HBP - Sepsis “Key indicators for early diagnosis”
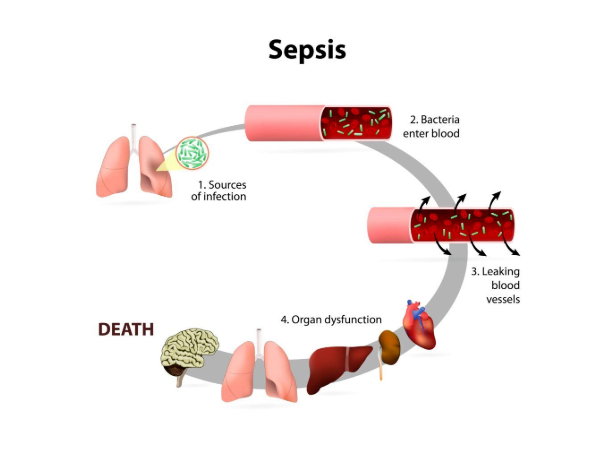
Sepsis
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria. Sepsis has an extremely high mortality rate of about 25%-30% and is responsible for more deaths than prostate cancer, breast cancer, and HIV combined. Sepsis is one of the deadliest and most expensive clinical conditions. Anyone can contract sepsis, and people with compromised immune systems are at higher risk for fatal sepsis, which kills 11 million people each year.
WHO call for a global response to sepsis includes an initiative to develop tests that are rapid, low-cost and easy to use, primarily for use at home and in the community, to improve the identification, surveillance, prevention and treatment of sepsis.
Heparin-binding protein (HBP)
Heparin-binding protein (HBP), also known as Azurocidin (AZU), is a multifunctional single-chain glycoprotein with antibacterial and chemotactic properties. It is part of the innate defense system of human neutrophils. As a multifunctional regulator of inflammation, HBP promotes monocyte recruitment, adhesion, and extravasation [1].
HBP has three main functions in biology:
1. Bactericidal and chemotactic: HBP has a wide range of antibacterial properties against Gram cells and others. HBP can activate monocyte and macrophage chemotaxis and activation, enhance the body's immune response to infection or injury, and enhance its phagocytosis. At the same time, the release of TNF-α, IL-1, INF-γ and other inflammatory factors aggravates the inflammatory response.
2. Regulation of coagulation function: HBP has a strong affinity with heparin, and its activity is inhibited after the combination of the HBP and heparin, which can regulate coagulation by binding to heparin.
3. Increase vascular endothelial cell (EC) permeability: HBP can regulate the function of vascular endothelial cells, increase its permeability leading to plasma permeability and edema formation, which is one of the characteristic manifestations of inflammatory response. Neutrophils, the first line of defense against bacterial infection, play an important role in the early stage of inflammation, migrating into tissues and degranulation, releasing more HBP.
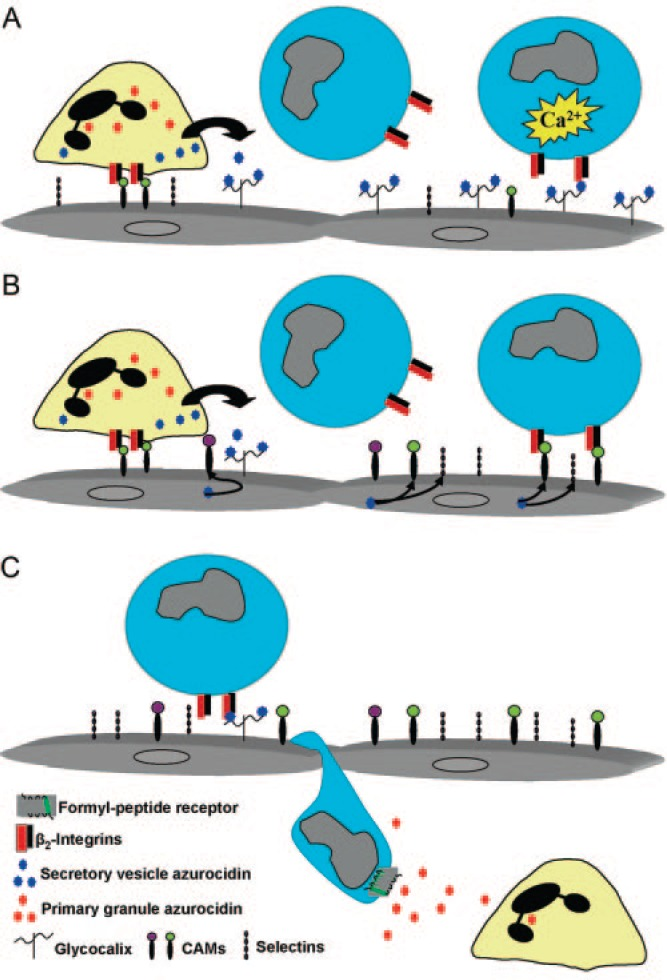
Effect of HBP on monocyte recruitment in inflammatory response
Clinically, high concentrations of HBP in plasma are associated with circulatory instability in severe infections. As an acute phase protein, HBP can predict the occurrence of sepsis 72 hours in advance, and warn the occurrence of organ dysfunction and shock in advance. It is an effective biomarker to evaluate the severity of sepsis. Its accuracy is higher than other cytokines, and it is more important in the early diagnosis and efficacy monitoring of patients with septic shock. Research have found that plasma HBP concentration ≥20 ng/mL can be used as a diagnostic index for severe sepsis. In order to accurately diagnose the degree of sepsis in clinical practice, it is necessary to combine the results of PCT and hs-CRP detection.
In addition to sepsis diagnosis, HBP can also be used as a diagnostic aid for local infection diseases such as acute bacterial meningitis and urinary tract infection in children. HBP can also be used as an auxiliary index for clinical diagnosis of sepsis. When the concentration of HBP is 70.35 ng/mL, the sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of sepsis are 78% and 88%, respectively. In ICU patients, HBP can predict the risk of shock, circulatory failure and cardiac arrest in patients with severe infection.
S-RMab® Recombinant Rabbit mAb
Starter Bio update 10 Paired antibodies with high specificity, sensitivity and stability, suitable for Sandwich Elisa and collaurum. We are looking forward to working with you to promote the development of immunodiagnostic technology and provide more accurate and reliable testing services for patients around the world.
Recommend Paired Antibody:
S0B3174 (Capture) - S0B3177 (Detection)
S0B3174 (Capture) - S0B3179 (Detection)
S0B3174 (Capture) - S0B3182 (Detection)
S0B3181 (Capture) - S0B3174 (Detection)
S0B3182 (Capture) - S0B3174 (Detection)
Product Information
| Gatalog Num | Product Name | Product Parameters | Price |
| S0B3180 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-97) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3179 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-99) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3178 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-95) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3177 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-82) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3176 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-22) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3175 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-57) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3183 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-109-1) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3182 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-109) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3181 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-96) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated | |||
| S0B3174 | HBP Recombinant Rabbit mAb (SDT-506-54) | Host : Rabbit | $270 |
| Conjugation : Unconjugated |





