Quality Optimization of Immune Cell Culture Strategy (5)

overview
There are six basic processes for immune cell culture: sample preparation, cell sorting, typing identification, expansion & culture, quality optimization, and follow-up studies. Xiaoai has given you a detailed introduction to the "Immune Cell Culture Strategy - Sample Preparation (1)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy - Cell Sorting (2)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy - Typing and Identification (3)", "Immune Cell Culture Strategy: Expansion & Culture (4)" Today, we continue to learn the relevant knowledge of quality optimization together.
Quality Optimization: For some undesirable factors, such as cell clumps and debris generated when the sample is prepared into a single-cell suspension; The effects of mycoplasma and endotoxin during cell expansion culture, and actively take corresponding measures.
Quality optimization
Mycoplasma is a prokaryotic cell-type microorganism that is intermediate between bacteria and viruses and has no cell wall.
1. Morphological characteristics
Mycoplasma is small in size, 0.1-0.3 μm, cannot be observed by light microscopy, cannot be filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, and conventional antibiotics are generally ineffective against mycoplasma. Mycoplasma can parasitize/symbiosis/independently survive in culture medium, and 98% adsorb to cell membranes or intercellular spaces.
2. Pollution sources
1) Cross-contamination of mycoplasma-positive cells, and because mycoplasma can be vertically infected, once the cells are contaminated, the next generation of cells will also have mycoplasma contamination;
2) The oral cavity and saliva of the experimental operators, and the operating habits of the experimental personnel, such as cross-use of culture medium and insufficient protection, will also become the source of mycoplasma contamination;
3) Incubation conditions, such as the operating environment, inadequate cleaning or sterilization of culture instruments and consumables, will also increase the risk of mycoplasma contamination.
3. Impact on cell research
1) Inhibition of cell growth and metabolism, causing death: In general, mild mycoplasma contamination has no obvious effect on the growth of cells, but due to the consumption of nutrients in the culture medium, the growth of cells will be slowed down, and mycoplasma may also inhibit key metabolic pathways by infecting cells and using their biosynthesis mechanisms, which will eventually lead to cell growth retardation and death;
2) Chromosomal aberration, destruction of nucleic acid synthesis, DNA fragmentation: mycoplasma may interact with cellular nucleic acids to trigger chromosomal structural variation, affect DNA synthesis and maintain chromosome integrity, such as mycoplasma infection can mimic shRNA-mediated p53 knockout, allowing Ras transformation, thereby inactivating the function of p53;
3) alteration of cell membrane antigenicity: mycoplasma affects cellular pathways involved in inflammation and cell transformation, such as mycoplasma's proteins interact with TLRs or enter cells, thereby altering several pathways responsible for inflammation and DNA repair;
4) Alter transfection efficiency: Mycoplasma may slow down or interfere with DNA transfection efficiency by affecting gene transport and expression mechanisms in cells;
5) Increased sensitivity to apoptosis inducers: Mycoplasma can regulate key molecules in the apoptosis pathway through certain proteins, increasing the sensitivity of cells to apoptosis inducers, such as the interaction between NAE and mycoplasma enzyme MGA-0676, which induces apoptosis in DF-1 cells.
4. Prevention of mycoplasma
Mycoplasma pollution prevention and control is also very important, for example: mycoplasma detection is carried out daily for 1-2 weeks, and mycoplasma detection should be carried out for newly arrived cell lines, before cryopreservation, and before the start of important experiments. 10 tips for mycoplasma prevention that you can save and learn:
1) Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (gloves, special clean lab coats, goggles) and disinfect gloves;
2) Wipe down the work table in the safety cabinet before the start of cell processing and between handling different cell lines;
3) Avoid talking or sneezing on your cells;
4) Avoid splashes, spills and aerosols;
5) Use the designated media bottle for each cell line;
6) Clean the incubator regularly, including the water tray;
7) Empty and clean the bath equipment regularly;
8) test new cell cultures for mycoplasma contamination a few days after cell thawing;
9) isolate all cell cultures entering the laboratory until they are tested for mycoplasma;
10) Don't forget to get routinely tested for mycoplasma every 2 weeks.
Table 1 Reagents for the prevention of mycoplasma contamination
|
Catalog number |
name |
specification |
characteristic |
|
abs9376 |
Mycoplasma prophylaxis |
500uL |
Mycoplasma prophylactic agent (domestic cost-effective) |
5. Detection methods for mycoplasma
There are also many detection methods for mycoplasma, and Xiaoai also sorted out the principles, advantages and disadvantages of each method (table below).
Table 2 Comparison of mycoplasma detection methods
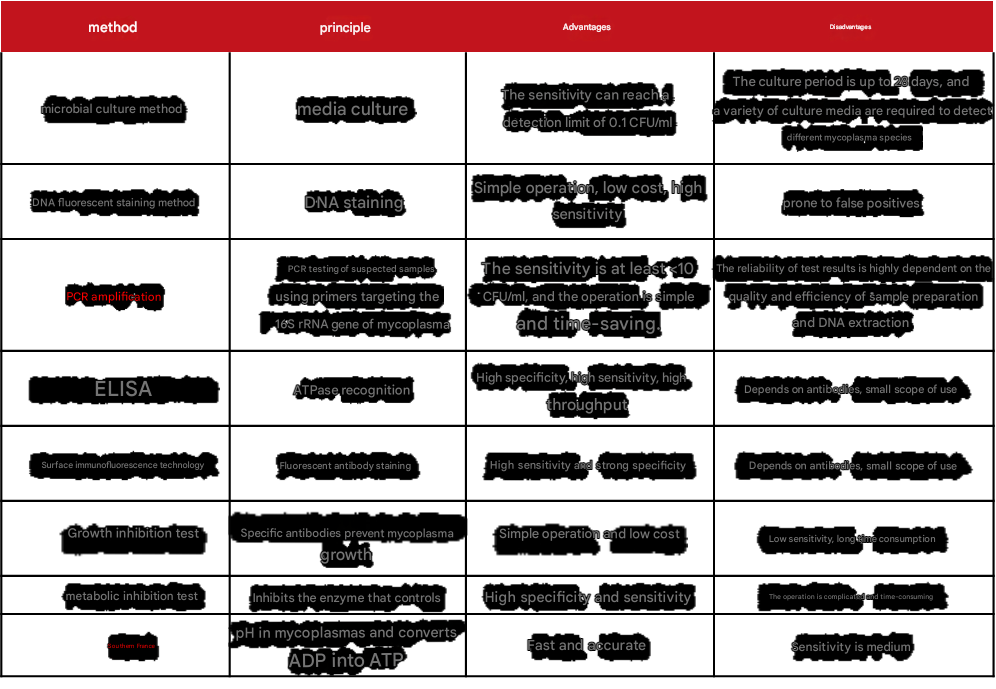
Table 3 Mycoplasma detection test kit
|
Catalog number |
name |
specification |
characteristic |
|
abs9252 |
Mycoplasma staining detection kit |
100T |
It's quick and easy |
|
abs9588 |
Mycoplasma test kit (PCR method) |
50T |
Strong specificity and high sensitivity |
6. Removal of mycoplasma
The most effective method of mycoplasma removal is the use of mycoplasma scavengers, but other methods such as wash and purification (using centrifugal force, poor buoyancy of cells, microbial mass, and suspension) or mycoplasma-specific serum can also be tried.
Table 4 Mycoplasma removal reagents
|
Catalog number |
Product name |
specification |
|
abs9254 |
Mycoplasma Clearance Reagent Plus |
10mg |
endotoxin
Endotoxin is a component in the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria, and its chemical nature is a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in EU/mg or EU/U. One EU is equivalent to approximately 0.1 to 0.2 ng of endotoxin/mL solution. Endotoxins are only released when the bacteria die, dissolve, or are destroyed by artificial means.
1. Features
Endotoxins are very heat-resistant, and their biological activity can only be destroyed by heating at 160 °C for 2-4h, or by heating and boiling with a strong alkali / strong acid / strong oxidant for 30 min.
2. Pollution sources
1) Water for preparing various reagents and buffers;
2) "Mixing" in various media, serum, and additives;
3) Surfaces such as plastic utensils and glassware.
3. Impact on cells
1) Cell function changes: endotoxin can stimulate some cells to secrete inflammatory factors, resulting in local inflammatory responses, such as endotoxin treatment as low as 0.5ng/mL for 6 hours can increase the secretion of IL-6 in equine peritoneal macrophages;
2) Cause cell sub-health: Endotoxins can accelerate cell senescence, apoptosis, and even death;
3) Activated cells: In the presence of monocytes, 100ng/mL endotoxin can stimulate the proliferation of human T cells and the production of lymphokines;
4) Reduced transfection efficiency of eukaryotic cell lines: Endotoxins in purified plasmid DNA can reduce transfection efficiency and viability in all cell lines, and endotoxin content (>10EU/μg) can negatively affect transfection, protein expression, and viability in standard cell lines.
4. Prevention of endotoxin
1) Select high-quality/low-endotoxin media, serum and reagent consumables, in the process of cultivating immune cells, you can choose serum-free medium for immune cells, if you choose the classic culture system, you should choose low-endotoxin serum and basal medium; At the same time, the growth factors added in the process of immune cell culture should also be of high quality and low endotoxin;
2) Reused experimental consumables can be processed with high temperature and high pressure: 250°C, 30min, or 180°C, 3h;
3) The water quality of cell culture is also very important, enzyme-free sterile water (ABS9259) can meet the daily dosage of 15mL pure water/ultrapure water in the laboratory, caring for every cell baby;
4) In addition, some buffers prepared by themselves during the culture process can be filtered and sterilized, so that potential endotoxins can be eliminated before being added to cells.
Table 5 Related products
for endotoxin prevention
| Catalog number | name | specification | characteristic |
| abs972 | Fetal bovine serum (Premium) | 500mL | It is used for refractory and precious cells such as primary cells and stem cells |
| abs9772 | Serum-free medium for immune cells | 1L | Contains gentamicin, phenol red |
| abs9823 | Human T cell expansion medium | 1kit | |
| abs9824 | Human Natural Killer Cell (NK) Amplification Kit | 1kit | |
| abs9259 | Enzyme-free sterile water | 500mL | sterile, ultra-pure deionized water; No nuclease and protease activity |
5. Detection of endotoxin
Xiao Ai also sorted out the principles, advantages and disadvantages of each endotoxin detection method (Table 6). The commonly used methods are the horseshoe crab reagent method and the recombinant C-factor method, which can no longer be used on a large scale because it is a national second-class protected animal. Therefore, we recommend that you use the recombinant factor C (rFC) method to detect endotoxin.
Table 6 Methods for the detection of endotoxins

6. Endotoxin removal
There is no effective way to remove endotoxins in cell culture for the time being, so Xiaoai recommends that everyone do a good job of prevention, after all, prevention is better than cure!
That's all for today's explanation, and we'll see you for the next quality optimization! If you have any questions about cell culture, please join the group to communicate!
This issue is recommended by Xiaoai
|
Catalog number |
Product name |
specification |
|
abs9376 |
Mycoplasma prophylaxis |
500uL |
|
abs9252 |
Mycoplasma staining detection kit |
100T |
|
abs9588 |
Mycoplasma test kit (PCR method) |
50T |
|
abs9254 |
Mycoplasma Clearance Reagent Plus |
10mg |
|
Fetal bovine serum (Premium) |
500mL |
|
|
abs9772 |
Serum-free medium for immune cells |
1L |
|
abs9823 |
Human T cell expansion medium |
1kit |
|
abs9824 |
Human Natural Killer Cell (NK) Amplification Kit |
1kit |
|
Enzyme-free sterile water |
500mL |
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |




