Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Human |
| Synonyms | Cystatin-C,Cystatin C,Cystatin-3,CST3 |
| Accession | P01034 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Ser27-Ala146, with N-6*His MHHHHHHDDDDKSSPGKPPRLVGGPMDASVEEEGVRRALDFAVGEYNKASNDMYHSRALQVVRARKQIVAGVNYFLDVELGRTTCTKTQPNLDNCPFHDQPHLKRKAFCSFQIYAVPWQGTMTLSKSTCQDA |
| Expression System | E.coli |
| Molecular Weight | 14.9 kDa(Reducing) |
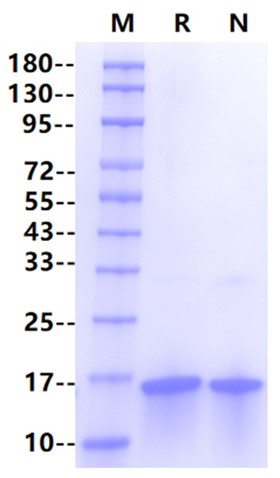
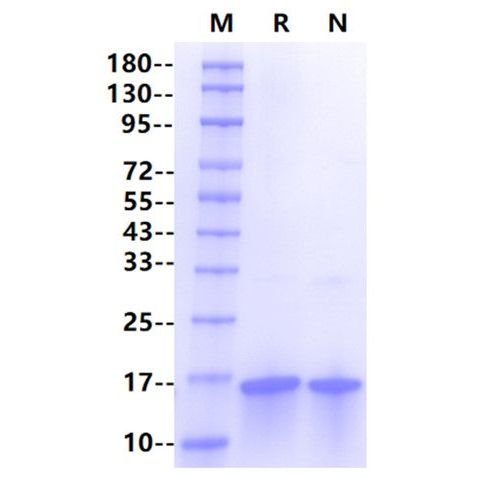
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <2EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | 20mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH8.0 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1mg/mL according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
Background
Human cystatin C (hCC) belongs to a family of proteins called cystatins. There are three distinct types of cystatins that share sequence and structure homology but differ in size, site of action, and disulfide bond topology. Human cystatin C belongs to the type 2 cystatins that are generally secreted as extracellular polypeptides. hCC is broadly distributed and found in most body fluids. This small protein consists of 120 amino acids forming a single polypeptide chain. Cystatin C contains four conserved cysteine residues that can form two disulfide bonds but, unlike other family members, was neither shown to be glycosylated (cystatin E/M and cystatin F) nor phosphorylated (chicken cystatin). Furthermore, hCC can be found in monomer, dimer, oligomer, and fibril states.
In terms of biological function, hCC is a target of proteolysis, and primarily functions as a protease inhibitor. It is degraded by cathepsin D and elastase.Uncontrolled proteolysis leads to an imbalance between active proteases and endogenous inhibitors,eventually leading to disease.The hCC concentration in blood correlates with the glomerular filtration rate(GFR), an important marker of kidney health and the progression of diabetes, chronic kidney disease.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE