Antibody/Protein Labeling Dyes Selection Guide and FAQs

In today's biomedical research, accurate and efficient identification and tracking of target molecules is key to unlocking disease mechanisms, developing novel medicines, and advancing personalized medicine. Antibody/protein labeling technology plays an irreplaceable role in this process as a powerful tool. By covalently binding specific chemical tags, such as fluorescent dyes, enzymes, or radioisotopes, to antibodies or proteins, researchers are able to visualize and quantify molecules of interest in complex biological systems with greater sensitivity and specificity.
Common antibody/protein labeling techniques
Fluorescein labeling: fluorescein such as Alexa Fluor series (AF488\AF594\AF647, etc.), Cy series (Cy3\Cy5\Cy7, etc.), FITC, etc., is commonly used in flow cytometry, immunofluorescence and in vivo imaging experiments;
Enzyme labeling: such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) labeling, which generate colored products or chemiluminescence by catalyzing substrates for ELISA, Western blot, immunohistochemistry and other experiments;
Biotin labeling: Biotin labeling is the use of biotin to bind to biological macromolecules such as antibodies or proteins, and is widely used in the qualitative and quantitative detection of trace antigens and antibodies, as well as localization observation and research.
1. Overview of Alexa Fluor series dyes
Alexa Fluor dyes are derivatives of dyes such as rhodamine or coumarin, which are synthesized using sulfonic acid or sulfonate instead of hydrogen atoms in dyes such as rhodamine or coumarin. It is mainly used in the labeling and localization of tissues, cells and biomolecules in biological research. Table 1 shows the emission spectra, excitation spectra, commonly used excitation light, and equivalent dyes of the Alexa Fluor series of dyes labeled with antibodies and proteins. The most commonly used of these is the green fluorescent probe, Alexa Fluor 488. Compared to most commonly used green fluorescent probes, Alexa Fluor 488 is brighter, less prone to fluorescence quenching, and has lower background.
Table 1 Alexa Fluor dyes commonly used to label antibodies/proteins
|
Fluorescent dyes |
Abs(nm) |
Em(nm) |
Excitation light source |
Equivalent dye |
|
Alexa Fluor 350 |
346 |
442 |
UV excitation |
AMCA,AMCA-X |
|
Alexa Fluor 405 |
402 |
421 |
Blue laser excitation |
Pacific blue dye |
|
Cascade blue dye |
||||
|
Alexa Fluor 430 |
434 |
540 |
Blue laser excitation |
Lucifer yellow |
|
Alexa Fluor 488 |
495 |
519 |
488 nm argon and Kr/Ar laser line |
Fluorescein,Cy2 |
|
Alexa Fluor 532 |
531 |
554 |
Frequency-doubled Nd-YAG laser |
Rhodamine 6G |
|
Alexa Fluor 546 |
556 |
573 |
Hg lamp, red filter set |
Cy3, TMR |
|
Alexa Fluor 555 |
555 |
565 |
Hg lamp & 543nm green HeNe |
Cy3 |
|
Alexa Fluor 568 |
579 |
604 |
568nm Kr/Ar laser line |
Lissamine rhodamine B |
|
Alexa Fluor 594 |
591 |
618 |
647nm Kr/Ar laser line |
Texas red |
|
Alexa Fluor 647 |
650 |
665 |
647nm Kr/Ar laser line |
Cy5 |
|
Alexa Fluor 660 |
650 |
690 |
647nm or 633nm laser lines |
Cy5 |
|
Alexa Fluor 680 |
679 |
702 |
Xenon-are or far-red diode laser |
Cy5.5 |
|
Alexa Fluor 700 |
696 |
719 |
Xenon-are or far-red diode laser |
Cy5.5 |
|
Alexa Fluor 750 |
752 |
779 |
Xenon-are or dye pumped lasers |
Cy7 |
Antibody/Protein Alexa Fluor Labeling Principles and Benefits
Alexa Fluor labeling utilizes a highly efficient and simple N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester chemistry to selectively combine Alexa Fluor dye with the amino group (-NH) of a neighboring protein2, including lysine side chains and amino terminations) and covalently bound to form a stable succinimidyl ester structure (Figure 1).
