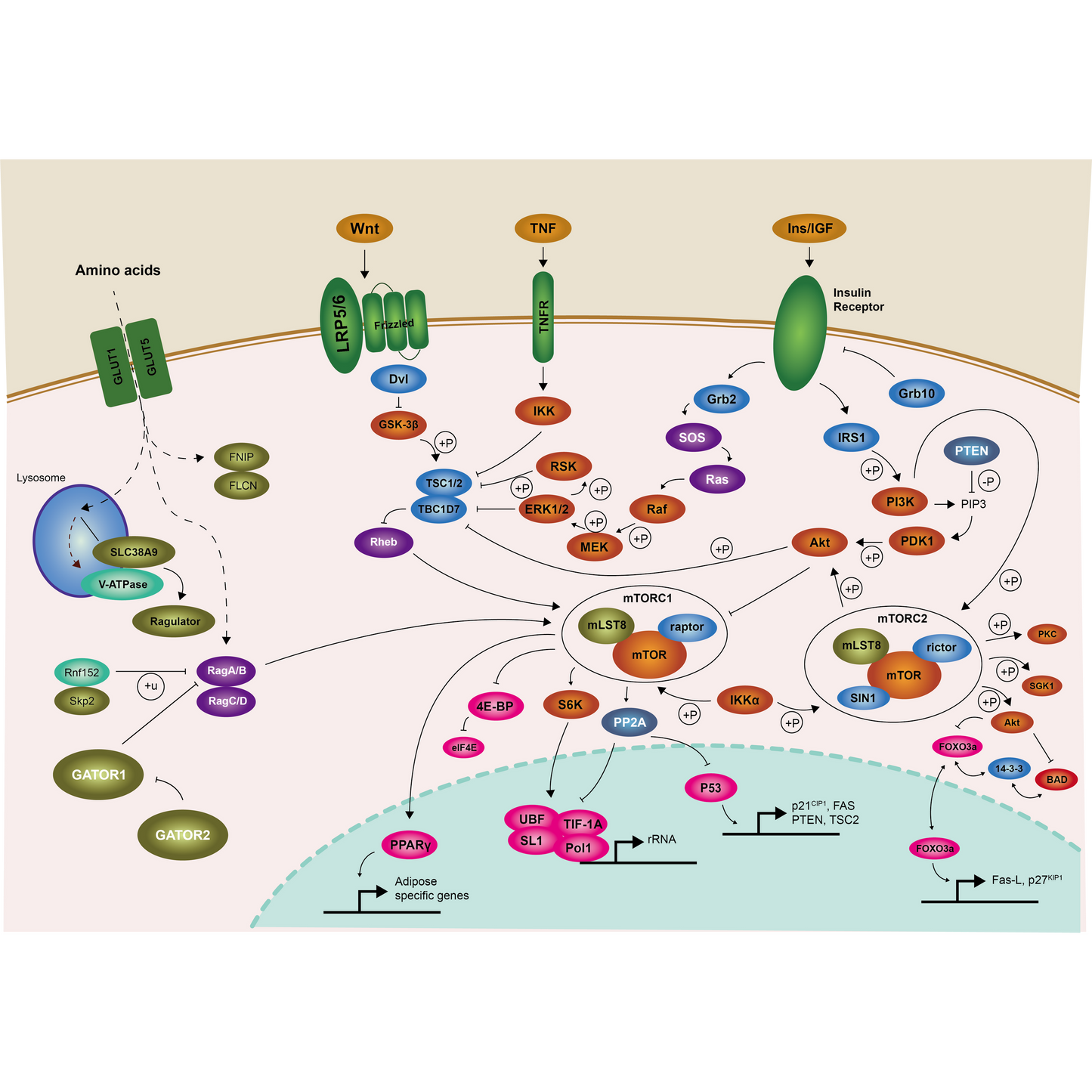
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Reference:
DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.010
| Application | WB |
| Reactivity | Hu |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, 40% Glycerol, 0.05% BSA, 0.03% Proclin 300 |
| Stability & Storage | 12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, -20 °C as supplied |
The PI3K-AKT signaling pathway is a crucial cellular signaling pathway that plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including growth, proliferation, survival, and metabolism。
Components:
PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase): A family of enzymes that phosphorylate the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol (PI) to produce phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PIP3).
AKT (also known as Protein Kinase B): A serine/threonine kinase that is activated by PIP3 and plays a central role in mediating the effects of growth factors and insulin.
PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog): A tumor suppressor that dephosphorylates PIP3 back to PIP2, thus negatively regulating the pathway.
Activation:
The pathway is typically activated by various growth factors, hormones, and cytokines that bind to receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) or G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs).
Upon activation, these receptors recruit and activate PI3K, leading to the conversion of PIP2 to PIP3 in the plasma membrane.
Downstream Effects:
AKT Activation: PIP3 recruits AKT to the membrane, where it is phosphorylated and activated by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) and mTORC2.
Cell Survival and Growth: Activated AKT promotes cell survival by inhibiting pro-apoptotic factors (e.g., BAD, caspase-9) and enhancing the activity of anti-apoptotic factors (e.g., Bcl-2).
Metabolism: AKT regulates glucose metabolism by promoting glucose uptake and glycolysis through the activation of glucose transporters and enzymes involved in metabolic pathways.
Cell Cycle Progression: AKT influences cell cycle progression by regulating cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs).
Clinical Relevance:
Dysregulation of the PI3K-AKT pathway is implicated in various diseases, particularly cancer, where mutations in components like PI3K or loss of PTEN function can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and survival.
The pathway is a target for therapeutic interventions, with several inhibitors of PI3K and AKT currently being investigated or used in clinical settings.
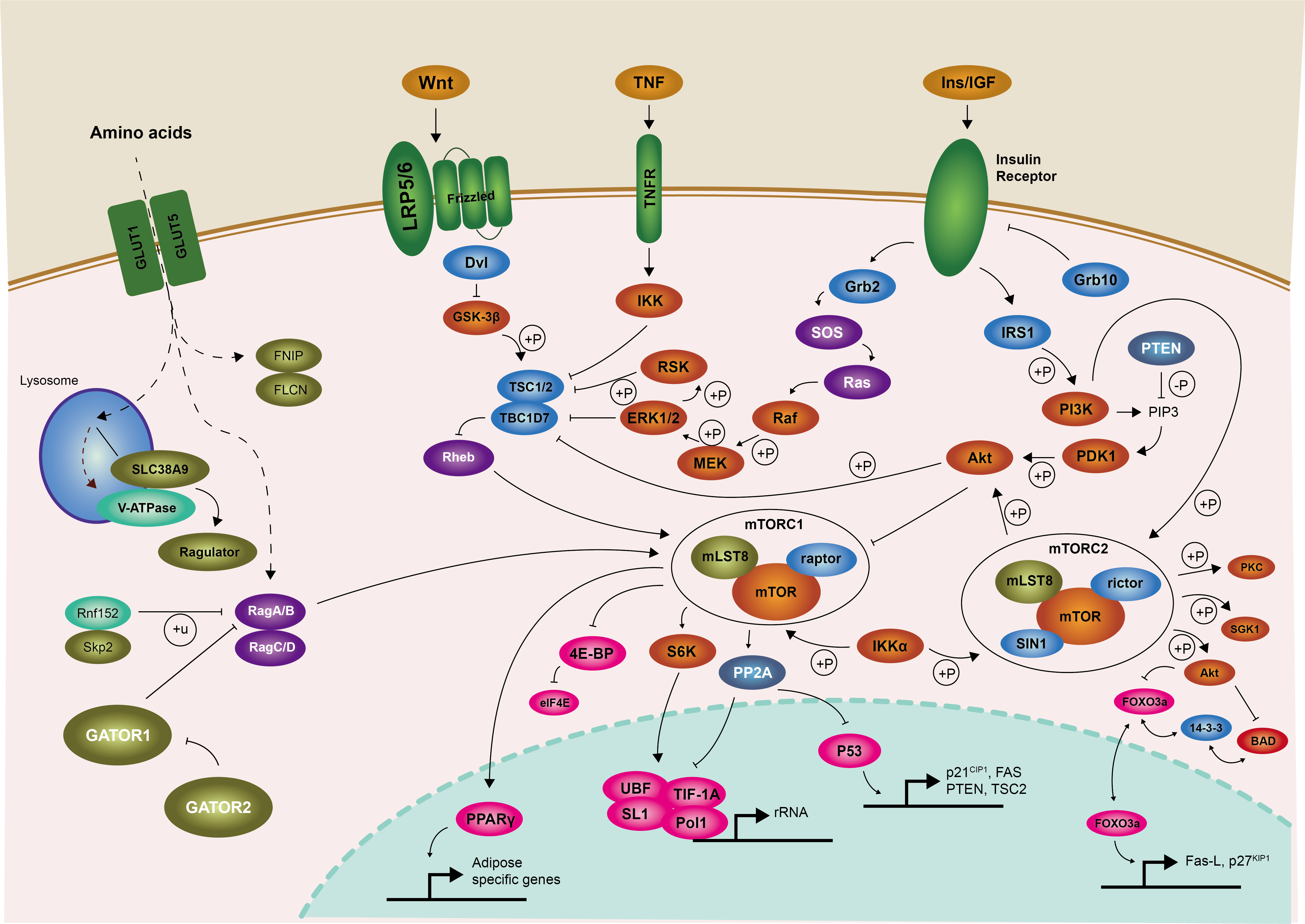
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Reference:
DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.010