Efficient CAR Positive Rate Detection! FAC2 antibodies for Anti-G4S Linker and Whitlow/218 Linker Are Ready to Help You!
CAR-T cell therapy, also known as Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy, is a revolutionary immunotherapy. CAR-T therapy involves the use of genetic engineering techniques to introduce the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) gene into the patient's T cells. The CAR is composed of a single-chain variable fragment (scFv), which can recognize and bind to specific antigens on the surface of tumor cells. When CAR-T cells recognize tumor antigens, they activate the cytotoxic function of T cells, releasing cytotoxins such as perforin and granzymes, directly killing tumor cells. In addition, CAR-T cells can also activate other immune cells by releasing cytokines, enhancing the overall anti-tumor response. As an emerging immunotherapy, CAR-T cell therapy has shown great potential and broad application prospects in the field of cancer treatment.
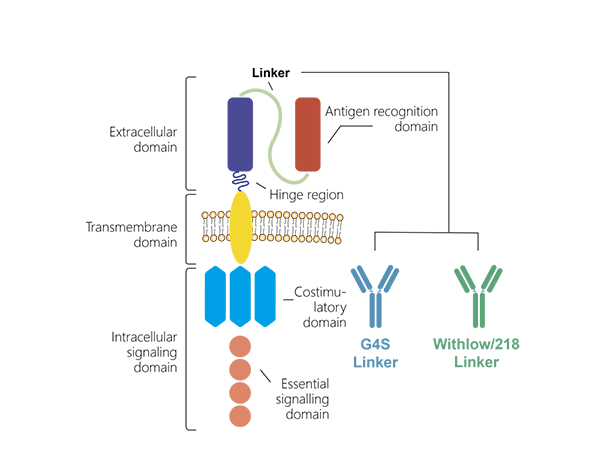
Introduction to CAR Structure
The structure of CAR consists of three main parts: the extracellular domain, the transmembrane domain, and the intracellular signaling domain.
Extracellular Domain
√ Antigen recognition region: It usually composed of a single-chain variable fragment (scFv), which is formed by connecting the variable heavy chain (VH) and variable light chain (VL) of an antibody through a flexible linker. The scFv endows CAR with the ability to specifically recognize and bind to target antigens.
√ Hinge region: It cConnects the scFv and the transmembrane domain, providing structural flexibility and stability. The length and source of the hinge region (such as IgG hinge or CD8α/CD28 extracellular domain) can affect the function of CAR.
Transmembrane Domain
Function: It anchors CAR on the cell membrane, ensuring stable expression of CAR. The design of the transmembrane domain has an important impact on the expression level and stability of CAR.
Intracellular Signaling Domain
√Signaling transduction domain: It usually contains the CD3ζ chain, providing T-cell receptor activation signals.
√Costimulatory domain: To enhance the activation and persistence of CAR-T cells, the second-generation CAR introduced costimulatory domains, such as CD28 or 4-1BB. These costimulatory signals help improve the proliferation and effector function of CAR-T cells.
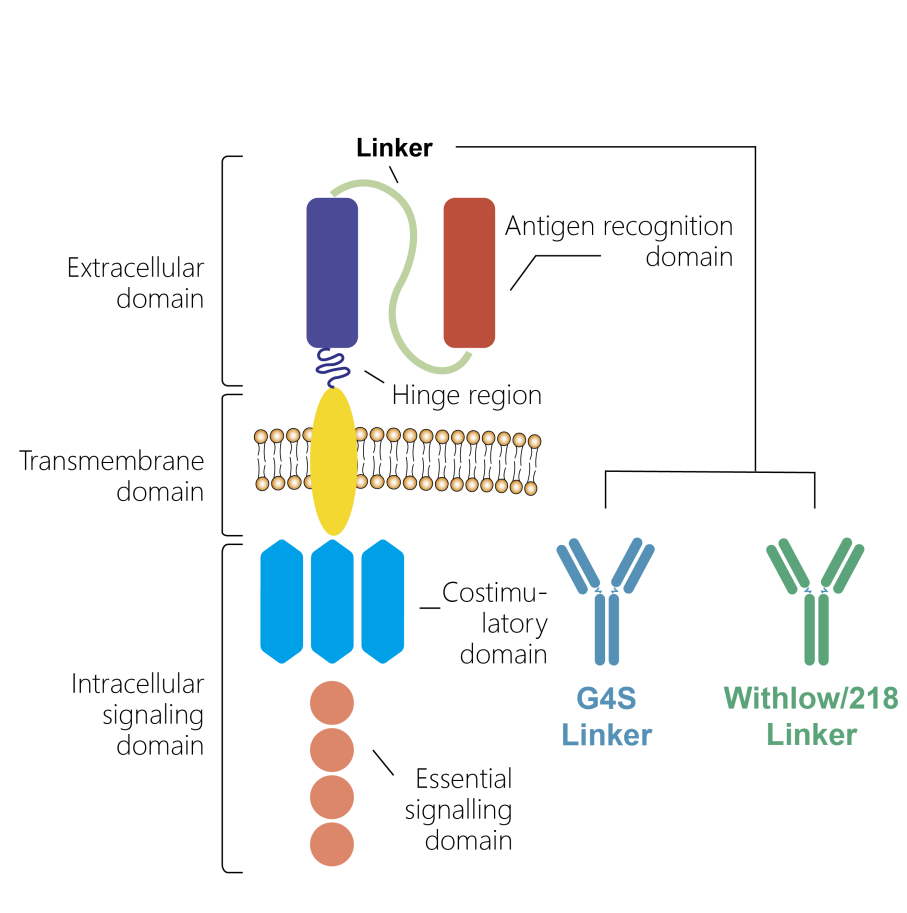
Illustration of CAR Structure
G4S linker and Whitlow/218 Linker are the two most common flexible linkers.
