Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Accession | P0DTC2 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Arg319-Phe541, with N-terminal 8*His HHHHHHHHGGGGSDYKDDDDKRVQPTESIVRFPNITNLCPFDEVFNATRFASVYAWNRKRISNCVADYSVLYNLAPFFTFKCYGVSPTKLNDLCFTNVYADSFVIRGDEVRQIAPGQTGNIADYNYKLPDDFTGCVIAWNSNKLDSKVSGNYNYLYRLFRKSNLKPFERDISTEIYQAGNKPCNGVAGFNCYFPLRSYSFRPTYGVGHQPYRVVVLSFELLHAPATVCGPKKSTNLVKNKCVNF |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
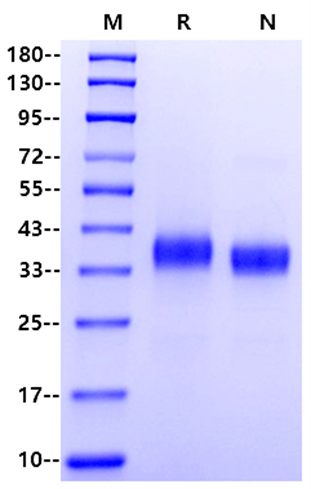
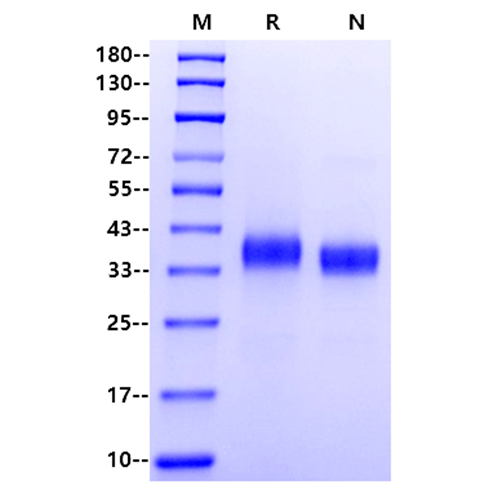
| Molecular Weight | 35-43kDa (Reducing) |
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. |
Background
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are enveloped viruses with a positive sense RNA genome, that belong to the subfamily Coronavirinae within the family Coronaviridae, which is part of the Nidovirales order. The CoVs virion contains at least four structural proteins: spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M) and nucleocapsid (N). Among them, the S protein plays an essential role in viral attachment, fusion, entry, and transmission. It comprises an N-terminal S1 subunit responsible for virus–receptor binding and a C-terminal S2 subunit responsible for virus–cell membrane fusion. S1 is further divided into an N-terminal domain (NTD) and a receptor-binding domain (RBD). During infection, CoV first binds the host cell through interaction between its S1-RBD and the cell membrane receptor, triggering conformational changes in the S2 subunit that result in virus fusion and entry into the target cell.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE