A Comprehensive Overview of the Major Categories of Cell Viability Assays

As the smallest autonomous structural and functional unit of living organisms, the cell remains the cornerstone of life-science research and occupies a central position in the quest to unravel the mysteries of life:
1.In scientific research, dynamic processes such as cell proliferation and differentiation, signal transduction, and metabolic regulation serve as pivotal targets for elucidating physiological mechanisms and pathogenesis, establishing the cell as the core instrument for decoding the continuum of life.
2.In drug discovery, cellular models constitute the primary platform for high-throughput screening, toxicity assessment, and pharmacodynamic validation; cell-viability assays are integral from early compound triage through pre-clinical development. With the advent of genome-editing technologies (e.g., CRISPR) and the evolution of cell-based therapeutics, cells themselves have emerged as cutting-edge “drugs” for disease intervention.
3.In biomanufacturing, cells function as microscale bioreactors, enabling the efficient production of antibodies, proteins, peptides, and other reagents or biotherapeutics, thereby propelling both life-science research and industrial translation.
“How are my cultured cells responding to the applied stimulus?” is the first question investigators must address when cells are exposed to any agent or perturbation. This query can be answered by interrogating multiple biomarkers of cellular viability. The following review systematically introduces three major categories—comprising six distinct methodologies—for assessing cell viability, enabling researchers to select the most appropriate assay and rapidly achieve reliable quantification of cellular viability.
1、Gold-standard methodology: assessment of cellular viability via quantification of intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content serves as a direct readout of cellular energy metabolism. ATP-bioluminescence assays quantify cellular ATP levels to assess viability. The protocol is streamlined to a simple “add–incubate–read” workflow, offering exceptional sensitivity and a broad dynamic range, making it particularly well suited for high-throughput applications that demand maximal analytical sensitivity.

|
Catalog Number |
Category |
Salient features |
|
2D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit |
Standard configuration |
|
|
#abs50059 |
2D/3D/Organoid ATP Viability Assay Kit |
Optimized for organoids |
|
#abs50189 |
CTG-LTM 2D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit 2.0 |
Increased stability |
2、Compatible with CTG-L reagent; enables non-lytic fluorometric assessment of cell viability via live-cell protease activity.
cell-viability assays, the inclusion of an internal reference frequently necessitates multiplexed analysis—simultaneous application of orthogonal, non-interfering methodologies targeting distinct biochemical mechanisms on the same sample. This approach permits direct cross-validation and effectively eliminates data variability attributable to non-experimental factors.
The assay exploits a highly conserved intracellular protease whose activity is strictly confined to intact, viable cells. A cell-permeable fluorogenic substrate enters live cells and is specifically cleaved by this protease, generating a fluorescent signal that is directly proportional to the number of viable cells. Upon loss of membrane integrity, the protease is released into the extracellular medium, where its activity is instantaneously abolished owing to the altered physicochemical environment.
Employing a mechanistically distinct principle from the CTG-L luciferase reagent series, this assay detects subtle, early-stage cellular damage with superior sensitivity. Owing to excellent compatibility, the two reagents can be multiplexed without interference. The workflow is reduced to a simple “add-incubate-read” triad, rendering the method ideally suited for high-throughput applications.
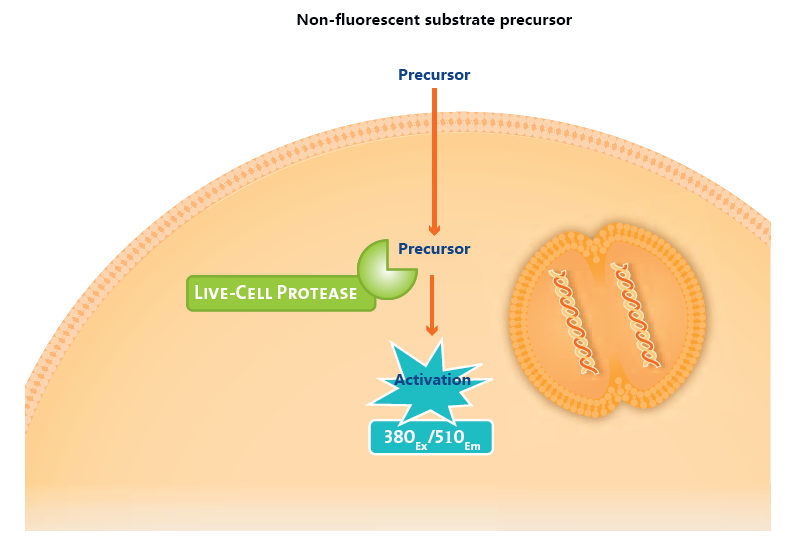
Schematic illustration of the principle for assessing live-cell protease activity
|
Catalog Number |
Category |
Salient features |
|
#abs50193 |
CTF-LTM 2D Fluorescent Cell Viability Assay Kit |
Fluorometric, non-lytic assay; excitation 380 nm / emission 510 nm |
3、Traditional gold-standard method: assessment of cell viability based on the reductive activity of mitochondrial dehydrogenases.
Cell-viability assays predicated on mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity exploit the pivotal role of these enzymes in cellular metabolism. Localized at the inner mitochondrial membrane, mitochondrial dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative removal of hydrogen from substrates, transferring electrons to an exogenous chromogenic electron acceptor—e.g., the tetrazolium salt MTT—thereby enabling spectrophotometric quantification of metabolic competence.
In viable cells with intact mitochondrial function, dehydrogenase activity is robust, driving efficient reduction of the substrate and eliciting a pronounced colorimetric shift (e.g., MTT is reduced to purple formazan crystals). Conversely, loss or attenuation of cellular viability compromises mitochondrial integrity, leading to diminished dehydrogenase activity and a correspondingly weaker substrate reduction, reflected by a reduced color change.
Owing to the diversity of reducible substrates, these methods can be further subclassified as follows:
① MTT assay: Requires prior admixture of two components. Mitochondrial dehydrogenases reduce the reagent to water-insoluble, blue–purple formazan crystals. After medium removal and solubilization, absorbance is measured at 570 nm.
②MTS assay (an upgraded MTT analogue): Requires premixing of two components prior to use. Mitochondrial dehydrogenases reduce the reagent to a water-soluble formazan product, eliminating the need for medium exchange and simplifying the workflow; absorbance is read at 490 nm.
③CCK-8 assay (a second-generation MTT substitute): Supplied as a ready-to-use reagent that can be added directly to the cell culture without pre-formulation. It affords rapid readout and exhibits minimal cytotoxicity. The active substrate, WST-8, is reduced to an orange-yellow formazan dye by mitochondrial dehydrogenases in the presence of an electron-coupling mediator; no medium exchange is required, and absorbance is measured at 450 nm.
④Alamar Blue assay, whose active constituent is resazurin, employs a cell-permeant, non-toxic, weakly blue-fluorescent indicator that serves as an MTT alternative. In its oxidized state, resazurin appears purple-blue and is essentially non-fluorescent; upon reduction by metabolically active cells it is converted to resorufin, which is pink and strongly fluorescent. The resulting fluorescence intensity is directly proportional to the number of respiring cells. The colorimetric shift can be monitored with a standard spectrophotometer at 570 nm (reference 600 nm), while the fluorometric signal is measured using excitation 530–560 nm and emission 590 nm.

Schematic illustration of the principle underlying cell-viability assessment via mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity.
|
Catalog Number |
Category |
Salient features |
|
MTT Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit |
Requires pre-mixing and medium exchange |
|
|
MTS Cell Proliferation Assay Kit |
Requires pre-mixing; no medium exchange necessary |
|
|
CCK-8 Kit |
No pre-mixing or medium exchange required |
|
|
Alamar Blue Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Detection Reagent |
No pre-mixing or medium exchange required; compatible with both absorbance and fluorescence detection |
The three categories outlined above represent the principal methodologies currently employed for assessing cell viability. Herein, we have also compiled the salient features of these methods to facilitate the selection process based on specific experimental requirements.
|
Methodology |
Catalog Number |
Category |
Signal half-life |
Throughput |
Sensitivity |
Detection time required |
|
ATP-based assay |
2D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit |
Bioluminescence > 0.5h |
96/384 |
A cell density of 100 cells |
10 min |
|
|
#abs50059 |
2D/3D/Organoid ATP Viability Assay Kit |
Bioluminescence> 0.5h |
96/384 |
A cell density of 100 cells |
30 min |
|
|
#abs50189 |
CTG-LTM 2D Luminescent Cell Viability Assay Kit 2.0 |
Bioluminescence>2h (2-4h) |
96/384 |
A cell density of 50 cells |
10 min |
|
|
Live-cell protease |
#abs50193 |
CTF-LTM 2D Fluorescent Cell Viability Assay Kit |
Fluorescence, Ex: 380nm Em: 510nm
|
96/384 |
A cell density of 100 cells |
0.5-3h |
|
Mitochondrial dehydrogenase |
MTT Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit |
Absorbance, OD570 nm |
96 |
A cell density of 1000 cells |
4h |
|
|
MTS Cell Proliferation Assay Kit |
Absorbance, OD490 nm |
96/384 |
A cell density of 500 cells |
1-4h |
||
|
CCK-8 Kit |
Absorbance, OD450 nm |
96/384 |
A cell density of 200 cells
|
1-4h |
||
|
Alamar Blue Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Detection Reagent |
Absorbance, OD570 nm Fluorescence, Ex: 560nm Em: 590nm |
96/384 |
A cell density of 100 cells |
1-4h |




