Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Host | Rabbit |
| Antigen | Tau (phospho T217) |
| Synonyms | P-tau217, Phospho-tau217 |
| Immunogen | Synthetic Peptide |
| Clone Number | SDT-176-213 |
| Antibody Type | Recombinant mAb |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Application | CLIA, Sandwich ELISA |
| Reactivity | Hu |
| Predicted Reactivity | Mouse |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross-reactivity against Total tau, P-tau181, P-tau212, P-tau205. |
| Purification | Protein A |
| Concentration | 2 mg/ml |
| Purity | >95% by HPLC |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | PBS pH7.4, 0.03% Proclin 300 |
| Stability & Storage | 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied |
Background
Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease that detect beta-amyloid (Aβ) and phosphorylated tau (pTau) proteinopathy are rapidly developing. The utility and convenience of an accurate blood test has clear implications for accelerating and improving clinical research and practice. Several candidate markers exist including mass spectrometry and immunoassay measured Aβ42 and Aβ40 and their ratio and phosphorylated tau at threonine 217 (pTau217), 181 (pTau181), and other phosphorylated sites, as well as non-specific markers of neurodegeneration and astrogliosis, including neurofilament light (NfL) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Tau is a microtubule-associated protein important for neuronal stability. One of the major neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein which is thought to lead to pathological tau spread and neuronal death. Recent, research studies have shown that plasma levels of p-Tau 217 are elevated in AD patients. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that plasma p-Tau 217 levels are increased in the early stages of the AD continuum and are correlated with amyloid-PET positivity. These findings suggest that p-Tau 217 may serve as a promising blood-based biomarker to aid in AD research, drug development, diagnosis, disease monitoring and patient care. Recently, interest has turned to pTau217, as cerebrospinal fluid levels increase early in autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease and better discriminate Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s subgroups of cognitively impaired adults, compared to pTau181. In plasma, pTau217 accurately differentiates persons with neuropathologically defined Alzheimer’s disease from other dementia. Further, in vivo plasma pTau217 levels correlate with ex vivo protein levels and spatial burden in post-mortem brain tissue. Next, plasma pTau217 levels discriminate diagnostic groups informed by amyloid PET. pTau217 levels are elevated among impaired (Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment (MCI)) Aβ+ participants compared to cognitively unimpaired (CU) Aβ− participants, and plasma pTau217 and tau PET signal show moderate to high agreement. Serial plasma pTau217 levels also differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from non-Alzheimer’s MCI, remaining stable and non-elevated in Aβ− patients and increasing over time in Aβ+ patients. These findings suggest that p-Tau 217 may serve as a promising blood-based biomarker to aid in AD research, drug development, diagnosis, disease monitoring and patient care.
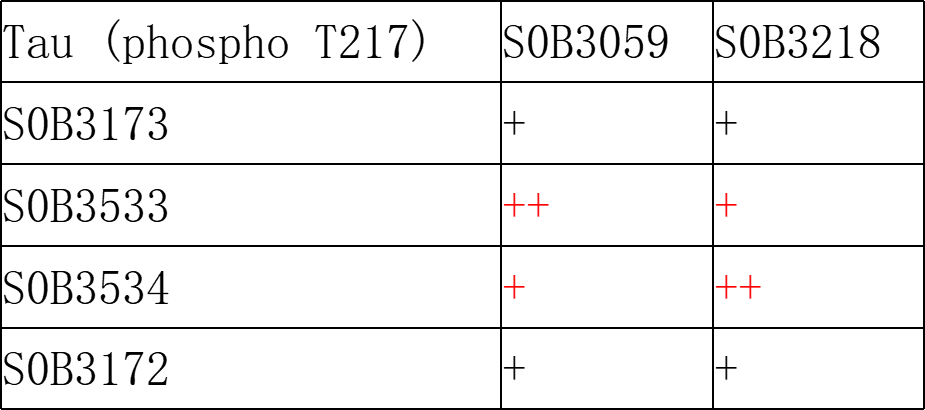
Picture
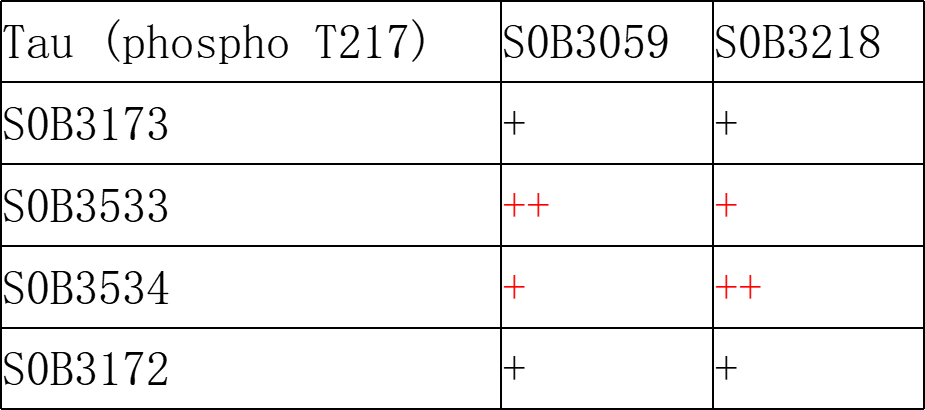
Picture
Paired Recommendations