Lactylation: Cell Metabolism's Hidden Modification and Disease's Potential Key
16 Jun 2025
by AntBio
Lactylation is a newly discovered post-translational modification of proteins, involving the binding of lactate molecules to amino acid residues of proteins. This process not only reflects changes in cellular metabolism but also plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, cell function, and disease progression. As research on lactylation deepens, scientists are increasingly recognizing its significant role in biology.
一.Mechanism of Lactylation
Lactylation primarily occurs on lysine residues, where lactate molecules form ester bonds with lysine, resulting in lactylated proteins. This process is closely related to the metabolic state of the cell, particularly in hypoxic or high-energy-demand environments where lactate production increases, thereby promoting lactylation.
二.Biological Functions
Lactylation plays a significant role in various biological processes, including:
-
Gene Expression Regulation: Lactylation can influence the activity of transcription factors, thereby regulating gene transcription levels. For example, lactylated transcription factors may enhance or suppress the expression of specific genes.
-
Cell Metabolism Regulation: Lactylation is closely associated with cellular energy metabolism, affecting the utilization of nutrients and energy production within the cell.
-
Immune Response: In immune cells, lactylation has been found to be involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses and immune responses.
三.Lactylation and Disease
Abnormal lactylation is closely linked to the development of various diseases, including:
-
Cancer: Tumor cells often exhibit high metabolic activity, and increased lactylation may promote tumor growth and metastasis.
-
Metabolic Diseases: Lactylation plays an important role in metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity, influencing insulin signaling pathways and lipid metabolism.
-
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Studies suggest that lactylation may be associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
四.Detection of Lactylation
To study the biological functions of lactylation and its role in diseases, scientists require effective detection methods. The development of lactylation-specific antibodies has provided important tools for this field. These antibodies can specifically recognize and bind to lactylated proteins, enabling researchers to detect lactylation levels in cell or tissue samples using techniques such as immunoprecipitation, Western blot, and immunofluorescence.
Staart Lactylation Antibody: Your Solution for Lactylation Detection
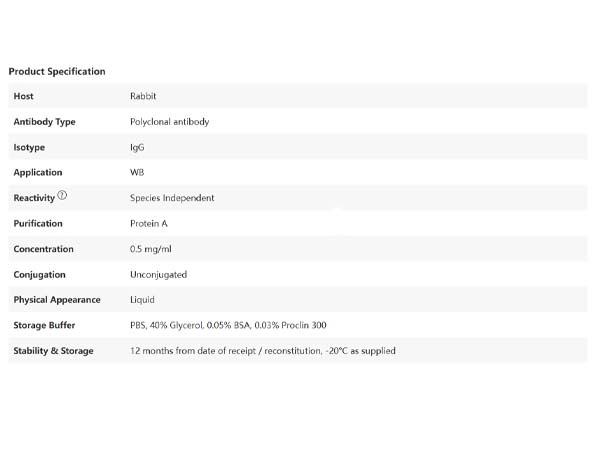
L-Lactyl Lysine Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Catalog Number: S0B0719
Validation Data:
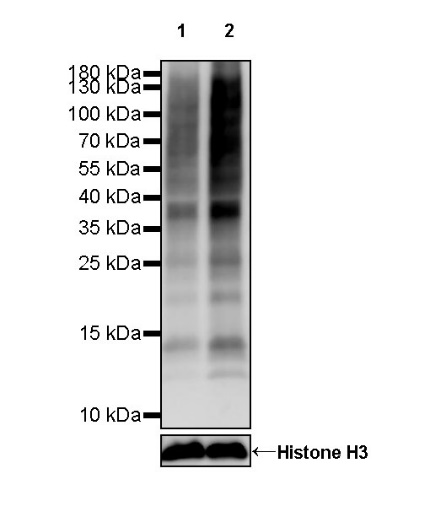
WB result of L-Lactyl Lysine Rabbit pAb
-
Primary antibody: L-Lactyl Lysine Rabbit pAb at 1/1000 dilution
-
Lane 1: untreated HeLa whole cell lysate 20 µg
-
Lane 2: HeLa treated with 100 mM Lactate sodium for 24 hours whole cell lysate 20 µg
-
Secondary antibody: Goat Anti-rabbit IgG, (H+L), HRP conjugated at 1/10000 dilution
-
Predicted MW: Multiple
-
Observed MW: Multiple
Conclusion
As an emerging post-translational modification, lactylation is gradually revealing its importance in cellular metabolism and biological functions. With the deepening of research into lactylation mechanisms, related detection technologies (such as lactylation antibodies) will provide deeper insights, helping us explore the potential roles of lactylation in health and disease.




