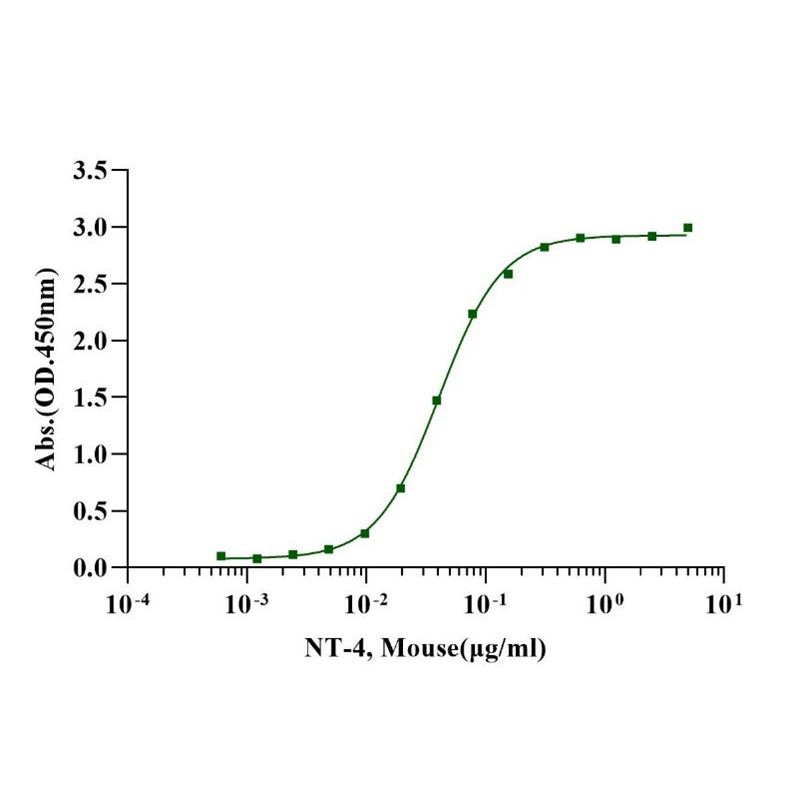
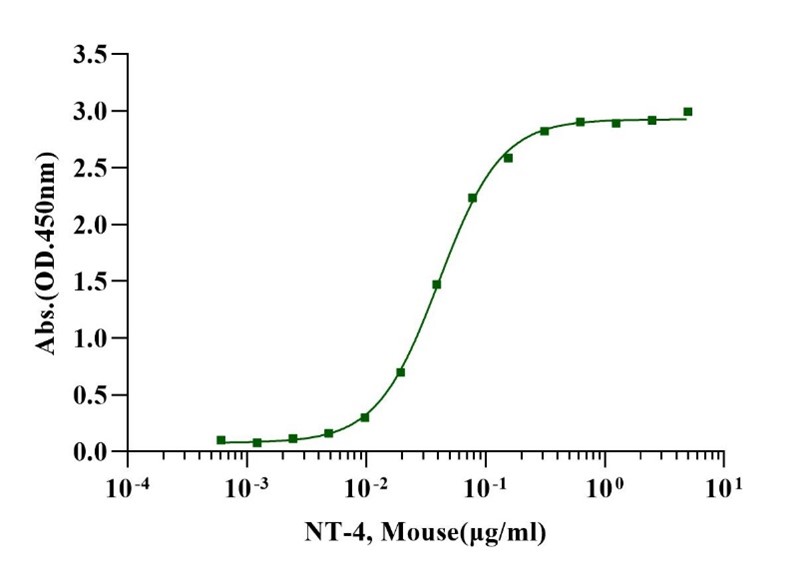
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Recombinant Mouse NT-4 is immobilized 2µg/mL (100 µl/well), Recombinant Human TrκB Fc binds with an EC50 of 0.03-0.04μg/ml.
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Mouse |
| Antigen | NT-4 |
| Synonyms | neurotrophic factor 4, neurotrophic factor 5, neurotrophin 4;Neurotrophin-4 |
| Accession | Q80VU4 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Gly80-Ala209 |
| Expression System | E.coli |
| Molecular Weight | 16kDa |
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | No Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH8.0 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage |
· 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference | 1. Cheryl L Stucky 1, Jung-Bum Shin, Gary R Lewin. Neurotrophin-4: a survival factor for adult sensory neurons. Curr Biol. 2002 Aug 20;12(16):1401-4. |
Background
Neurotrophin 4 (NT-4) is a neurotrophic factor which supports the survival and outgrowth of sensory neurons from embryonic chicken dorsal root ganglia, but has no significant effect on embryonic day 8 sympathetic ganglia1. It has a strong survival/proliferative action on NIH 3T3 cells expressing trkB but little activity on 3T3 cells expressing trkA. NT-4 was originally identified in Xenopus and viper, and was subsequently identified in rat and humans. Neurotrophin 4 is the least studied member of the neurotrophin family. Genetic knockout of NT4 does not result in loss of any DRG sensory neurons, although this factor does influence survival of spinal motor neurons. NT4 is expressed in muscle, and its expression is regulated by activity of innervating motor neurons, which increase its production, thereby providing trophic support to those innervating neurons. This provides an excellent example of bidirectional communication between the target and the afferent neurons, in which the activity of the innervating neurons and the release of trophic factor from the target influence each other to fine-tune the synaptic connections.
Picture
Picture
Bioactivity
SDS-PAGE
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).