√ G4S linker is a commonly used flexible amino acid chain, usually composed of glycine (Gly, G) and serine (Ser, S), with the sequence (GGGGSGGGGSGGGGS), abbreviated as (G4S)3. This sequence does not lead to the formation of specific secondary structures, and is therefore widely used in protein fusion. The main function of G4S linker is to connect different protein domains, providing structural flexibility to reduce the mutual influence between different domains. In CAR cell therapy, G4S linker is used to connect the variable heavy chain (VH) and variable light chain (VL) in the single-chain variable fragment (scFv), forming a flexible structure. This design helps improve the recognition ability and function of CAR cells.
√ Whitlow/218 Linker mainly used to connect the variable heavy chain (VH) and variable light chain (VL) in the single-chain variable fragment (scFv). Its sequence is based on the research published by Whitlow et al. in 1993, aiming to improve the stability and functionality of scFv. The specific sequence of Whitlow/218 Linker is GSTSGSGKPGSGEGSTKG. In CAR cell therapy, the use of Whitlow/218 Linker can increase the affinity of scFv for tumor antigens. This is very important for the targeting ability and therapeutic effect of CAR-T cells, because higher affinity means that CAR-T cells can more effectively recognize and bind to tumor cells. It also helps reduce the aggregation and degradation of scFv, thereby improving the stability and functionality of CAR-T cells. This is crucial for maintaining the persistence and activity of CAR-T cells in the body.
Comparison of different CAR detection methods
|
Level |
Method |
Detection Mechanism |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Genome
|
qPCR |
Based on the upstream and downstream sequences of the CAR structural enzyme cleavage site and the intracellular domain of CAR as a template for primer design |
High sensitivity and specificity, can measure CAR vector delivery efficiency, on-treatment expansion kinetics, and persistence to predict clinical response |
Requires known concentration standards and cannot differentiate subtle copy number differences. Some CAR-T products like Relmacabtagene autoleucel lack effective primers and probes
|
|
Digital PCR |
Higher sensitivity, can achieve absolute quantification without making standard curves |
Relatively high equipment cost |
||
|
Transcriptome |
RNAseq |
Detection of CAR mRNA sequence |
Can distinguish CAR-T and non-CAR-T cells during analysis, help characterize how viral promoters influence CAR transcription and in vivo differentiation
|
Cannot capture factors that influence CAR translation, such as ribosome, initiation factors, and amino acid availability
|
|
RNAscope Hybridization |
spatial resolution spanning the single-molecule and cellular levels;ability to probe subcellular mRNA localization; capability for multiplex detection; and compatibility with microscopy
|
Can correlate the number of CAR mRNA in CAR-T cells with the relative position of CAR-T cells in tissue samples |
Cannot be used for live cell RNA imaging |
|
|
Protein |
Protein L |
Binding to the k light chain of antibodies |
Has a certain level of universality, can detect CARs with different targets |
Can only recognize human VkIVkIII and VkIV subtypes and mouse VKI subtype, but not human VkII subtype and other subtypes of mouse Ig light chains |
|
Anti-Fab Antibody |
Binding to the Fab segment of antibodies |
Has a certain level of universality, can detect CARs with different targets |
High background, inconsistent quality among commercial products, mostly polyclonal, with poor batch-to-batch consistency |
|
|
Anti-idiotype Antibody |
Specific binding to the antigen recognition region of scFv |
High specificity, high sensitivity, low background |
Few commercial products available, requires custom development, with a long customization period (about 6 months) |
|
|
Target Protein |
Specific binding to the antigen recognition region of scFv |
Has target specificity, can evaluate the binding ability of CAR to the target |
Detection sensitivity is limited by the affinity between scFv and the target protein |
|
|
Linker-specific Antibody |
Binding to the flexible linker |
Has a certain level of universality, easy to operate, can detect CARs with different targets |
CAR structure design needs to include the specific linker |
Rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibodies specifically targeting G4S linker and Whitlow/218 Linker can be used for the detection and analysis of CAR-T and other cells containing these linkers. This is very useful in the research and development process of CAR-T and other cell therapies. Starter Bio launched G4S linker and Whitlow/218 Linker FACS antibodies for CAR positive rate detection and functional assessment.
