Chip-seq+ multi-color Absin power! To explore the underlying mechanism of p53 regulating the tumor immune microenvironment
As the most common genetic alteration in cancer, more than half of all human cancers have p53 mutations, resulting in transcriptional inactivation. However, it is still elusive how p53 regulates the "immune landscape" and creates powerful conditions for immune escape. In this study, it was found that cancer stem cells (CSCs) establish an interleukin-34 (IL-34) coordinated niche to promote tumorigenesis and progression of p53-deficient liver cancer. Mechanistically, IL-34 was found to be a gene that was transcriptionally repressed by p53, and p53 deletion led to the secretion of IL-34 by CSCs. IL-34 induces elevated CD36-mediated fatty acid oxidative metabolism, thereby driving M2-like polarization of foam-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). These IL-34-coordinated TAMs inhibit CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity to promote immune escape. Blockade of the IL-34-CD36 axis can elicit anti-tumor immunity and synergize with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, resulting in a complete response. The results of this study reveal the underlying mechanism by which p53 regulates the tumor immune microenvironment and provide a potential target for p53-inactivated cancer immunotherapy.

Article: Interleukin-34-orchestrated tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming is required for tumor immune escape driven by p53 inactivation IF=25.5
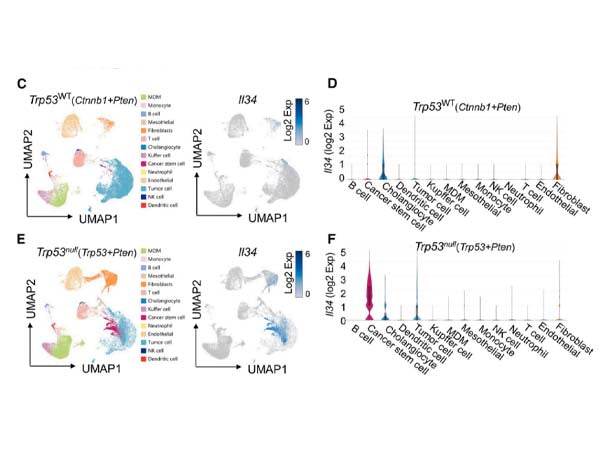
RNA sequencing was performed on Trp53WT and Trp53-deletion tumors, combined with q-PCR, ELISA and immunoblotting results, it was found that the expression of IL-34 by CSCs in Trp53-deletion tumor samples was significantly increased, multiplex immunohistochemical staining showed that IL-34 and EpCAM co-localized in Trp53-deletion tumors, and EpCAM+ CD47+ CSCs did not express p21 in Trp53-deletion tumors. Together, these results suggest that p53-inactivated CSCs are the predominant cellular subset that secretes IL-34.


Fig.1 Abnormally high secretion of IL-34 by CSCs inactivated by p53 promotes the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
In order to verify the hypothesis that p53 may inhibit IL34 transcription, p53 was confirmed to directly inhibit IL34 transcription using a combination of ChIP-seq(K) + ChIP-qPCR(L) + DNA pull down (M) using the abs50034 chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) kit!

Fig.2 ChIP-seq(K)+ChIP-qPCR(L)+DNA pull down(M)
(K) Chromosome view plot showing the binding of p53 at the promoters of IL34 and CDKN1A (p21; positive control).
(L) Chromatin immunoprecipitation of HepG2 cells with control antibody IgG or anti-p53 or anti-RNA polymerase II, followed by PCR with IL34 promoter primers.
(M) Pull-down pellet of biotinylated and non-biotinylated IL34 promoter probes (with HepG2 cell extracts) for western blotting
Considering that IL-34 is a cytokine involved in the proliferation, survival and differentiation of monocytes into macrophages, the researchers used CIBERSORT to study the composition of liver tumor immune 4 cells, and found that the expression of IL-34 was positively correlated with the proportion of macrophages. Spatial transcriptome sequencing and multiplex immunohistochemistry showed that most of the tams in Trp53null tumors were monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs), and further studies found that in trp53-deleted tumors, tam accumulated near IL-34-secreting CSCs, gene set enrichment analysis showed that tam from Trp53null tumors was enriched on lipid droplet characteristics, and BODIPY fatty acid probe staining for tam showed that TAM in TRP53-deletion tumors resembles foam-like macrophages, and differential gene analysis showed an increased proportion of CD206+ and CD163+ macrophages in TRP53null tumors, and these results together suggest that TAM accumulating in the vicinity of CSCs exhibits a lipid-loaded pro-tumor phenotype. After Trp53 or Trp53 co-cultured with bone marrow-derived macrophages, IL-34 promoted lipid accumulation and pro-tumor polarization of TAM in Trp53null tumors.+/+-/-

