Starter Modified Antibodies: Empowering PTM Research with Precision and Versatility, Making Post-Translational Modification Studies Effortless and Comprehensive.

Recent Advances
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) significantly influence the structure, function, stability, and localization of proteins. PTMs have long been a hot research topic in the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC). Since 2021, the NSFC has launched the "Major Research Plan on Dynamic Modifications of Biomacromolecules and Chemical Interventions," which highlights key areas such as the detection of dynamic modifications in biomacromolecules, the synthesis of ubiquitination modifications, and the identification of novel anti-tumor targets based on protein modifications. These projects are of significant interest and importance in the field.
In the 2023 NSFC, modifications such as lactylation, methylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation have garnered considerable attention due to their critical roles in regulating protein function, stability, subcellular localization, and protein-protein interactions.
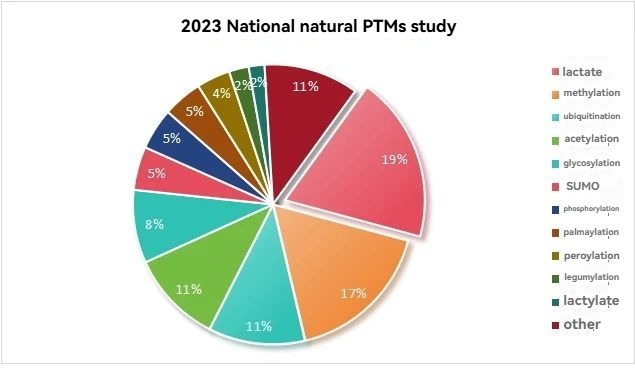
Key PTMs
Lactylation
Lactylation involves the formation of an amide bond between the carboxyl group of lactate and the ε-amino group of lysine residues on proteins, creating a lactylation mark. This modification not only influences gene expression regulation but also participates in various biological processes, including macrophage homeostasis, tumor metabolism, and immunity. Lactylation primarily occurs on lysine residues, with histone lactylation being the most extensively studied. Research has shown that lactylation marks on histones are associated with gene expression regulation. Lactate, even under aerobic conditions, acts as an important metabolic signaling molecule, serving as a precursor that modifies histones through lactylation, affecting chromatin openness and transcriptional activity, thereby regulating cellular metabolic processes and functions.
Methylation
Methylation, one of the most common epigenetic modifications, is catalyzed by enzymes and plays a role in embryonic development, cell differentiation, X-chromosome inactivation, genomic imprinting, and tumorigenesis. Abnormal methylation patterns are associated with various diseases, particularly cancer. In tumors, methylation imbalance manifests as global hypomethylation accompanied by local hypermethylation, and this abnormal methylation state can serve as a biomarker for cancer. Histone methylation can occur on lysine (K) and arginine (R) residues, and it can be mono-, di-, or tri-methylated. Depending on the site of modification, it can either activate or repress gene expression.
Ubiquitination
Ubiquitination regulates protein degradation, signal transduction, cell cycle control, and other cellular processes by adding ubiquitin molecules to lysine residues on proteins. Ubiquitination is a dynamic and reversible process, with deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) capable of removing ubiquitin marks to restore the protein's original state or prevent its degradation. Dysregulation of ubiquitination is linked to various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and immune system diseases, making it an important target for drug development.
Acetylation
Acetylation involves the addition of acetyl groups to lysine residues, altering the charge and conformation of proteins, thereby affecting their stability, activity, or interactions with other molecules. Acetylation plays a central role in regulating metabolic enzyme activity, transcription factor function, and cellular signaling. It is also a key mechanism in regulating autophagy:
Acetylation can directly act on core autophagy proteins such as ATG3, ATG4B, and ATG5. For example, acetylation of ATG3 mediated by the acetyltransferase TIP60 promotes autophagy, while certain deacetylases inhibit autophagy by removing acetyl groups.
Acetylation also regulates the expression of autophagy-related genes by influencing the activity of transcription factors such as FOXO1, FOXO3, and TFEB. The acetylation state of these transcription factors can alter their DNA-binding capacity or transcriptional activity, thereby affecting the expression of autophagy genes.
S-RMab® PTM Antibodies
Starter offers a wide range of pan-modification antibodies (e.g., ubiquitination, lactylation, acetylation, phosphorylation) and protein modification antibodies (e.g., methylated histones, phosphorylated histones, phosphorylated AKT). We also provide custom modification antibody services!
Our single B-cell platform screens for highly sensitive rabbit monoclonal antibodies. Rabbits, as hosts, exhibit a broader antibody repertoire and generate strong immune responses to PTM immunogens. Recombinant technology ensures the retention of antibody sequences, guaranteeing batch-to-batch consistency and stable experimental results.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B0332 | Propionyl-Histone H4 (Lys5) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R093) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0054 | Tau (phospho T231) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-177-1) | Host : Rabbit | $350 |
| S0B0029 | Tau (phospho T181) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R045) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| S0B0462 | Tau (phospho S396) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R276) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0285 | RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S7) Recombinant Rat mAb (S-R198) | Host : Rat | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0284 | RNA polymerase II CTD repeat YSPTSPS (phospho S2) Recombinant Rat mAb (S-R199) | Host : Rat | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0748 | Phospho-Stat1 (Tyr701) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-601-78) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0282 | Phospho-S6 Ribosomal Protein (Ser235/236) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R203) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0784 | Phospho-p70 S6 Kinase (Ser371) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-1239-6) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0597 | Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-705-7) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0257 | Phospho-IκBα (Ser36) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R102) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0631 | Phospho-IκBα (Ser32/36) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-751-40) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0518 | Phospho-GSK-3β (Ser9) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-748-20) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0596 | Phospho-Akt (Ser473) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-763-7) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0611 | Phospho-Akt (Ser473) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-622-64) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0363 | Phospho-Akt (Ser473) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-510-64) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0789 | Phospho-Histone H3 (Ser28) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-1025-45) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0751 | Phospho-Histone H3 (Ser10) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0296 | Histone H3 (mono methyl K36) Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R211) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0876 | 2-hydroxyisobutyryllysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0737 | 4-Hydroxynonenal Recombinant Mouse mAb (S-R405) | Host : Mouse | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0373 | O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R256) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0735 | Phosphotyrosine Recombinant Mouse mAb (S-R433-2) | Host : Mouse | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0749 | Phosphotyrosine Recombinant Mouse mAb (S-R433-1) | Host : Mouse | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0319 | Phosphotyrosine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R207) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0719 | L-Lactyl Lysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0740 | Butyryllysine Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-R399) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0655 | Acetyllysine Rabbit polyclonal antibody | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B0087 | Ubiquitin Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R095) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |




