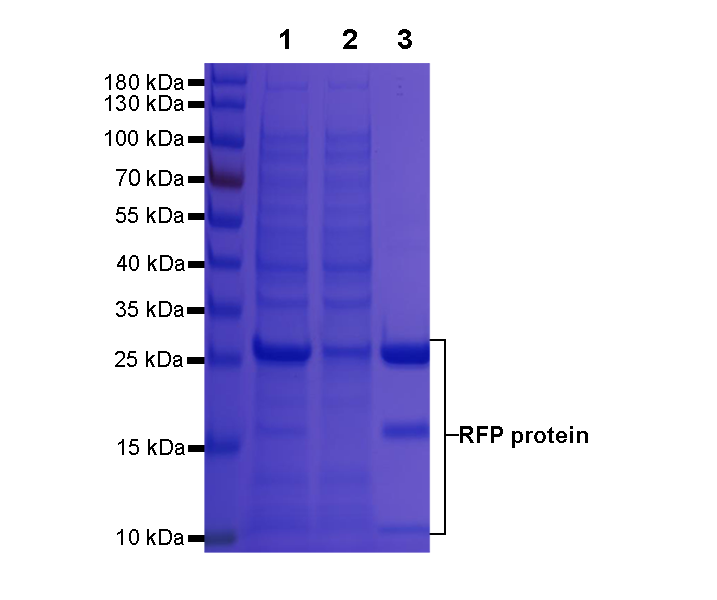
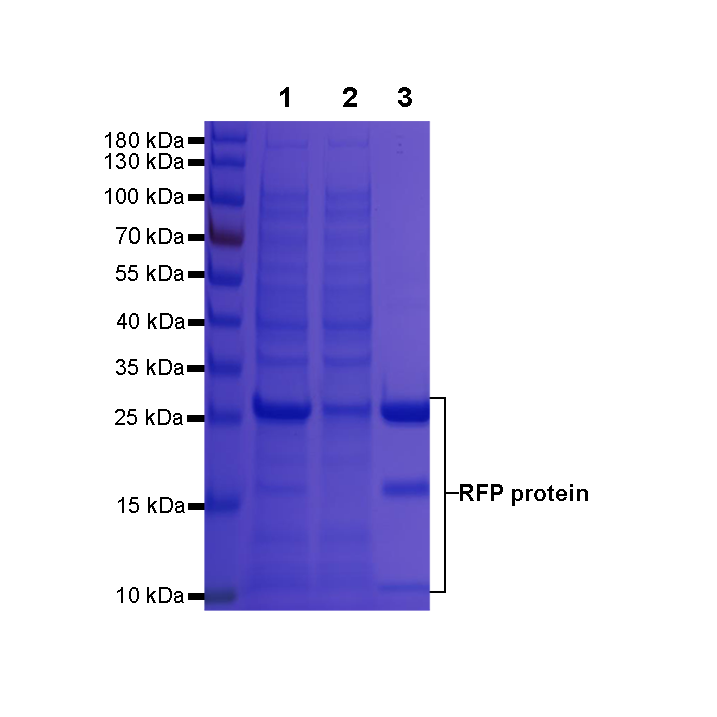
Anti-RFP/mcherry agarose beads were used to immunoprecipitated Red fluorescent protein (RFP). During elution with Acidic elution buffer buffer, the enriched RFP fusion protein are released from the agarose beads.
SDS-PAGE analysis was performed.
Lane 1: Input
Lane 2: Flow-through
Lane 3: RFP fusion protein
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Host | Rabbit |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Protein |
| Antibody Type | Recombinant mAb |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Application | IP, Protein purification, Co-IP |
| Reactivity | Species Independent |
| Purification | Protein A |
| Conjugation | Agarose beads |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | 50% slurry in PBS pH7.4, 0.05% Proclin 300 |
| Stability & Storage | 12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, 2 to 8 °C as supplied |
Background
Reliable and robust pull-down of mCherry and RFP-fusion proteins. Red fluorescent protein, also known as RFP, is a type of protein that emits red fluorescence under ultraviolet light. It is an essential optical imaging tool in the field of life science. RFP can be used for live cell imaging, marking protein expression, and various protein-related experiments. It is one of the most commonly used fluorescent proteins, along with green fluorescent protein (GFP) and orange fluorescent protein (OFP). RFP has several advantages compared to GFP. Firstly, RFP can be used in combination with GFP to address scientific issues that GFP alone cannot solve. Secondly, RFP has longer excitation and emission wavelengths, which results in a lower background during intracellular imaging.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE