cell resistance to radiotherapy;

• Reverse VEGF-induced abnormal angiogenesis: CD31 staining showed that Y332D combined with radiotherapy significantly reduced tumor microvessel density (MVD) and improved oxygen supply in the TME;

• Inhibit EMT and CAF activation: IHC staining confirmed that Y332D downregulated the expression of N-cadherin, vimentin (Vimentin), and α-SMA (a marker of CAFs), reducing the tumor stromal barrier.
2.2 Amplify the Immune Activation Effect of Radiotherapy to Achieve "Cold-to-Hot Tumor Conversion"
Y332D not only counteracts the immunosuppression caused by radiotherapy but also enhances its immune priming effect:
• Promote DC maturation and M1 macrophage polarization: Flow cytometry showed that the proportion of CD86+ mature DCs and the M1/M2 macrophage ratio were significantly increased in the combined treatment group;

• Enhance T cell infiltration and function: The combined treatment group showed a significant increase in the infiltration of intratumoral CD3+ T cells, CD8+ T cells (especially activated CD25+/CD69+ CD8+ T cells and cytotoxic Gzmb+ CD8+ T cells), and an elevated CD8+ T/Treg ratio;

• Activate the IFN-I pathway and chemokine secretion: In this process, Absin's Mouse CXCL10/IP-10/CRG-2 ELISA Kit (abs520013) played a key role. By detecting the expression of CXCL10 (a key IFN-I-induced chemokine that recruits CXCR3+ T cells) in cell supernatants, it was confirmed that radiotherapy combined with Y332D significantly upregulated the mRNA and protein levels of CXCL10, providing evidence of "chemotactic signals" for T cell infiltration.
2.3 Activate the Abscopal Effect and Inhibit the Growth of Metastatic Lesions
The "abscopal effect" refers to the induction of systemic anti-tumor immunity by local radiotherapy, which inhibits the growth of non-irradiated metastatic lesions. It is one of the core goals of combining radiotherapy with immunotherapy. The study found that:
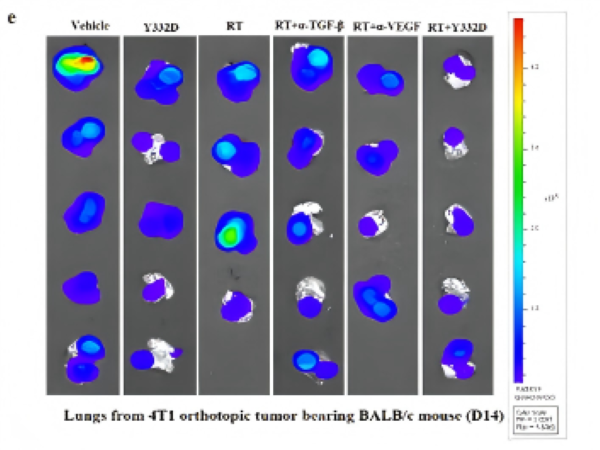
• In the 4T1 breast cancer lung metastasis model, radiotherapy alone had no significant inhibitory effect on lung metastatic lesions, while Y332D combined with radiotherapy significantly reduced the bioluminescent signal of lung metastatic lesions;

• Mechanistically, the combined treatment promoted the infiltration and activation of CD8+ T cells and NK cells in metastatic lung tissues, while reducing the proportion of immunosuppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), providing an immunocellular explanation for the abscopal effect.

3. Absin abs520013: The "Key Tool" for Verifying Immune Chemotactic Mechanisms
In the exploration of the immunological mechanism in this study, the expression level of the chemokine CXCL10 was a core indicator for verifying "how radiotherapy + Y332D recruits T cells to the TME." Absin's Mouse CXCL10/IP-10 ELISA Kit (Catalog No.: abs520013) accurately detected the concentration of CXCL10 in the following samples, leveraging its advantages of high specificity and sensitivity:
1. In vitro cell supernatants: Detected the secretion of CXCL10 in tumor cells (e.g., 4T1, CT26, H22, GL261) after radiotherapy, confirming that radiotherapy significantly induces CXCL10 expression;
2. In vivo tumor tissue homogenates: Verified that Y332D combined with radiotherapy further upregulates CXCL10 levels in the TME, providing chemotactic signals for T cell infiltration.

The detection results of this kit directly supported the core mechanism that "radiotherapy + Y332D upregulates CXCL10 to recruit CXCR3+ T cells to the TME," serving as a key data bridge connecting "signaling pathway activation" and "immune cell infiltration."
Product Advantages of abs520013 Aligned with Research Needs:
• High specificity: Designed for mouse CXCL10/IP-10 with no cross-reactivity, avoiding interference from other chemokines;
• High sensitivity: The minimum detection limit reaches the pg level, enabling accurate capture of subtle changes in CXCL10 expression after radiotherapy;
• Easy operation: Suitable for batch sample detection, meeting the experimental needs of multiple models and time points.
4. Research Significance and Future Prospects
This study not only confirms the synergistic anti-tumor effect of Y332D combined with radiotherapy but also proposes a new strategy of "bispecific antibody + radiotherapy" for TME remodeling. By "blocking immunosuppressive pathways + amplifying immune activation signals," it converts local treatment into a systemic anti-tumor immune response, providing a new direction for the treatment of metastatic solid tumors.
As a tool service provider in life sciences, Absin has always supported scientific research breakthroughs with "high-precision and highly reliable" reagents. In addition to the abs520013 CXCL10 ELISA Kit used in this study, Absin also provides a "comprehensive solution for tumor immunology research," including cytokine detection reagents (e.g., IFN-β, TGF-β, VEGF), immune cell staining antibodies, and cell function analysis reagents.
References:
Bispecific Antibody Targeting VEGF/TGF‐β Synergizes with Local Radiotherapy: Turning Tumors from Cold to Inflamed and Amplifying Abscopal Effects. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun 5.
Products Used
|
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Application Scenarios |
|
Mouse CXCL10/IP-10/CRG-2 ELISA Kit |
Detecting CXCL10 levels in serum, bone marrow fluid, and cell supernatants |
More ELISA Kits
|
Catalog No. |
Name |
Number of Citations |
|
Mouse TNF-α ELISA Kit |
92 |
|
|
Mouse IL-6 ELISA Kit |
86 |
|
|
Mouse IL-1β ELISA Kit |
81 |
|
|
Human TNF-α ELISA Kit |
52 |
|
|
Human IL-6 ELISA Kit |
34 |
|
|
Mouse IFN-γ ELISA Kit |
32 |
|
|
Human IFN-γ ELISA Kit |
22 |
|
|
Mouse IL-10 ELISA Kit |
21 |
|
|
Human IL-1β ELISA Kit |
16 |
|
|
Human IL-10 ELISA Kit |
15 |
|
|
Mouse IL-4 ELISA Kit |
15 |








