Recommend | Starter Bio - Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Development Platform
The rabbit as an animal models play an important role in immunology. Rabbit monoclonal antibodies, owing to their distinct advantages, have found extensive applications in areas such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diverse diagnostic and therapeutic modalities. Notably, the FDA has granted approval for 11 rabbit monoclonal antibodies for clinical in vitro diagnostic applications, with 10 specifically designated for use as tumor markers."
Advantages of Rabbit mAb
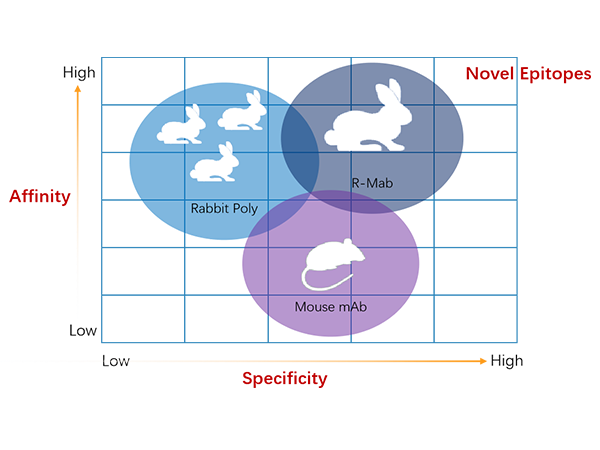
Higher specificity and affinity:
Rabbit monoclonal antibody have higher specificity and affinity, which can identify antigen epitope more accurately. Most murine are inbred and have small spleens, and rabbits have a broader repertoire of immune repertoires. And rabbit monoclonal antibody have the dissociation constant (KD) at the picomolar level with strong affinity.
Broader antibody expression profile:
Due to the differences in species evolution, the immune system of rabbits can not only recognize the homologous antigens of rodents and humans, but also produce antibodies that recognize more epitopes, with a broader antibody expression profile. Different from murine antibody, for short peptide, small molecules, point mutation and posttranslational modifications (PTMs) can also produce a strong immune response.
Higher sensitivity:
In IHC related research, compared rabbit monoclonal antibody and murine monoclonal antibody with the same human antigen, rabbit mAb shows higher sensitivity.
Simpler Immunoglobulin structure:
Rabbit immunoglobulin can be categorized into four classes (excluding IgD). Among these, IgG exhibits the highest concentration in serum. Unlike IgG in other animals, rabbit IgG has no sub-classes. This unique attribute simplifies molecular cloning and engineering processes, playing a critical role in the development of antibody drugs.
Easy humanization:
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies are easier to be humanized, which reduces immunogenicity and improves treatment safety.

Based on the single B cell technology and S - RMab® recombinant antibody platform, we aim to provide high quality recombinant antibodies.
√ High sensitivity and specificity
√ Stable batch to batch consistency
√ Efficient in vitro production
√ Sustainable supply
Reference
[1] Bystryn JC, Jacobsen JS, Liu P, Heaney-Kieras J. Comparison of cell-surface human melanoma-associated antigens identified by rabbit and murine antibodies. Hybridoma. 1982;1:465–472
[2] Raybould TJ, Takahashi M. Production of stable rabbit-mouse hybridomas that secrete rabbit mAb of defined specificity. Science. 1988;240:1788–1790.
[3] An Z. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: From Bench to Clinic. Wiley. 2009
[4] Klebe S, Swalling A, Jonavicius L, Henderson DW . An immunohistochemical comparison of two TTF-1 monoclonal antibodies in atypical squamous lesions and sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung, and pleural malignant mesothelioma. J Clin Pathol 2016; 69: 136–141.
[5] Hoang LL, Tang P, Hicks DG, Chen H, Yang Q, Haas TS et al. A new rabbit monoclonal E-cadherin antibody [EP700Y] shows higher sensitivity than mouse monoclonal E-cadherin [HECD-1] antibody in breast ductal carcinomas and does not stain breast lobular carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2014; 22: 606–612.
[6] Weber J, Peng H, Rader C. From rabbit antibody repertoires to rabbit monoclonal antibodies[J]. Experimental & molecular medicine, 2017, 49(3): e305-e305.




