Emerging Star in Post-Translational Modifications: UFMylation.

Recent Advances
UFMylation is a post-translational modification (PTM) that involves the covalent attachment of ubiquitin (Ub) or its derivatives (such as ubiquitin-like proteins) to specific amino acid residues of target proteins. This modification process plays a variety of biological roles within cells, including protein degradation, signal transduction, cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, and transcriptional regulation.
The term "UFMylation" is derived from "ubiquitination" and "ubiquitin-like modification." It represents a relatively new type of PTM, similar to ubiquitination but involving distinct ubiquitin-like proteins. The discovery of UFMylation has expanded our understanding of the diversity and complexity of the ubiquitin system.
Core Molecules and Enzymatic System of UFMylation
Core Protein: UFM1
UFM1 is a ubiquitin-like protein with approximately 30% sequence homology to ubiquitin (Ub) but a three-dimensional structure more similar to SUMO. It forms an isopeptide bond with the lysine (Lys) residue of target proteins via its C-terminal glycine.
Enzymatic Cascade:
-
E1 Activating Enzyme: UBA5 (Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 5), responsible for activating UFM1.
-
E2 Conjugating Enzyme: UFC1 (UFM1-conjugating enzyme 1), transfers activated UFM1 to the E3 ligase.
-
E3 Ligase: UFL1 (UFM1-specific ligase 1), mediates the specific binding of UFM1 to target proteins.
-
DeUFMylation Enzyme: UFSP2 (UFM1-specific protease 2), responsible for removing UFM1 modifications.
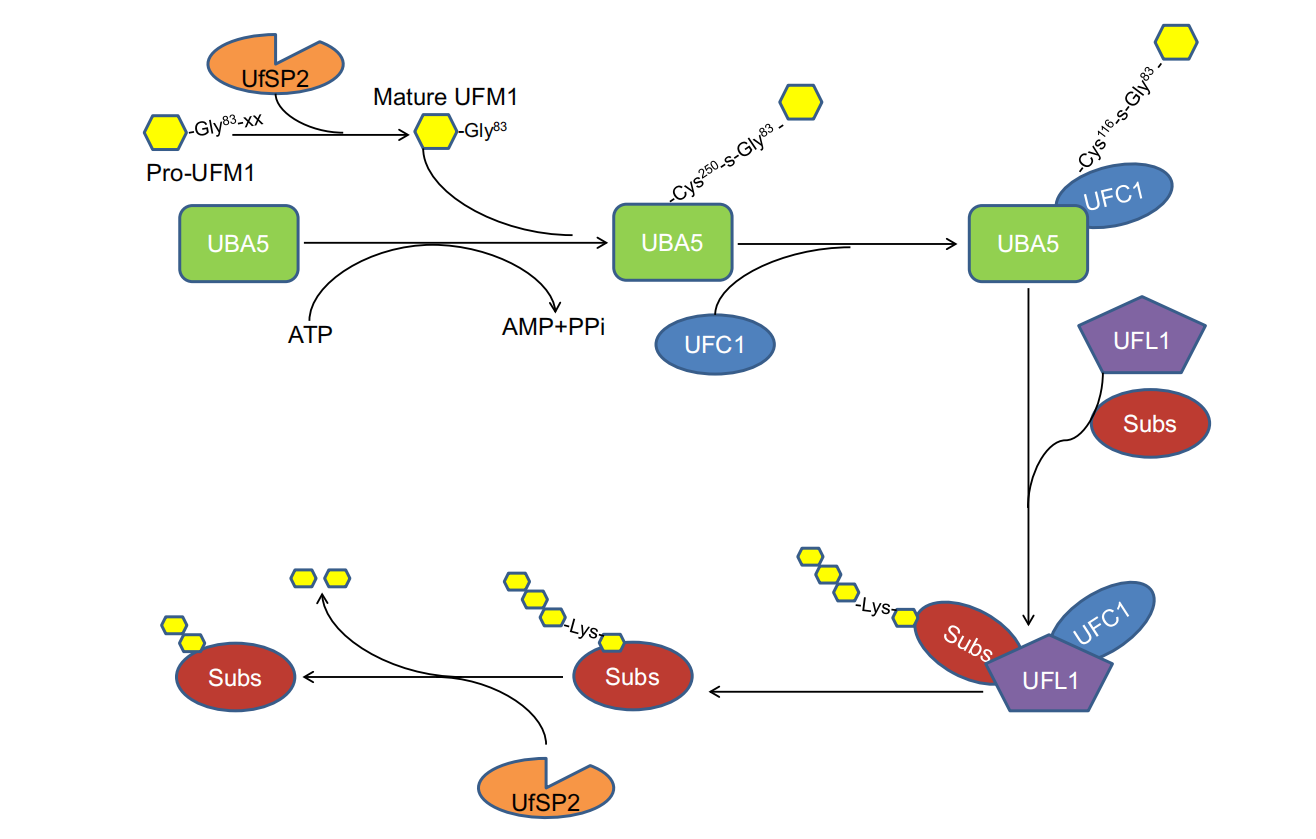
Schematic Diagram of the Human UFMylation Pathway
Basic Process of UFMylation
-
Activation: UFM1 is first activated by the UFM1-activating enzyme (UBA5), forming a UFM1-AMP complex.
-
Conjugation: Activated UFM1 binds to the UFM1-conjugating enzyme (UFC1), forming a UFM1-acylated complex.
-
Transfer: UFM1 is then transferred to target proteins, forming UFMylated proteins. This process typically requires the participation of the UFM1 ligase (UFL1).
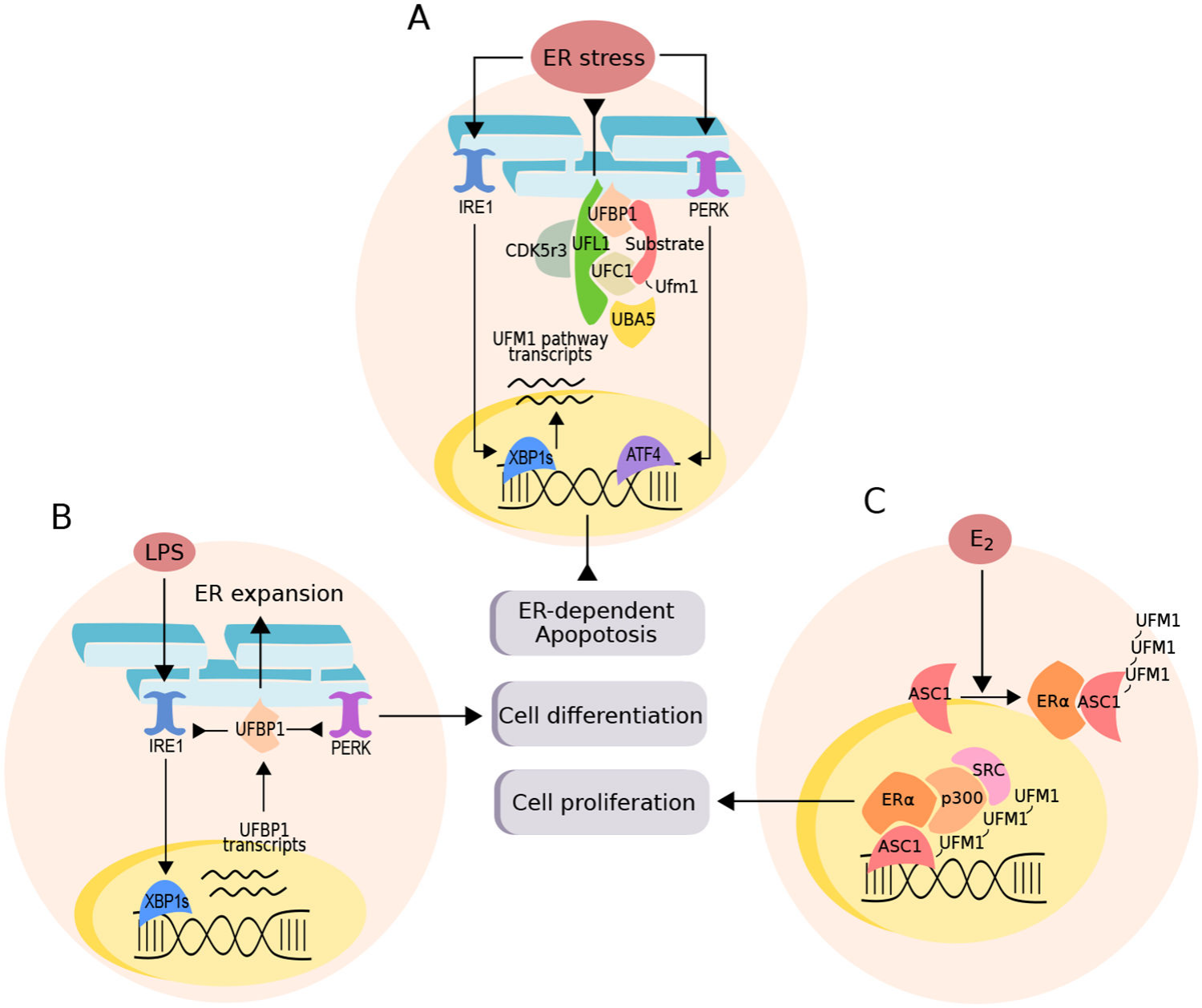
Schematic Diagram of the Interaction Between the UFM1 Pathway, ER Stress, and Cell Fate
The UFMylation pathway can regulate different physiological processes depending on stimuli and cellular context:
-
A. UFM1 Pathway and ER Stress Response: The UFM1 pathway is often associated with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response, and its expression is controlled by the major transcription factor XBP1. Gene deletions in this pathway are implicated in ER-dependent apoptosis in various contexts, while its expression helps counteract drug-induced ER stress.
-
B. Plasma B-Cell Differentiation: Activated by LPS, which increases the transcription of UFBP1 (a UFM1 pathway interaction factor) through XBP1 expression. UFBP1 inhibits the activation of sensors IRE1 and PERK, promoting ER expansion and immunoglobulin production as a feedback response.
-
C. Breast Cancer Cell Lines: Exposure to estradiol (E2) promotes the interaction and subsequent polymerization of nuclear receptor ERα with ASC1. ASC1 UFMylation forms a scaffold to recruit p300 and SRC, activating cell proliferation. ASC1 is also a key regulator of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation, and its deletion in mouse models is associated with pancytopenia.
Biological Functions of UFMylation
Protein Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
UFMylation primarily participates in ER-associated degradation (ERAD):
-
When unfolded proteins accumulate in the ER (ER stress), UFMylation is activated.
-
It targets ribosomal proteins (e.g., RPL26) and ER membrane proteins, promoting the degradation of misfolded proteins.
-
Forms a complex with UFBP1 (UFM1-binding protein 1) to regulate ER homeostasis.
Ribosome Biogenesis and Translation Regulation
UFMylation modifies ribosomal proteins (e.g., RPL26), influencing ribosome assembly and translation efficiency.
-
Knockout of UFM1 in mice results in embryonic lethality, highlighting its critical role in development.
DNA Damage Repair and Cell Cycle Regulation
UFMylation participates in the DNA damage response, such as by modifying C53 (also known as CDK5RAP3) to regulate the ATM/ATR signaling pathway.
-
It is associated with cell cycle checkpoints (e.g., G2/M phase arrest).
Other Functions
UFMylation may also play roles in mitochondrial function, autophagy, and immune regulation, though the mechanisms remain to be elucidated.
UFMylation and Diseases
Cancer
Dysregulation of UFMylation is associated with various cancers:
-
Breast Cancer: UFL1 deletion leads to genomic instability and tumorigenesis.
-
Leukemia: UBA5 mutations are linked to myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).
-
It may influence tumor progression by regulating ER stress and DNA repair.
Neurological Disorders
UFM1 deletion in mouse models causes cerebellar developmental abnormalities and motor dysfunction.
-
It is associated with protein homeostasis imbalances in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
Hematological Disorders
UFSP2 mutations cause recessive hereditary blood disorders (e.g., congenital dyserythropoietic anemia).
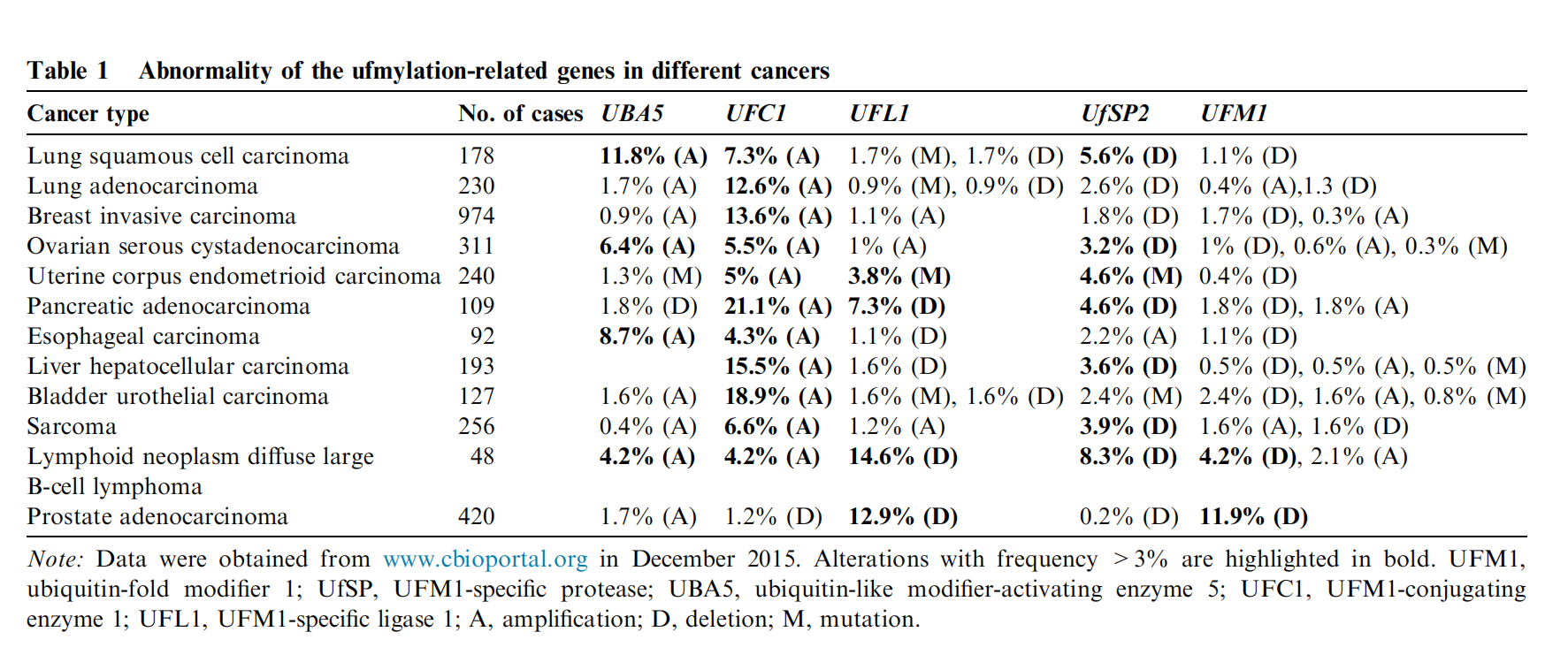
UFMylation-Related Genes in Different Cancers
START provides specific antibodies and agarose beads for UFMylation research:
-
Polyclonal Antibody: K-ε-GV Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog Number: S0B1323).
-
Monoclonal Antibody: Anti-K-ε-GV Agarose Beads (Catalog Number: S0F0013).
Data Presentation
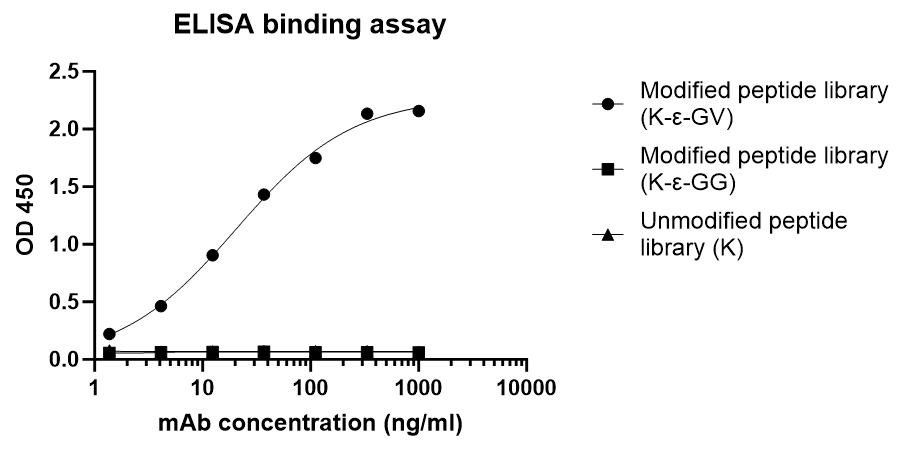
ELISA binding assay shows K-ε-GV Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody specifically binds to K-ε-GV peptide
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B1322 | Fumaryllysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B1324 | Crotonyllysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B1272 | Succinyllysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0004 | Anti-acetyllysine agarose Beads | Inquiry | |
| S0B0655 | Acetyllysine Rabbit polyclonal antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0009 | Anti-O-GlcNAc agarose Beads | Conjugation : Agarose beads | Inquiry |
| S0B0373 | O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R256) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0003 | Anti-L-lactyllysine agarose Beads | Conjugation : Agarose beads | Inquiry |
| S0B0719 | L-Lactyl Lysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0007 | Anti-Phosphotyrosine agarose Beads | Conjugation : Agarose beads | Inquiry |
| S0B0319 | Phosphotyrosine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R207) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0F0010 | Anti-Succinyllysine agarose Beads | Conjugation : Agarose beads | Inquiry |
| S0F0005 | Anti-K-ε-GG agarose Beads | Inquiry | |
| S0B0965 | K-ε-GG Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0087 | Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R095) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| S0B0740 | Butyryllysine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R399) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B1323 | K-ε-GV Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |