Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Human |
| Synonyms | Mucin1, MUC1, CD227, EMA, H23AG, KL6, MAM6, MUC1, ZD, PEM, PEMT, PUM, CA15-3 |
| Accession | P15941 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Ser116-Gly173, with C-terminal Human IgG1 Fc SVVVQLTLAFREGTINVHDVETQFNQYKTEAASRYNLTISDVSVSDVPFPFSAQSGAGIEGRMDPKSSDKTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVVDVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTISKAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSRDELTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLTVDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGK |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
| Molecular Weight | 36-42kDa |
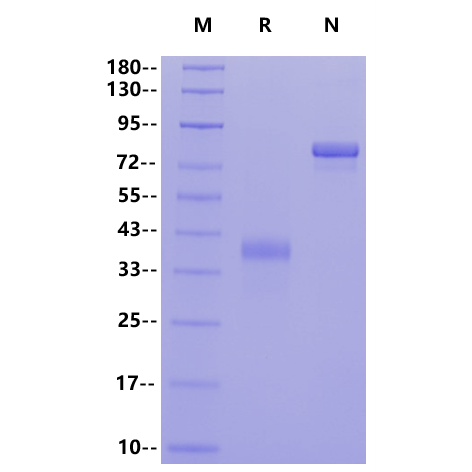
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | Human Fc Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference |
1、Brayman M. et al. (2004) MUC1: a multifunctional cell surface component of reproductive tissue epithelia. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2: 4. 2、Schroeder J A. et al. (2001) Transgenic MUC1 interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor and correlates with mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in the mouse mammary gland. J Biol Chem. 276(16): 13057-64. 3、Li Y. et al. (2001) The epidermal growth factor receptor regulates interaction of the human DF3/MUC1 carcinoma antigen with c-Src and beta-catenin. J Biol Chem. 276(38): 35239-42. |
Background
Mucin 1, cell surface-associated (MUC1) or polymorphic epithelial mucin (PEM) is a membrane-bound protein that is a member of the mucin family. Mucins are heavily glycosylated proteins that give the mucosa viscous gel-forming properties, and contribute to the structural organization of secretory epithelia. The mucosa serves as a physical barrier to protect the epithelium from harsh environments such as low pH and microbial infections. Cell surface associated mucins, such as Mucin-1 (Muc-1), are important components of the mucosal barrier that exist at the interface of the apical surface between secreted mucins and the cell surface. In addition to the mucus-type functions of its extracellular mucin domain, Muc-1 is a transmembrane protein with a cytoplasmic tail that is a known target of multiple kinases that has been shown to participate in normal and oncogenic signaling.Muc-1 is overexpressed and aberrantly glycosylated in many cancers, where it has been documented to play an important role in inflammation and tumor progression.Muc-1 is also expressed on many non-epithelial cell types including leukocytes, where its function is less well characterized. It has been documented that Muc-1 controls inflammation resulting from Helicobacter pylori infection by suppressing activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Knockout of Muc-1 also results in aberrant expansion of myeloid derived suppressor cells from the bone marrow.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE
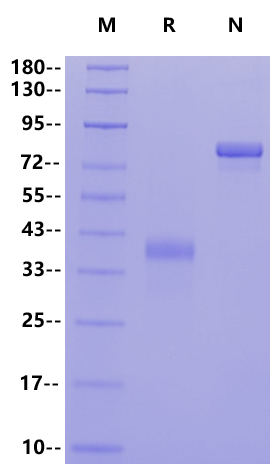
1μg (R: reducing conditions, N: non-reducing conditions).