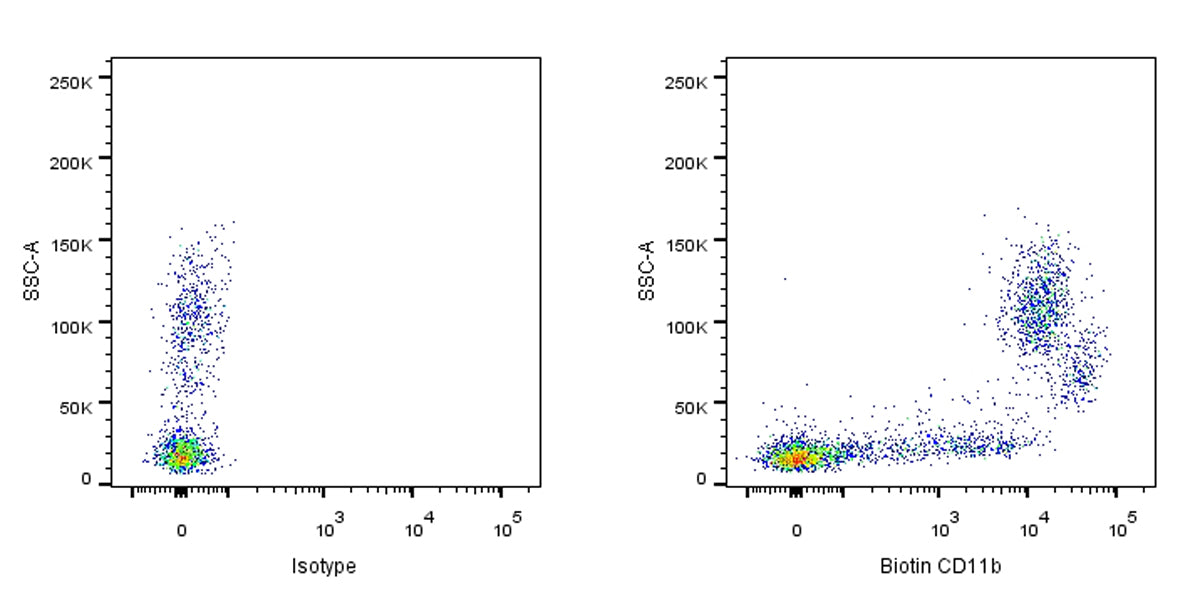
Flow cytometric analysis of CD11b expression on BALB/c mouse bone marrow. BALB/c mouse bone marrow was stained with Biotin Isotype Control (Left panel) or SDT Biotin Rat Anti-Mouse CD11b Antibody (Right panel) at 5μl/test followed by Sav-iFluor 488. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using BD FACSymphony™ A1 and FlowJo™ software.
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Host | Rat |
| Antigen | Mouse CD11b |
| Synonyms | Integrin alpha-M; CD11 antigen-like family member B; CR-3 alpha chain; Cell surface glycoprotein MAC-1 subunit alpha; Leukocyte adhesion receptor MO1; Itgam |
| Location | Cell membrane |
| Accession | P05555 |
| Clone Number | S-R574 |
| Antibody Type | Rat mAb |
| Isotype | IgG2b,k |
| Application | FCM |
| Reactivity | Hu, Ms |
| Positive Sample | BALB/c mouse bone marrow |
| Purification | Protein G |
| Concentration | 20 μg/ml |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300 |
| Stability & Storage | 12 months from date of receipt / reconstitution, 2 to 8 °C as supplied |
Dilution
| application | dilution | species |
| FCM | 5μl per million cells in 100μl volume | Ms |
Background
CD11b, also known as integrin αM or Mac-1, is an important cell membrane protein belonging to the integrin family. It is primarily expressed on the surface of leukocytes such as macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, and NK cells. By binding to its ligands, including ICAMs (Intercellular Adhesion Molecules), CD11b participates in cell-cell adhesion and migration processes, which are crucial for the normal function of the immune system. The primary functions of CD11b include participation in inflammatory responses, bacterial phagocytosis, and immune cell migration. It plays a key role in immune cell recognition and inflammatory reactions. Additionally, CD11b is involved in antigen presentation and T-cell activation, contributing to immune regulation. Recent research has also revealed the significant role of CD11b in tumor immunology. For example, in breast cancer, immature CD11b-NK cells are associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. In myeloid cells, CD11b can promote their development into M1 macrophage subtypes that suppress tumor growth. However, tumors often inhibit the activity of CD11b, leading to the development of M2 macrophages, which actually resist T cells that play a crucial role in fighting disease and promote new blood vessel formation, allowing cancer to grow and spread.
Picture
Picture
FC
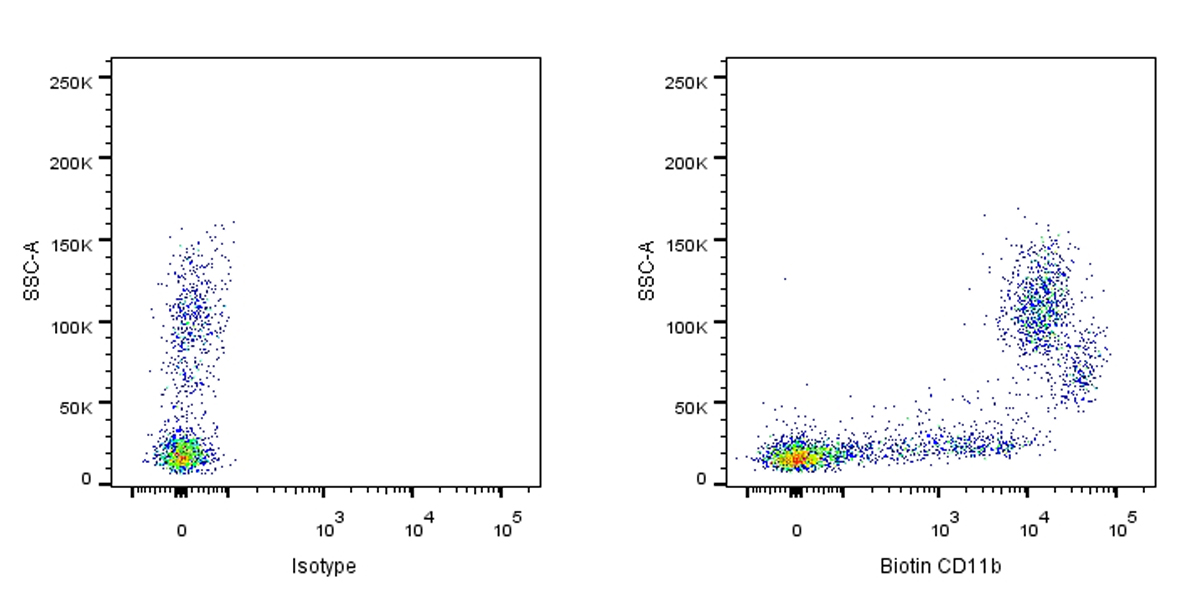
Flow cytometric analysis of CD11b expression on human peripheral blood cells. Human peripheral blood cells were stained with Biotin Isotype Control (Left panel) or SDT Biotin Rat Anti-Mouse CD11b Antibody (Right panel) at 5μl/test followed by Sav-PE. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using BD FACSymphony™ A1 and FlowJo™ software.