Performance
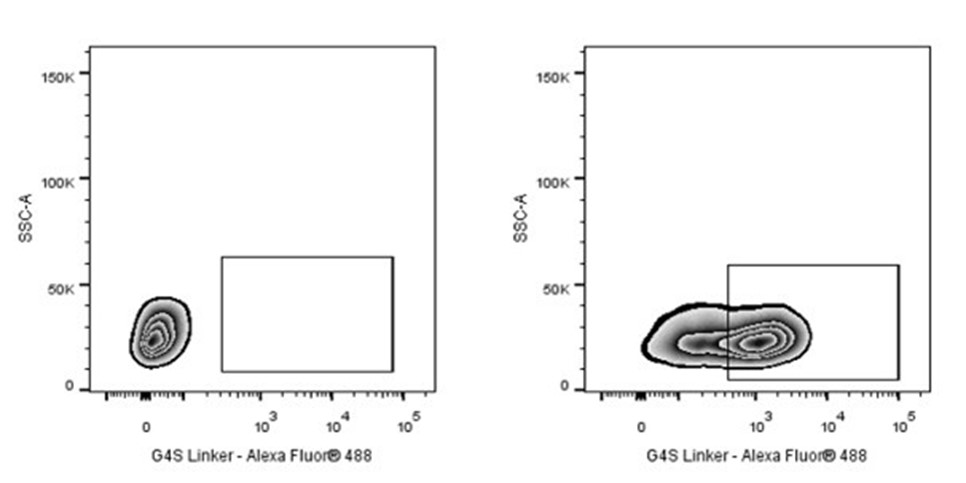
Flow cytometric analysis ScFv based CAR containing a G4S linker transfected 293T (Human embryonic kidney epithelial cell) (Right panel) or 293T (Left panel) was stained with SDT G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) at 0.1 μg/test. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using BD FACSymphony™ A1 and FlowJo™ software.
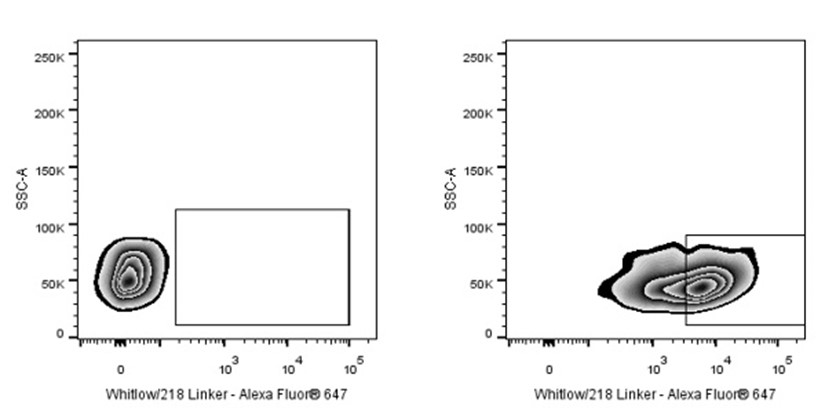
Flow cytometric analysis ScFv based CAR containing a Whitlow/218 linker transfected 293T (Human embryonic kidney epithelial cell, Right panel) or 293T (Left panel) was stained with SDT Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) at 0.01 μg/test. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using BD FACSymphony™ A1 and FlowJo™ software.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B1723 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Pacific blue Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Pacific Blue | |||
| S0B1724 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (APC Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : APC | |||
| S0B1721 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Biotin Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| S0B1711 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 555 | |||
| S0B1710 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 594 Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 594 | |||
| S0B1708 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 647 | |||
| S0B1793 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 488 | |||
| S0B1794 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 555 conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 555 | |||
| S0B1795 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 594 conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 594 | |||
| S0B1796 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 647 | |||
| S0B1797 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (APC conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : APC | |||
| S0B1799 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Biotin conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Biotin | |||
| S0B1789 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (PE-Cy7 conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : PE-Cy7 | |||
| S0B1275 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B1788 | Whitlow/218 Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (PE conjugate) (S-712-10) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : PE | |||
| S0B1178 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $100 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B1709 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : Alexa Fluor® 488 | |||
| S0B1725 | G4S Linker Recombinant Rabbit mAb (PE Conjugate) (S-711-23) | Host : Rabbit | $420 |
| Conjugation : PE |