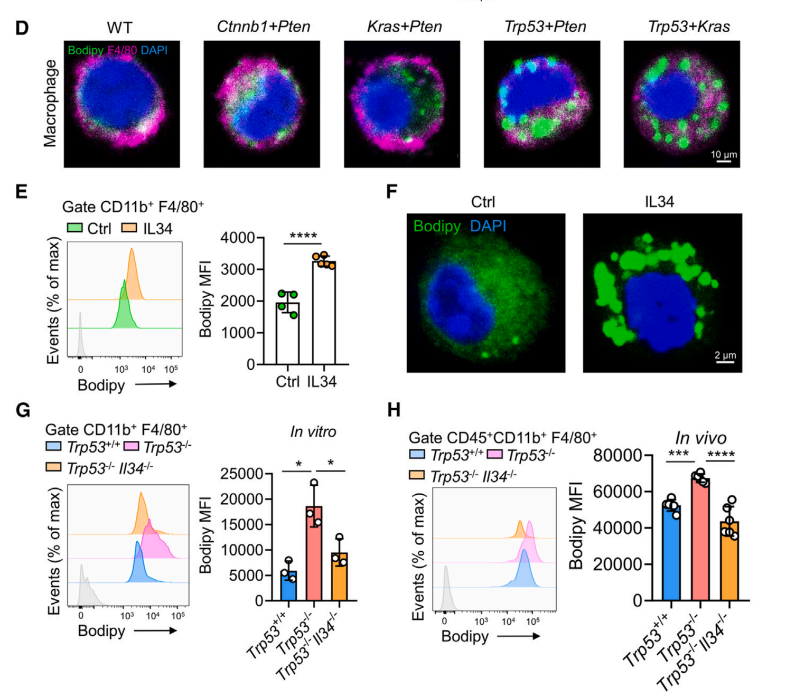
Fig.3 IL-34 induces foam-like tam near p53-inactivated CSCs
In the following experiments, the researchers demonstrated that IL-34 promotes fatty acid uptake through CD36 and induces pro-tumor polarization of macrophages through FAO metabolic reprogramming, and in order to provide direct evidence that the IL-34-CD36 axis promotes TAM lipid accumulation and m2-like macrophage polarization in vivo, the researchers inoculated Il34-overexpressing CT cells (Trp53+/+) and Il34 knockout PT cells into mice. It was found that the proportion of tam in Il34-overexpressing tumors was higher than that in CT tumors, systemic depletion of macrophages by injection of clodronate liposomes, tumor growth differences between IL-34-deficient PT tumors and control PT tumors were eliminated, and flow cytometry and co-culture experiments showed that IL-34-CD36 axis-coordinated TAM promoted tumor immune escape by inhibiting T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity in Trp53null hepatocellular carcinoma.
In subsequent mouse experiments, it was found that in mice treated with neutralizing antibodies against IL-34 or CD36 in Trp53/PT tumor mice, antibody blockade of IL-34 or CD36 resulted in significant limitation of tumor growth, and analysis of common single-cell RNA-seq data from TP53-mutated HCC showed that tumor cells were highly expressed IL34 and TAM exhibited strong CD36 expression, while its expression was weak in all other cell types. In conclusion, the results suggest that blocking IL-34 signaling may be a potential immunotherapy for TP53-mutated cancer patients.

Fig.4 Blocking IL-34 signaling inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and leads to p53 inactivation
Recommended products
|
Catalog number |
Product name |
specification |
|
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) kit |
22T |
|
|
DNA Pull Down Kit(Animal) |
6T |
|
|
Four-color multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemical staining kit (pika universal secondary antibody) |
20T/100T |
|
|
BODIPY 493/503 |
25mg |
|
|
Invivo anti-Mouse PD-1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody(R071) |
25mg |
|
|
FITC Rat anti-Mouse F4/80 Antibody(BM8) |
100T |
|
|
PE Mouse anti-Human CD206 Antibody(15-2) |
100T |
|
|
FITC Mouse anti-Human IFN-γ Antibody(GAMMA3-11.1) |
100T |
|
|
More...... |
||
Absin provides antibodies, proteins, ELISA kits, cell culture, detection kits, and other research reagents. If you have any product needs, please contact us.
|
Absin Bioscience Inc. Email: worldwide@absin.net |
 Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio Follow us on Facebook: Absin Bio |




