Antibodies Against Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4): Uncovering Their Diagnostic Potential in Disease Risk
05 Aug 2025
by AntBio
Retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) is a member of the lipocalin family and functions as the specific transport protein for the lipophilic vitamin A (retinol) in the bloodstream. RBP4 is predominantly expressed in adipocytes and hepatocytes. The human RBP4 comprises 201 amino acid residues and three pairs of disulfide bonds, and its structure has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The structural core of RBP4 is a typical β-barrel that can specifically accommodate a retinol molecule,rendering this hydrophobic vitamin soluble in an aqueous environment and transportable through the bloodstream.

Figure 1: The Three-Dimensional Structure of RBP4
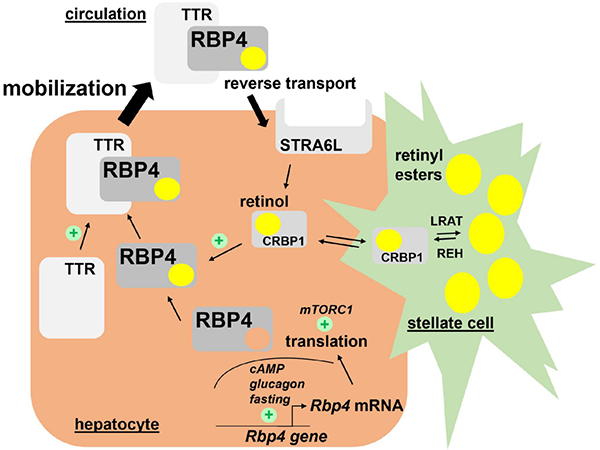
The RBP4 cycle is the principal mechanism for the distribution of vitamin A from hepatic storage to extrahepatic tissues. In the liver, the majority of vitamin A is stored as retinyl esters in hepatic stellate cells in an LRAT (lecithin retinol acyltransferase)-dependent manner. Upon hydrolysis by retinyl ester hydrolase (REH), retinol binds to RBP4 in hepatocytes and subsequently forms a complex with transthyretin (TTR). This retinol/RBP4/TTR complex enters the bloodstream. RBP4 then binds to the membrane receptor STRA6 on target cells, thereby delivering retinol to these cells. Additionally, STRA6 expressed by hepatocytes can also mediate the retrograde transport of retinol from the RBP4 cycle. Various organs and tissues, including the retinal pigment epithelium, the female reproductive system, testes, brain, and kidneys, require substantial uptake of retinol to exert their intrinsic functions.

Figure 2: Activation of Retinol in Hepatocytes by RBP4
According to relevant literature and research reports, RBP4 is associated with the risk of various diseases, including renal and hepatic disorders, fetal malformations, night blindness, cardiovascular diseases, and insulin resistance. RBP4 holds extensive diagnostic application value in clinical settings.
Renal Diseases
RBP4 has been recognized as an early diagnostic marker for tubular injury and is widely used in the clinical diagnosis of renal diseases. When renal disease occurs, the glomerular filtration capacity decreases, and tubular reabsorption is impaired, leading to a significant increase in serum and urinary RBP4 levels. The concentration of RBP4 is significantly associated with the degree of glomerular filtration dysfunction or proximal tubular reabsorption impairment. It is more sensitive than creatinine and blood urea nitrogen in the early stages and is not affected by diet.
Hepatic Diseases
Liver damage directly affects the synthesis of RBP4, resulting in decreased serum RBP4 levels, which can reflect early changes in hepatic synthetic function and catabolic metabolism. Studies have shown that serum RBP4 levels can serve as a marker for the degree of steatosis in individuals infected with hepatitis C virus. The levels of RBP4 in serum and urine also aid in the differential diagnosis of cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome.
Insulin Sensitivity
RBP4 is a lipocalin that impairs insulin sensitivity. It can activate macrophage surface receptors CD206+, leading to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, insulin resistance, and activation of both innate and adaptive immune systems. Multiple studies have reported the mechanisms by which elevated RBP4 affects insulin sensitivity: RBP4 induces the expression of gluconeogenic rate-limiting enzymes in hepatocytes, raising blood glucose levels and impairing insulin signaling. Serum RBP4 levels are correlated with endogenous insulin secretion (increased C-peptide levels) and insulin resistance (calculated by the homeostasis model assessment index).
Cardiovascular Diseases
Serum RBP4 levels are closely related to cardiovascular diseases and their risk factors, including atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hypertension, and heart failure. Numerous studies have shown that coronary artery disease is associated with elevated RBP4 levels. RBP4 can induce inflammatory effects in endothelial cells and promote the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by hyperinsulinemia. Additionally, chronic kidney disease can increase circulating RBP4 levels. A study involving 3,210 Chinese individuals demonstrated that mutations in RBP4 are significantly associated with plasma RBP4 levels and the risk of hypertriglyceridemia in the Chinese population.
Vision and Development
In the absence of RBP4, the eyes cannot effectively absorb retinol, leading to impaired vision, night blindness, and even complete blindness. Insufficient vitamin A intake during pregnancy can also directly result in visual impairment in newborns. Most RBP4 mutations are associated with vision impairment: studies have found that compound heterozygous mutations p.I59N and G74D in RBP4 protein lysates can cause night blindness and moderate retinal dysplasia. Mutations p.A73T and p.A75T can lead to microphthalmia, anophthalmia, and ocular tissue defects. RBP4 plays a crucial role in mammalian embryonic development. Severe vitamin A deficiency in fetuses can have a significant impact on the embryo, including midfacial deformities and even exencephaly.
As a sensitive biomarker, RBP4 holds significant clinical value in the diagnosis of renal diseases, assessment of liver function, evaluation of nutritional status, and detection of vitamin A deficiency. With the continuous advancement of medical research and expanding clinical applications, RBP4 is expected to provide robust support for the diagnosis and treatment of a broader range of diseases.
S-RMab® Monoclonal Antibody Pair
Starter has launched a new high-sensitivity RBP4 antibody pair. Validated on downstream chromatography platforms, the correlation with clinical samples exceeds 95%.
We are committed to providing high-quality raw materials for RBP4 detection to our global partners and offering more accurate and reliable diagnostic services to patients worldwide. Inquiries are welcome.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B3249 | RBP4 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-693-108) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3248 | RBP4 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-693-111) | Host : Rabbit | Inquiry |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |




