ROR1: A New Hope in Cancer Treatment, A New Focus in Drug Development

Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1, or ROR1 (Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1), is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor (ROR) family. ROR1 consists of an extracellular region (immunoglobulin-like domain, cysteine-rich domain, and Kringle domain), a transmembrane region, and an intracellular region (tyrosine kinase domain, serine/threonine-rich domain, and proline-rich domain).
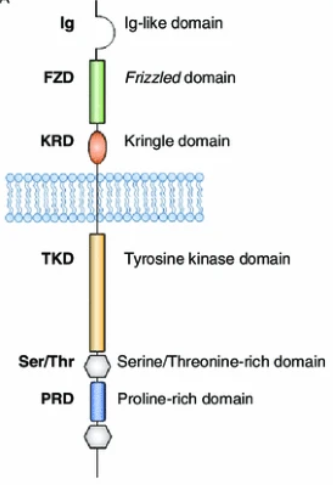
Figure 1 Structure of ROR1
ROR1 can mediate signal transduction in non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways, regulating biological processes such as cell separation, proliferation, and chemotaxis. It plays important roles in promoting tumor growth and metastasis, inducing tumor cell drug resistance, and inhibiting apoptosis. Wnt5a, as a ligand for ROR1, binds to ROR1 and mediates the activation of the NF-κB pathway in tumor cells, promoting cell migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and cancer metastasis.
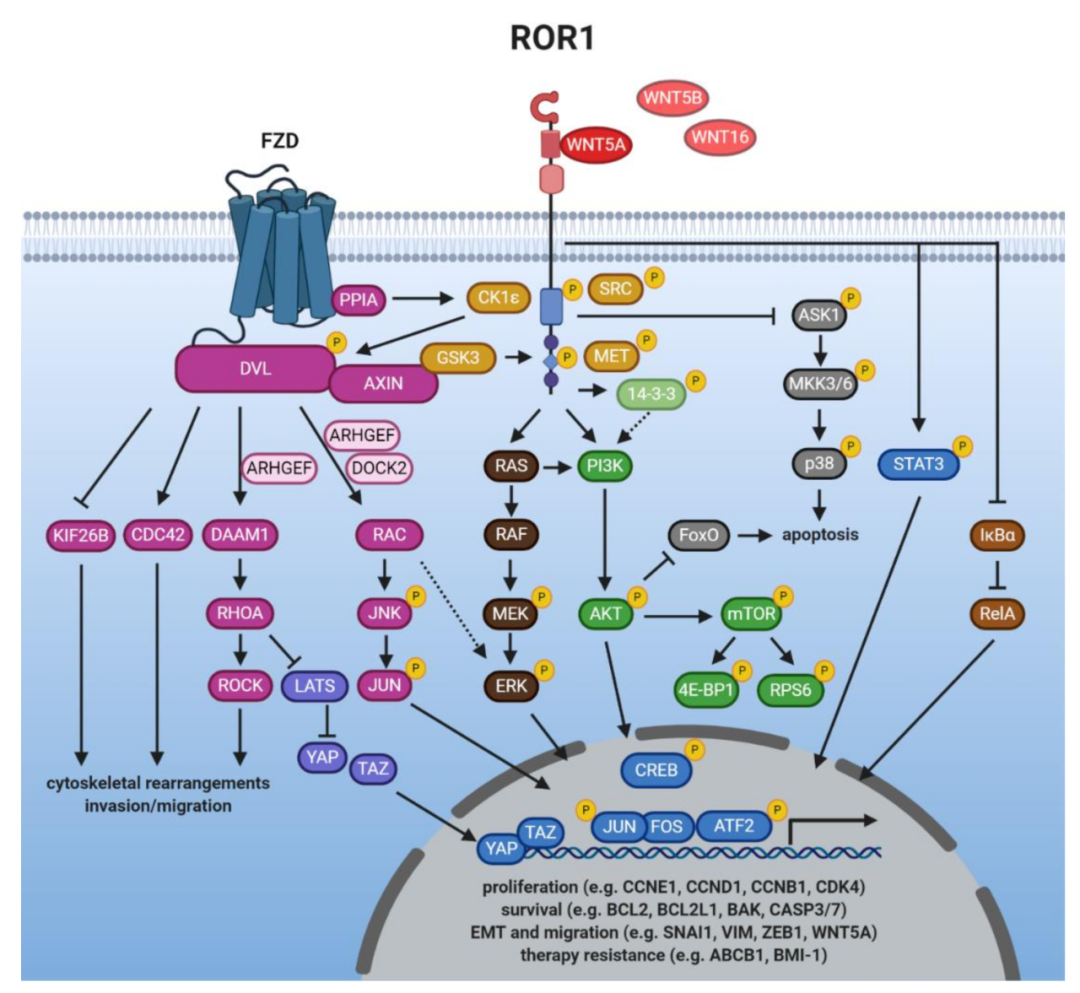
Figure 2 ROR1 Signaling Pathway
ROR1 is expressed at very low levels in the serum, cells, or tissues of healthy adults but is widely overexpressed in various malignant tumor tissues (solid tumors and hematological malignancies), such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lung adenocarcinoma, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, and melanoma, making it a tumor-specific marker. ROR1 expression is positively correlated with the clinical stage and lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer and can serve as an independent prognostic marker. In ovarian cancer, high ROR1 expression is also associated with tumor grade and lymph node metastasis. In circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of pancreatic cancer, ROR1 is a significant factor in their aggressive phenotype. [1]
ROR1 is considered a hot potential drug target. In immune checkpoint therapy (ICT), some tumor types exhibit low response rates due to moderate to high immune suppression and a lack of T-cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. Combining ICT with therapies targeting ROR1/Wnt5a may potentially address the issue of low response rates. The tumor-specific nature of ROR1 has already placed it on the global pharmaceutical industry's hotlist for drug development.
Drug types under development include antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), monoclonal antibody drugs, bispecific antibodies (BiTEs), and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Currently, no ROR1-targeted drugs have been approved for market release, but the druggability and safety of the ROR1 target have been preliminarily validated, with numerous products already in clinical Phase II/III trials.
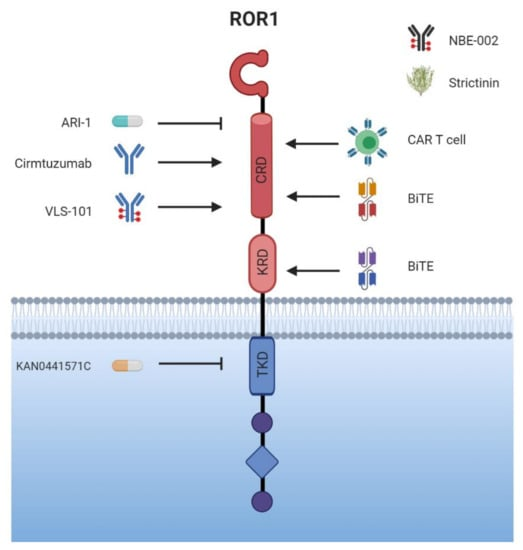
Figure 3 Strategies for ROR1-Targeted Tumor Immunotherapy
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
Antibody-drug conjugates are complexes formed by linking cytotoxic small-molecule drugs to monoclonal antibodies, enabling targeted delivery of cytotoxic drugs to tumor tissues. Most current ROR1-related ADCs are heterogeneous mixtures produced by chemically conjugating payloads to monoclonal antibodies via lysine or cysteine residues. Additionally, some drugs utilize SMAC technology, employing the transpeptidase Sortase A to catalyze the linkage of oligoglycine-containing molecules to proteins with the LPXTG sequence motif, thereby enzymatically conjugating ROR1 antibodies with anthracycline drugs.
Monoclonal Antibody Drugs
ROR1 monoclonal antibody drugs can block Wnt5a signaling by binding to ROR1, thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and survival, and inducing tumor cell differentiation. Several ROR1 monoclonal antibody drugs for treating CLL and MCL are already in clinical trials.
Bispecific Antibodies
Bispecific antibodies consist of two different heavy and light chains that can bind to two distinct antigen epitopes, selectively activating immune responses and mediating cancer cell apoptosis. A popular approach for ROR1 bispecific antibody drugs involves one single-chain variable region binding to the ROR1 Kringle domain and another variable region targeting the TCR CD3 subunit, directing polyclonal T cells to the tumor site. Phase I clinical trials have confirmed the efficacy of ROR1 bispecific antibody drugs in CLL and MCL patients. [2]
CAR-T Cell Therapy
ROR1-targeted CAR-T cell therapy is used to treat hematological and solid tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, CLL, and MCL. Studies in human tumor tissue xenograft mouse models have shown that ROR1 CAR-T can control the growth of solid tumors without causing safety-related toxicity. [3]
S-RMab® Recombinant Antibodies
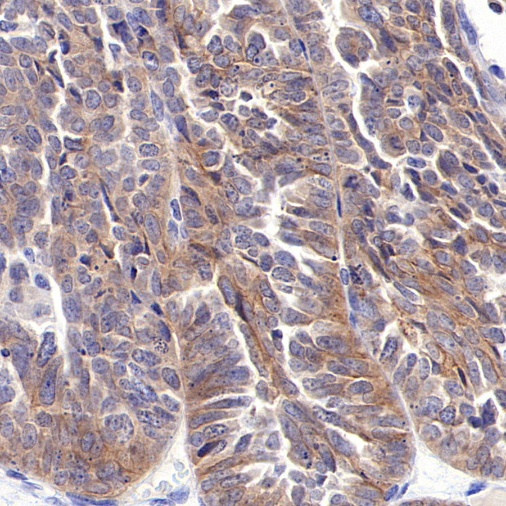
AntBio offers ROR1 recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies, which have been validated in human ovarian cancer, gastric cancer, endometrial cancer, and mantle cell lymphoma tissues. These antibodies exhibit higher specificity, sensitivity, and stability, providing more accurate diagnostic results for clinical applications.
| Product Number | Name | Application |
|---|---|---|
| S0B2299 | ROR1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R501-147) | IHC-P, WB |
| S0B2301 | ROR1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R501-148) | IHC-P, WB |
| S0B2300 | ROR1 Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-R501-178) | IHC-P, ICC, WB, IP |
Tissue Type: Human Ovarian Cancer
Tissue Type: Human Gastric Cancer
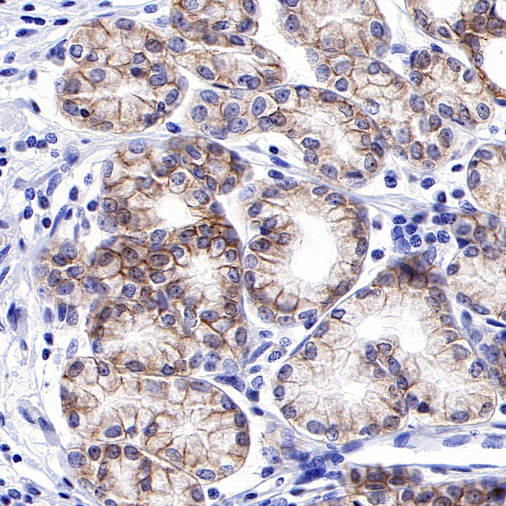
Tissue Type: Human Endometrial Cancer
Reference
[1] Chirmule, N., Jawa, V. & Meibohm, B. Immunogenicity to Therapeutic Proteins: Impact on PK/PD and Efficacy. AAPS J 14, 296–302 (2012).
[2] Plotkin S, Orenstein W. Vaccines. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1999.
[3] Schelpe,An-Sofie,Roose. Generation of anti-idiotypic antibodies to detect anti-spacer antibody idiotopes in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura patients[J].[2024-02-23].




