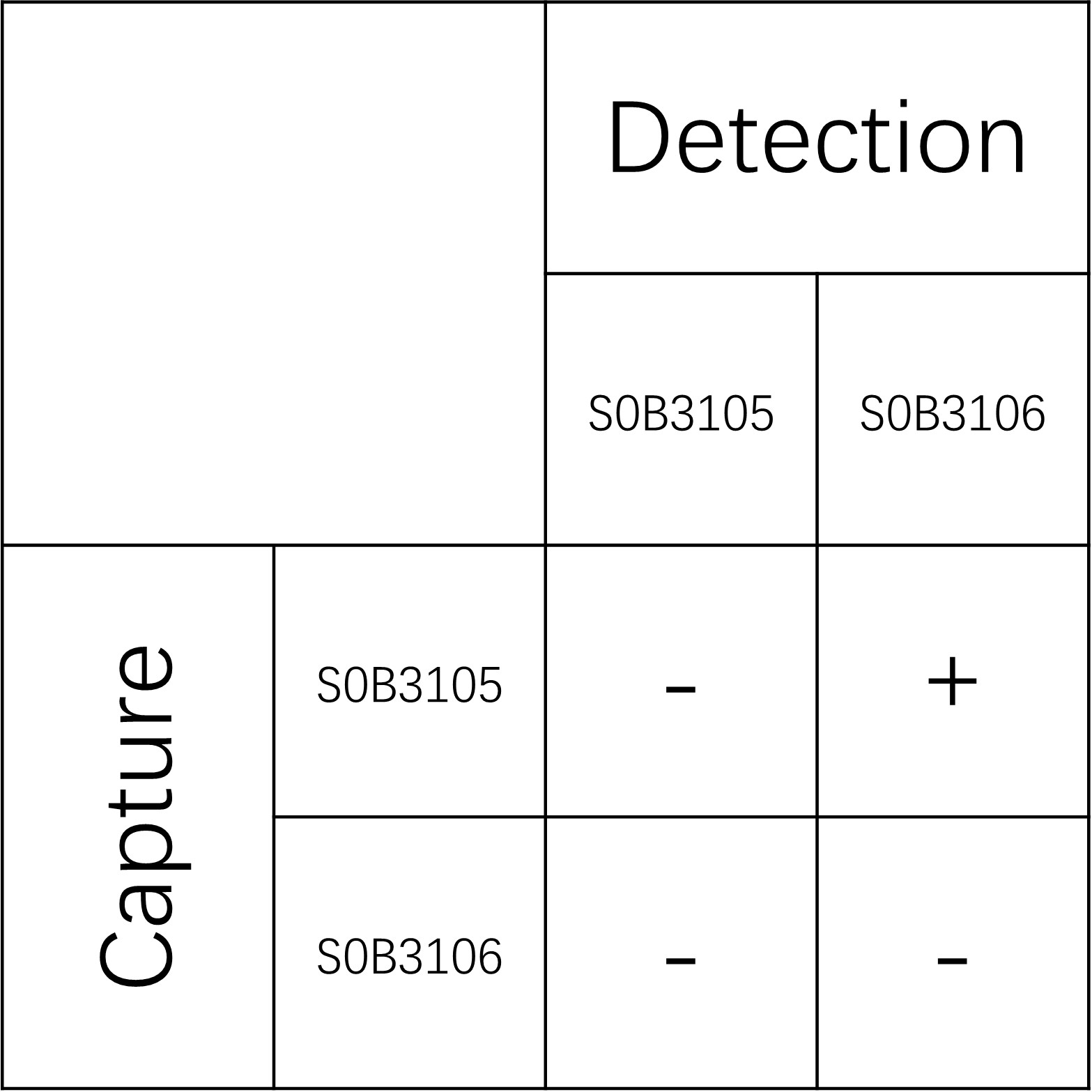
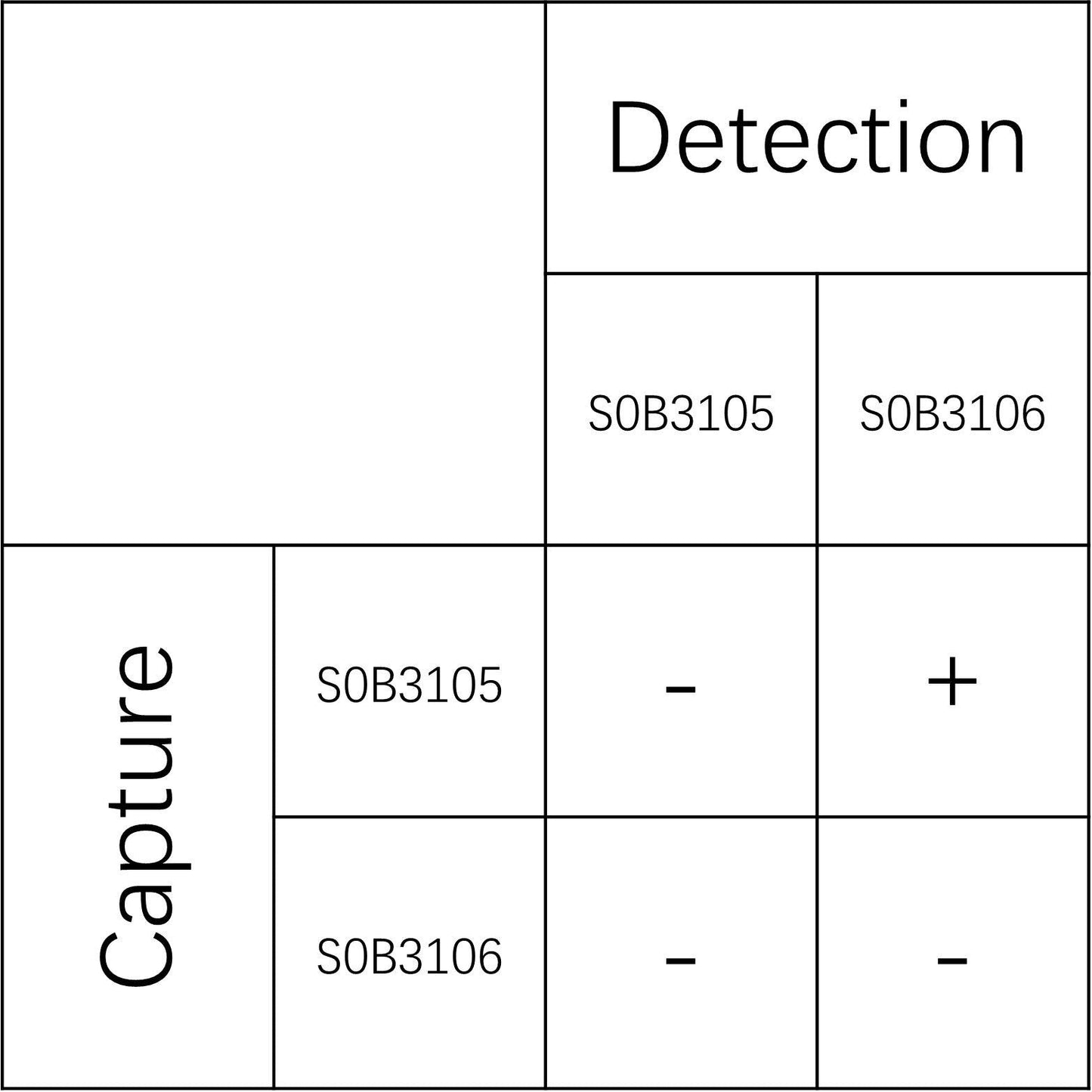
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Host | Rabbit |
| Antigen | D-dimer |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Immunogen | Native protein |
| Location | N/A |
| Clone Number | SDT-117-44 |
| Antibody Type | Rabbit mAb |
| Application | CLIA, Sandwich ELISA |
| Reactivity | Hu |
| Cross Reactivity | Does not recognize fibrinogen |
| Purification | Protein A |
| Concentration | 2 mg/ml |
| Purity | >95% by HPLC |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300 |
| Stability & Storage | 12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, 2 to 8 °C as supplied. |
Dilution
| application | dilution | species |
| Sandwich ELISA | N/A | |
| CLIA | N/A | |
| CLIA | N/A | |
| N/A |
Background
D-dimer (or D dimer) is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product (or FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link, hence forming a protein dimer. D-dimer concentration may be determined by a blood test to help diagnose thrombosis. Since its introduction in the 1990s, it has become an important test performed in people with suspected thrombotic disorders, such as venous thromboembolism. While a negative result practically rules out thrombosis, a positive result can indicate thrombosis but does not exclude other potential causes. Its main use, therefore, is to exclude thromboembolic disease where the probability is low. D-dimer levels are used as a predictive biomarker for the blood disorder disseminated intravascular coagulation and in the coagulation disorders associated with COVID-19 infection. A four-fold increase in the protein is an indicator of poor prognosis in people hospitalized with COVID-19.
Picture
Picture
Paired Recommendations