DT3C(Diphtheria Toxin Fragment A and Streptococcus Protein G C1, C2, C3)Empowers ADC Drug Development: Efficient Detection of Antibody Internalization Efficiency
Introduction
With the rapid advancement of biopharmaceutical technologies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have emerged as a highly effective and targeted class of therapeutics, demonstrating unique advantages in cancer treatment. The efficacy of ADC drugs largely depends on their internalization efficiency, which refers to the ability of the antibody to be effectively internalized by target cells and release the drug. In this context, DT3C recombinant protein, as a critical tool for evaluating antibody internalization efficiency, is garnering increasing attention from researchers.
Principle of ADC Internalization Efficiency
Detection
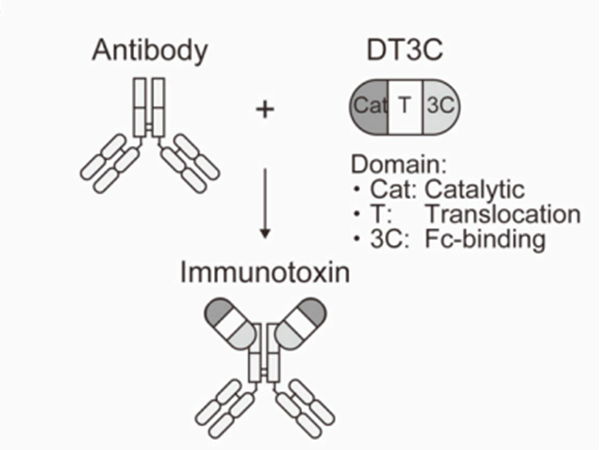
DT3C (Diphtheria Toxin Fragment A and Streptococcus Protein G C1, C2, C3) is a recombinantly expressed fusion protein composed of Fragment A of diphtheria toxin (the toxic moiety only) and the 3C fragment of Group G Streptococcus (the IgG-binding moiety). This protein exhibits high affinity for the Fc region of antibodies, allowing the DT3C molecule to be internalized into cells along with the antibody upon binding. Since DT3C can bind to any IgG-type antibody, it can be used to assess the internalization efficiency of antibodies from different species. The mAb-DT3C conjugate formed after DT3C binds to an antibody mimics the mechanism of action of ADC drugs in vitro, facilitating the evaluation of antibody internalization capability and drug release efficiency during the early stages of drug development.
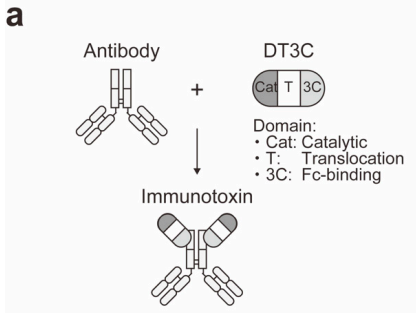
(a) DT3C consists of catalytic (Cat), translocation (T), and Fc-binding (3C) domains. The Fc-binding domain of DT3C specifically binds to antibodies.
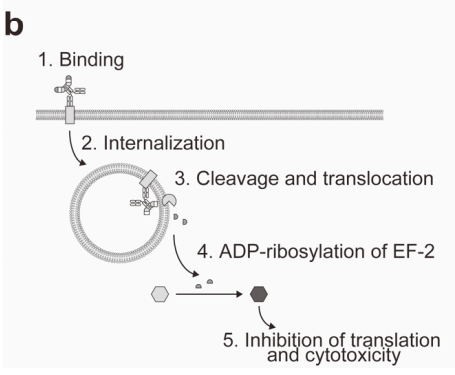
(b) After the mAb-DT3C conjugate recognizes and binds to cell surface antigens, the mAb-DT3C-antigen complex is internalized. The translocation domain of DT3C is cleaved by cellular furin proteases, releasing the catalytic domain of DT3C into the cytoplasm. The released DT3C exhibits toxic activity by inhibiting EF2-ADP ribosylation, blocking protein translation, and ultimately leading to cell death.
DT3C that does not enter the cells remains non-toxic, allowing the evaluation of antibody internalization efficiency based on cell cytotoxicity.
Detection Steps
-
Preparation of mAb-DT3C Conjugate
Incubate DT3C protein with the target antibody at room temperature for 30 minutes to form the mAb-DT3C conjugate. -
Co-Culture
Add the mAb-DT3C conjugate directly to complete medium containing antigen-positive cells (e.g., tumor cells) and incubate. -
Detection of Internalization Efficiency
Assess cell viability or cell death using methods such as flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy to evaluate the internalization efficiency of the antibody on the cell surface.
Advantages of DT3C in Detecting ADC
Antibody Internalization Efficiency
-
Broad Applicability: Can bind to any IgG from different species (e.g., human, mouse, rabbit, goat).
-
High Efficiency: The mAb-DT3C conjugate forms after 30 minutes of incubation at room temperature. DT3C rapidly releases toxic DT within cells, enabling quick assessment of antibody internalization efficiency.
-
High Internalization Efficiency: With a smaller molecular weight than Mab-ZAP, the mAb-DT3C conjugate exhibits higher internalization efficiency than mAb-Mab-ZAP.
-
Convenience: Internalization efficiency can be rapidly and accurately detected using methods such as flow cytometry or fluorescence microscopy.
Considerations
When conducting in vitro assays, ensure consistency in experimental conditions, such as cell type, cell concentration, the ratio of DT3C to antibody, and incubation time. Strict aseptic techniques must be maintained to avoid external interference.
Future Perspectives
As biopharmaceutical technologies continue to evolve, the application prospects of ADC drugs in cancer treatment are becoming increasingly promising. However, the efficacy of ADC drugs is influenced by multiple factors, among which antibody internalization efficiency is a critical one. Therefore, accurate evaluation of antibody internalization efficiency is of great significance for ADC drug development. DT3C recombinant protein, as an efficient, simple, and widely applicable evaluation tool, will play an increasingly important role in ADC drug development. In the future, with the continuous improvement and expanded application of DT3C technology, it is expected to provide stronger support for ADC drug development.
Starter
Provides high-purity DT3C protein to support ADC drug development.
DT3C (Diphtheria toxin & spg 3C domain) Protein, Corynephage beta UA070063
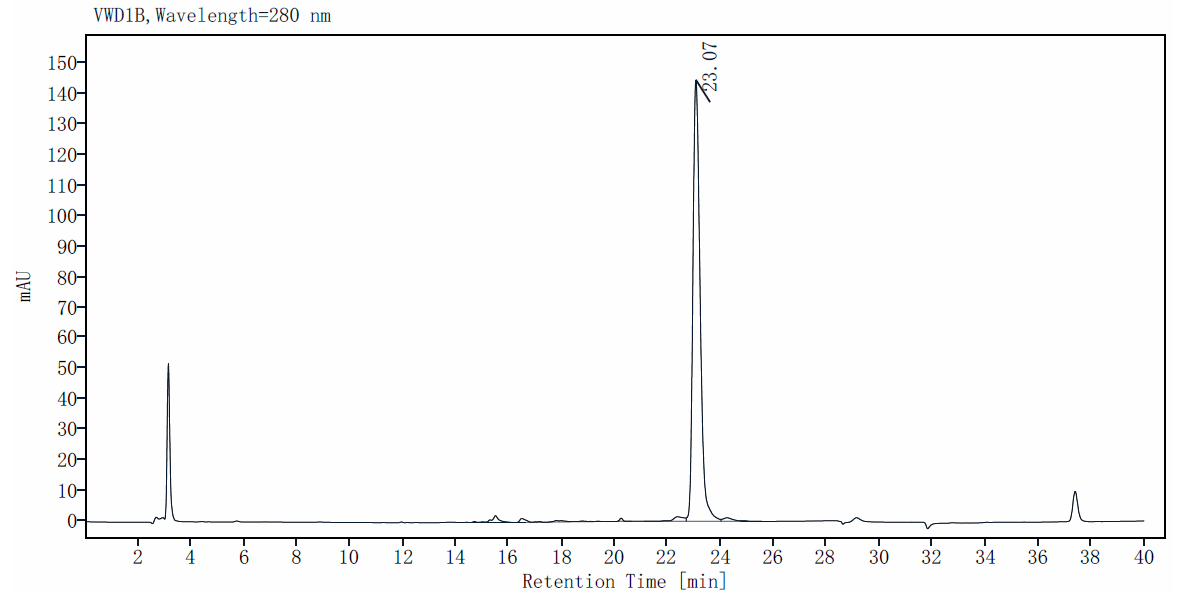
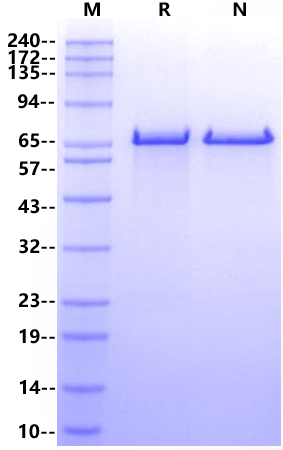
Purity: >90% by SDS-PAGE and HPLC.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA070063 | DT3C (Diphtheria toxin & spg 3C domain) Protein, Corynephage beta | Expression System : E.coli | $240 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