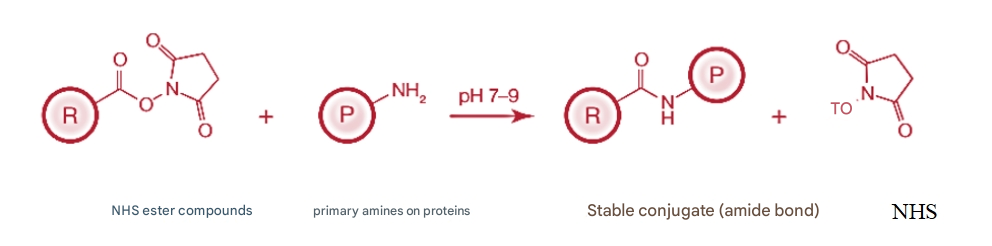
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of NHS ester reaction
R denotes one end of the labeling reagent or crosslinker with the NHS ester reactive group; P indicates the presence of primary amines (-NH2) protein molecules
Alexa Fluor dyes offer the following benefits:
(1) The emission spectrum is narrow. Compared to traditional organic fluorescent dyes, Alexa Fluor dyes have a narrow emission spectrum, which reduces the crossover level of different assays;
(2) Strong fluorescence intensity and good photostability;
(3) It is less affected by temperature and pH;
(4) It has good water solubility. Alexa Fluor dye does not require organic reagents to bind proteins, and storage is less prone to precipitation;
(5) Alexa Fluor series dyes have different colors, and different objects can be labeled with different Alexa Fluor dyes according to the needs of the experiment, so as to achieve distinction.
2. Overview of Cy series dyes
Cy is the abbreviation of Cyanine, also known as Cyanine dye. Cy dyes have excellent performance, and the molar absorbance coefficient is the highest among fluorescent dyes. In general, the appropriate activation (NHS esters, carboxylic acid groups, isothiocyanates, maleimides, etc.) dyes and reaction conditions are selected according to the labelable groups (e.g., amine, aldehyde, or sulfhydryl groups) and acidity and alkalinity of the biomolecule to be labeled. Its NHS ester is the most commonly used aliphatic amino labeling reagent, which is widely used for the labeling and detection of proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids and other biomolecules. Among them, cyanine dyes Cy3 and Cy5 have become the preferred fluorescent markers for gene chips. In addition, the absorption of Cy5, Cy5.5, and Cy7 is very low in the near-infrared region, making them the long-wavelength dyes with the highest fluorescence intensity and the most stable, especially suitable for in vivo imaging in vivo small animals instead of radioactive elements (Figure 2).
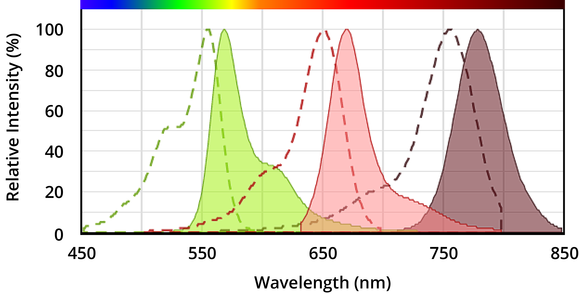
Figure 2 Maximum absorbance (dashed line) and emission (shadow area) of Cy3 (left), Cy5 (middle), and Cy7 (right) dyes
Advantages of Cy series dyes:
(1) The spectrum is narrow, the signal is strong, and the sensitivity is high;
(2) The molar absorbance coefficient of the dye is higher than that of other fluorescent dyes;
(3) The dye has low cytotoxicity and can be used to label antibodies, proteins, and cells;
(4) The fluorescence band has good tissue permeability in the near-infrared region, which is very suitable for in vivo imaging of mice.
3. Overview of HRP and ALP marking
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) are two commonly used enzyme markers that can be combined with antibodies and used in various immunological assays, such as ELISA, Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, etc. These enzyme-labeled antibodies are able to produce a detectable signal through a specific substrate reaction to help quantify or localize the antigen of interest.
Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) Features: HRP is a very stable enzyme that remains active over a wide pH range. It catalyzes hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) with certain hydrogen donors to produce colored products or luminescent signals.
Apply:
(1) ELISA: In enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies can be used to detect antigen-primary antibody complexes that are immobilized on plates.
(2) Western Blotting: HRP-labeled antibodies can be used to recognize and develop protein bands that are transferred to membranes.
(3) Immunohistochemistry: HRP-labeled antibody is used for antigen localization in tissue sections, and specific molecules in cells are observed by staining.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) characteristics: ALP is most active under alkaline conditions, it can remove phosphate group groups, and convert colorless phosphate substrates into colored products. ALP may show higher specificity and stability for some substrates than HRP. In some cases, ALP produces a longer-lasting signal than HRP, which helps improve the detection of low-abundance antigens.
Apply:
(1) ELISA: Similar to the application of HRP, but usually uses a different substrate.
(2) Immunohistochemistry: ALP is particularly suitable for situations where long-term staining or preservation of staining results is required.
