Analysis of the Impact of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT).

Recent Advances
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) is a biological process characterized by the loss of polarity and cell-cell adhesion properties in epithelial cells, leading to their transformation into mesenchymal-like cells with migratory and invasive capabilities. This phenomenon is extensively involved in embryonic development, tissue repair, cancer metastasis, and fibrotic diseases.
Classification of EMT
-
Type 1 EMT (Physiological): A normal process in embryonic development (e.g., neural crest cell migration, heart valve formation) and organogenesis.
-
Type 2 EMT (Pathological): Involved in tissue repair and fibrosis (e.g., renal fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis), triggered by chronic inflammation or injury.
-
Type 3 EMT (Cancer-Related): Tumor cells acquire invasiveness through EMT, promoting metastasis and drug resistance, which is a critical step in cancer progression.
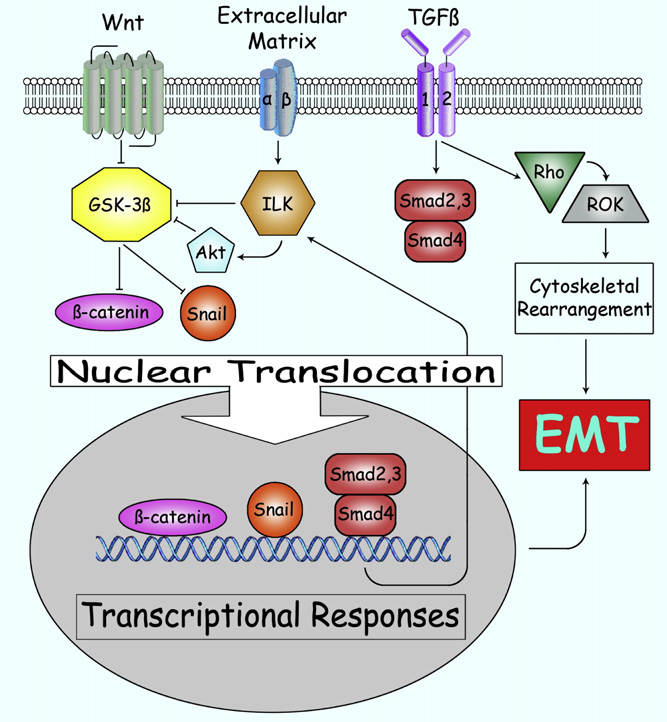
The Main Molecular Pathways Involved in the Induction of EMT
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is the non-cellular component of the extracellular environment, primarily composed of proteins and polysaccharides such as collagen, fibronectin, and laminin. It not only provides structural support for cells but also participates in cell signaling, migration, proliferation, and differentiation. The ECM plays a crucial regulatory role in EMT, as detailed below:
Influence of Physical Properties
-
Stiffness: The stiffness of the ECM can mimic the mechanical environment of different tissues in vivo. Epithelial cells are more likely to undergo EMT on stiffer ECM. For example, the ECM in tumor tissues is typically stiffer than in normal tissues, which activates intracellular mechanical signaling pathways such as the Rho-ROCK pathway. This activation leads to cytoskeletal rearrangement, transforming cells from an epithelial cobblestone morphology to a mesenchymal spindle-like morphology, while promoting the expression of EMT-related transcription factors (e.g., Snail, Slug, Twist) to induce EMT.
-
Topology: The topological structure of the ECM, such as fiber alignment and pore size, also influences EMT. Aligned fibers can guide cell migration direction and provide physical cues similar to those in tissues. When cells sense these cues, they activate corresponding signaling pathways, promoting cell movement and phenotypic changes. For instance, epithelial cells are more likely to undergo polarity changes and migration on ECM with aligned fiber structures, thereby inducing EMT.
Core Proteins
-
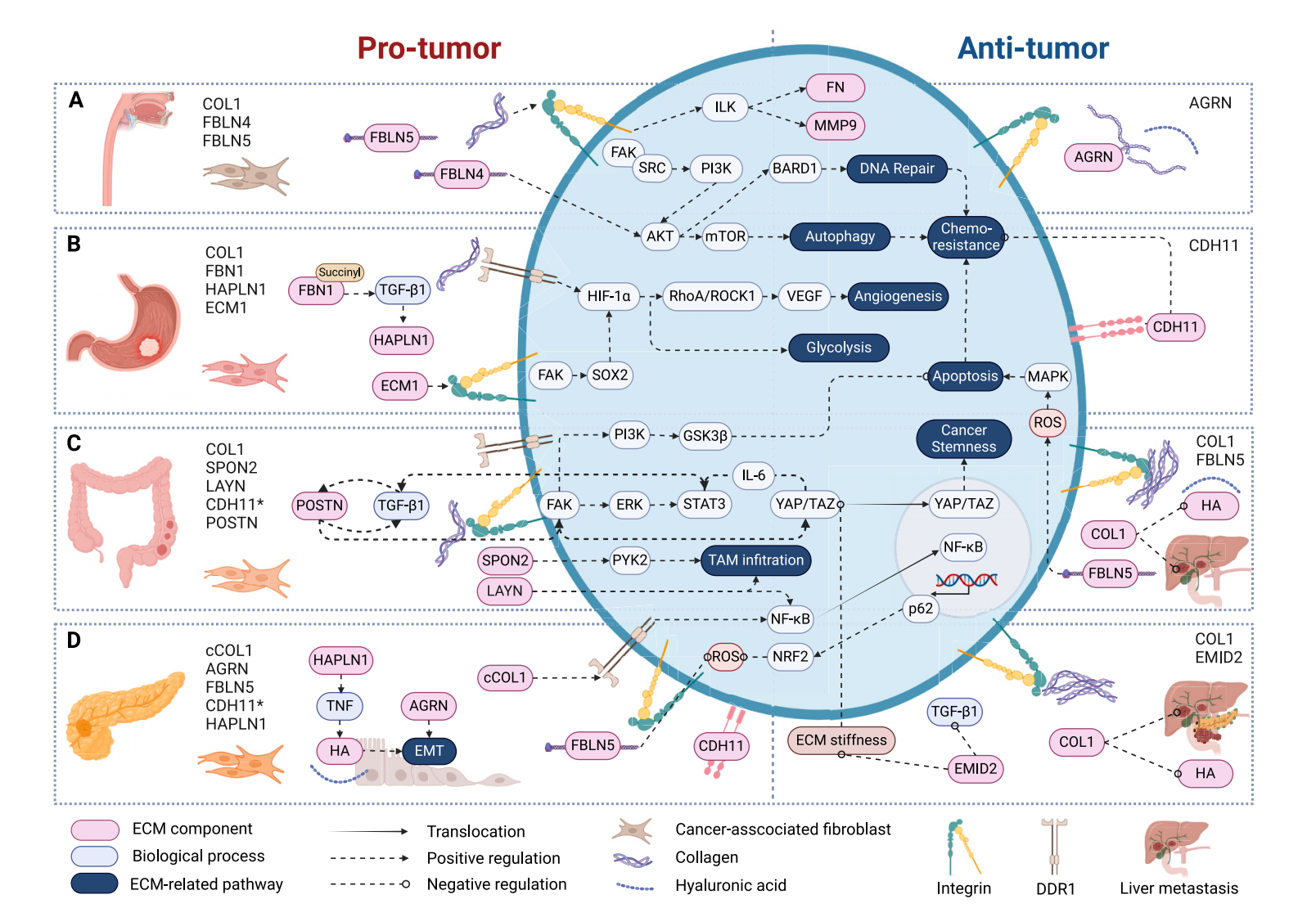
MMP Proteins: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of proteases that play a key role in the degradation and remodeling of the ECM. MMPs participate in ECM metabolism, degrading various ECM components and playing a critical role in tissue development, morphogenesis, and wound repair. For example, during embryonic development, MMPs are involved in tissue and organ formation by degrading the ECM to create space for cell migration and proliferation.
-
Collagen: Collagen is one of the main components of the ECM, and different types of collagen have varying effects on EMT. For instance, type I collagen can bind to integrin receptors on the cell surface, activating downstream signaling pathways such as FAK-PI3K-AKT. This pathway promotes cell survival, proliferation, and migration while upregulating EMT-related transcription factors. Additionally, type III collagen has been associated with tumor cell EMT and metastatic potential.
-
Fibronectin: Fibronectin is a multifunctional ECM protein that interacts with various cell surface receptors, including integrins. The interaction between fibronectin and integrins activates intracellular signaling cascades such as ERK and JNK, regulating cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation, and promoting the expression of EMT-related genes. Increased fibronectin expression in the tumor microenvironment is closely associated with tumor cell EMT and metastasis.
-
Laminin: Laminin, primarily found in the basement membrane, plays a crucial role in maintaining epithelial cell polarity and stability. However, specific laminin isoforms or their degradation products can induce EMT. For example, degradation products of LAMA5 can activate intracellular signaling pathways, leading to the loss of epithelial polarity and cell-cell junctions, thereby inducing EMT.
Related Signaling Pathways
-
Integrin Signaling Pathway: Cells interact with the ECM through integrin receptors. Upon binding to ECM components, integrins cluster and activate, recruiting intracellular signaling molecules to form focal adhesions. These adhesions activate downstream pathways such as FAK-Src, regulating cell adhesion, migration, and survival, and inducing EMT by influencing the activity of EMT-related transcription factors.
-
PI3K/AKT Pathway: The PI3K/AKT pathway is downstream of integrin-mediated outside-in signaling. It is activated by integrin clustering and subsequent adaptor proteins like FAK, playing a significant role in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and drug resistance in gastrointestinal cancers. Proteomic analyses have shown correlations between the ECM/PI3K-AKT pathway and resistance to anti-HER2 targeted therapies. Collagens such as COL8A1, COL1A1, and COL5A2 drive gastrointestinal tumor progression and resistance to gemcitabine and immunotherapy by modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Other ECM components, such as ECM1 and MXRA5, promote EMT through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Additionally, succinylation-induced FBN1 accumulation interacts with integrins β3 and β5 on gastric cancer cells, activating TGF-β1 and the PI3K/AKT pathway to promote tumor proliferation.
-
Growth Factor Signaling Pathways: The ECM can bind and store various growth factors, such as TGF-β and EGF. When the ECM is degraded or remodeled, these growth factors are released and bind to cell surface receptors, activating corresponding signaling pathways. For example, TGF-β activates the Smad pathway, promoting the expression of EMT-related transcription factors while suppressing epithelial markers, thereby inducing EMT.
ECM Components and Downstream Signal Pathways Across GI Cancers
START introduces the Contribution of Extracellular Matrix to EMT MiniAb Kit (Catalog Number: S0M1038) to facilitate research on the role of ECM in EMT. The kit includes 25 primary antibodies and one secondary antibody, supporting Western blot (WB) applications.
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| UA080088 | FGFR2[N549H] Protein | Host : Human | $767 |
| Expression System : Baculovirus-InsectCells | |||
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0M1037 | STING pathway MiniAb Kit(Mouse) | $480 | |
| S0M1036 | Adherens junctions MiniAb Kit | $750 | |
| S0M1035 | Adherens junctions MiniAb Kit (Human Only) | $1,020 | |
| S0M1034 | PI3K-AKT Pathway MiniAb Set | $570 | |
| S0M1033 | PI3K-AKT Pathway MiniAb Set(Human Only) | $750 | |
| S0M1031 | DNA Damage MiniAb Set | $570 | |
| S0M1030 | Cellular Senescence MiniAb Set | $750 | |
| S0M1029 | SRC Related MiniAb Set | $660 | |
| S0M1028 | SRC Related MiniAb Set(Human Only) | $1,020 | |
| S0M1027 | Apoptosis MiniAb Set II | $930 | |
| S0M1026 | JAK-STAT Pathway MiniAb Set | $660 | |
| S0M1023 | Stat Family MiniAb Set | $390 | |
| S0M1022 | Autophagy Antibody MiniAb Set II | $570 | |
| S0M1021 | mTOR Signaling Antibody MiniAb Set | $480 | |
| S0M1019 | Protein kinase C Antibody MiniAb Set | $660 | |
| S0M1009 | SMAD2/3 Antibody MiniAb Set | $300 | |
| S0M1008 | Human-Reactive STING Antibody MiniAb Set | $390 | |
| S0M1006 | Cell Cycle Regulation Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $685 |
| S0M1005 | Autophagy Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $390 |
| S0M1004 | NF-κB Pathway Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $390 |
| S0M1003 | MAPK Family Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $480 |
| S0M1002 | Apoptosis Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $480 |
| S0M1001 | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Antibody MiniAb Set | Conjugation : Unconjugated | $480 |
| S0M1038 | Contribution of Extracellular Maxtrix to EMT MiniAb Kit | $2,280 |