Recombinant UAF1&USP1 Complex His&Flag Tag Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010009) is a Ubiquitin-specific deconjugating enzyme heterodimer. Reaction conditions will need to be optimized for each specific application. We recommend an initial Recombinant Human USP1/UAF1 complex concentration of 0.05-0.2 μM.
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Human |
| Synonyms | UAF1&USP1 Complex |
| Accession | O94782、Q8TAF3 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | O94782:Pro2-Leu785(G670A, G671A) with Flag at N-Terminus |
| Expression System | Baculovirus-InsectCells |
| Molecular Weight | 80(UAF1)&110kDa(USP1)(Reducing) |
| Purity | >90% by SDS-PAGE |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag, Flag Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer | 50 mM Hepes,150mM NaCl,2mM TCEP,5%Glycerol, pH7.5. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. |
| Reference | 1. iScience. 2024 Mar 11;27(4):109456. |
Background
Multiple deubiquitinating enzymes have been implicated in spermiogenesis, but the effects of deubiquitination on this process are not well understood. UAF1 is essential for spermiogenesis and male fertility, regulating this process through the deubiquitinating enzyme USP1. USP1 controls the cellular levels of Ub-FANCD2, a key protein in the Fanconi anemia DNA repair pathway.
In vitro studies using ubiquitin-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (Ub-AMC) or purified monoubiquitinated FANCD2 protein as substrates demonstrate that UAF1 activates USP1. While UAF1 binding increases the catalytic turnover of USP1, it does not enhance the enzyme's affinity for the substrate. DNA damage leads to an immediate cessation of USP1 gene transcription, resulting in a rapid decline in the USP1/UAF1 protein complex.
Picture
Picture
Bioactivity
SDS-PAGE
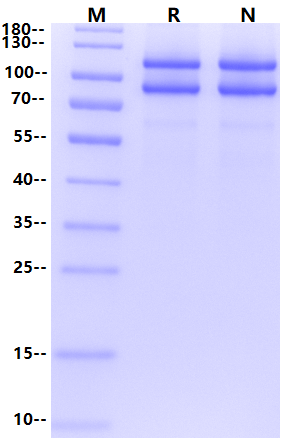
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).