(3) In situ hybridization: ALP is also commonly used for the labeling of nucleic acid probes in order to locate DNA or RNA in cells.
4. Overview of biotin labeling
Biotin is a small molecule vitamin, also known as vitamin H or B7. After activation, Biotin-NHS can bind to the amino groups of biological macromolecules such as proteins/antibodies, which can not only maintain the biological activity of macromolecules well, but also have a multi-stage amplification effect when combined with avidin, making it widely used in qualitative and quantitative detection of trace antigens and antibodies, as well as localization observation and research.
There are a few key points to note when performing biotin labeling:
(1) The concentration of the substance to be labeled should not be too low to ensure the labeling efficiency;
(2) The ratio of biotin to the target should be appropriate to avoid affecting the activity of the target marker;
(3) In order to reduce the effect of steric hindrance, a cross-linked arm structure can be added between biotin and the labeled object;
(4) The purification step after the labeling reaction is critical to remove unreacted biotin and other impurities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What about protein labeling FITC loss?
A1: The loss is relatively small, with a yield of more than 95%.
Q2: How does AF488 label antibody work?
A2: Based on a chemical reaction based on N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters, which can form stable amide bonds with the primary amine group (-NH2) in the antibody molecule, after which the desalting column removes the free dye.
Q3: What dyes are recommended for antibody labeling in flow cytometry experiments?
A3: Flow cytometry experiments need to be purified, PE (yield is only about 20%) and APC labeling (yield is about 50%) can be recommended, small molecule fluorescent labeling, such as FITC, AF series, Cy series, etc., the labeling efficiency is very high, which can fully meet the flow cytometry experiment.
Q4: The antibody contains 50% glycerol, can it be labeled?
A4: Yes, we will perform dialysis first to remove glycerin before labeling.
Q5: Is there any labeling efficiency and COA for biotinylated proteins?
A5: >95% labeling efficiency, normally distributed, 1:3 for protein and biotin, labeling according to standard protocols. COA does, which contains concentration, volume, and buffer information.
Q6: How are labeled antibodies/proteins stored?
A6: Whether it is a fluorescent dye-conjugated antibody, an enzyme-conjugated antibody, or a biotin-conjugated antibody, it needs to be stored in a dark vial or wrapped in aluminum foil. Aliquot the product as soon as it is received to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Do not add sodium azide to HRP-conjugated antibodies, as this protectant inhibits the activity of HRP. Store at 4 °C (1-2 weeks) for short-term storage, and at -20 °C with the addition of cryoprotectants (e.g., glycerin) if long-term storage is required.
Absin can provide a variety of common fluorescein FITC\AF488\AF594\AF647/CY3/CY5/CY5.5/CY7 and HRP or biotin labeling, the system is mature, and the current conventional dye labeling cycle is 1-2 weeks. Tag Requirement Link: https://www.absin.net/custom/conjugated.html
In addition, our company can also provide product customization and experimental services, including custom antibodies, custom peptides, custom proteins, custom mRNA, custom tumor/infectious disease antigen-specific T cell content detection stimuli, multiplex fluorescence immunohistochemistry services, ELISA services, biochemical testing services, TR-FRET services, labeling, purification and other services. For more customization needs, please contact us for info@absin.net
Product recommendations in this issue:
Antibody/protein labeling reagents
|
Catalog number |
Product name |
CAS number |
specification |
|
abs47047679 |
Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) |
9003-99-0 |
5mg |
|
abs42018594 |
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (5-FITC) |
3326-32-7 |
500mg |
|
abs47048093 |
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |
9001-78-9 |
1mg |
|
abs42235702 |
Polydinoflagellin flavin-chlorophyll-protein complex (PerCP) |
- |
1mg |
|
abs45153587 |
B-Phycoerythrin(B-PE) |
- |
1mg |
|
abs45153588 |
Cross Linked-Allophycocyanin(CL-APC) |
- |
1mg |
Flow cytometry antibody tandem dyes
|
Catalog number |
Product name |
specification |
λEx(nm)/ λEm(nm) |
|
|
abs47048236 |
Tandem dye APC-Cy7 |
1mg |
651/780 |
|
|
abs47048237 |
Tandem dye PerCP-Cy5.5 |
1mg |
489/679 |
|
|
abs47048238 |
Tandem dye PE-Cy5 |
1mg |
565/670 |
|
|
abs47048239 |
Tandem dye APC-Cy5.5 |
1mg |
651/700 |
|
|
abs47048240 |
Tandem dye PE-Cy7 |
1mg |
565/780 |
|
|
Tandem dye PE-Cy5.5 |
1mg |
565/700 |
||
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |




