Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | African Swine Fever |
| Synonyms | pE183L |
| Accession | Q65194 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Protein sequence(Q65194 Ser54-Leu183, with C-10*His) |
| Expression System | E.coli |
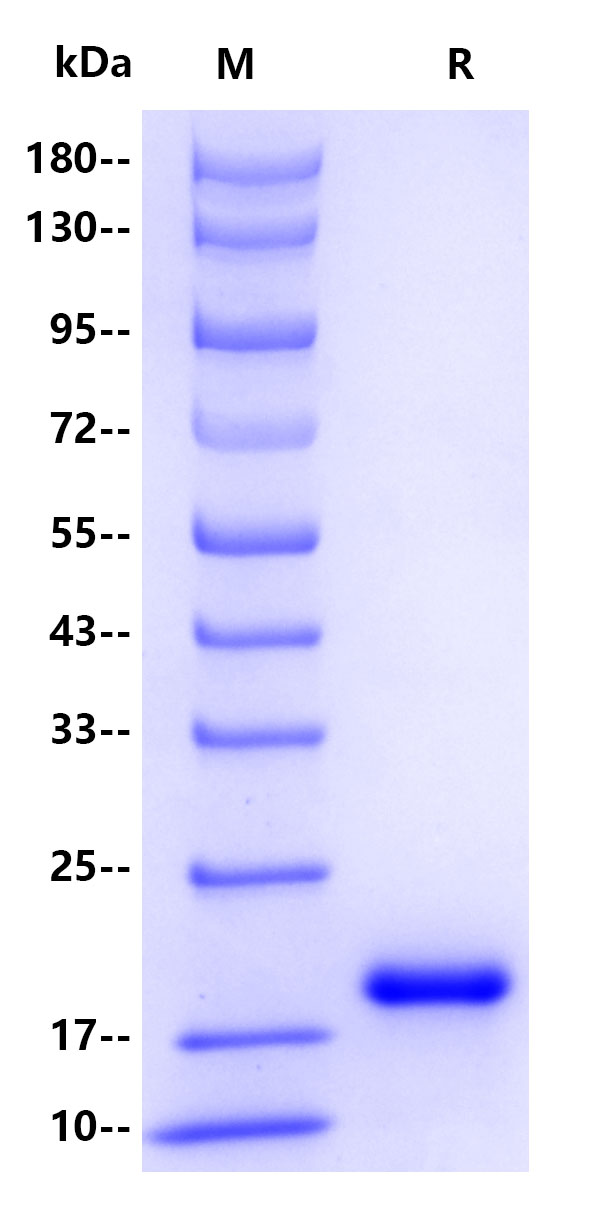
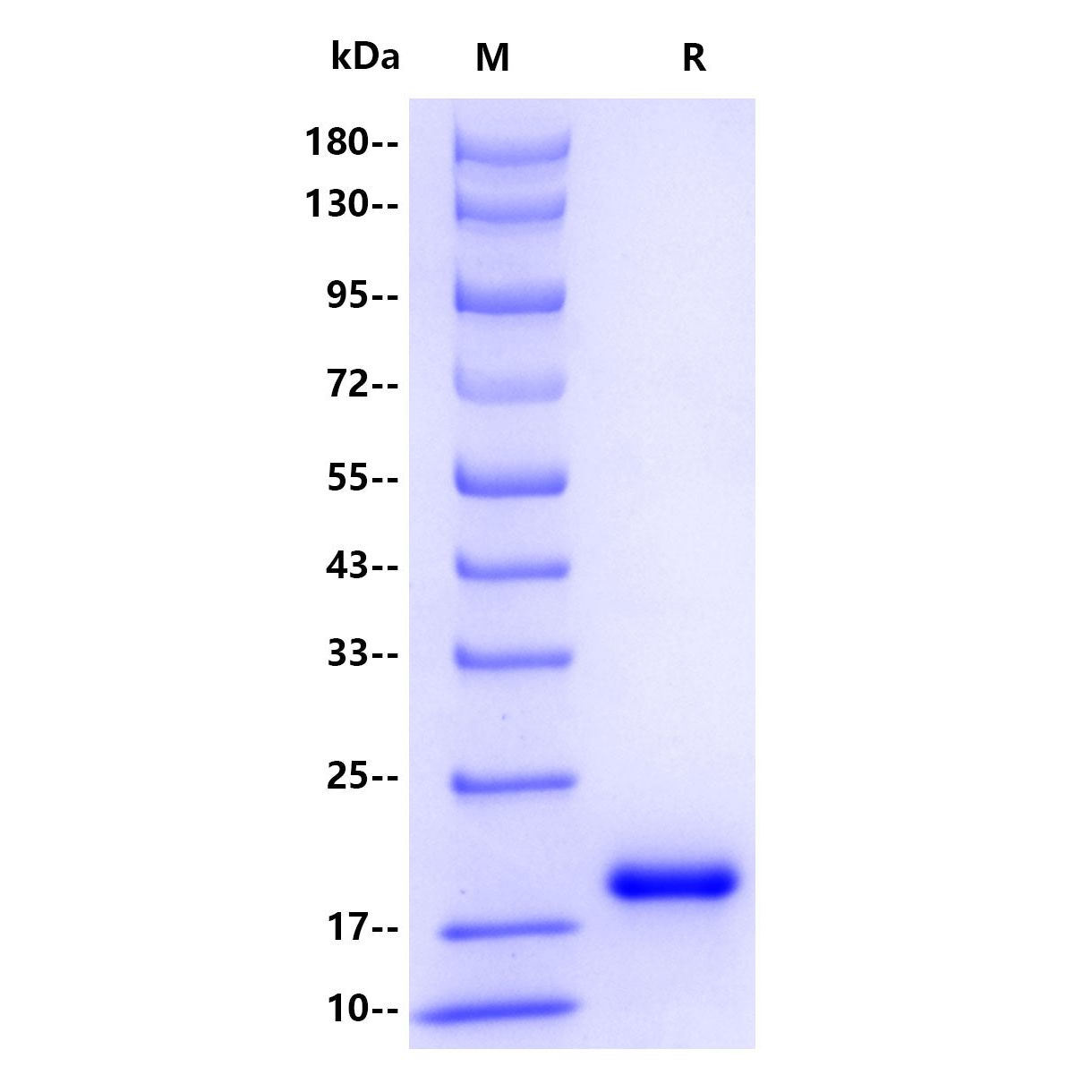
| Molecular Weight | Theoretical:15.5kDa Actual: 20kDa |
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 0.2M PBS, 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, pH7.4. Normally trehalose is added as protectant before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute no more than 1mg/mL according to the size in deionized water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. |
Background
African swine fever (ASF) is a highly lethal hemorrhagic viral disease of swine that usually results to a mortality rate approaching 100% in domestic pigs and is classified as a notifiable disease by the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE). A number of studies have reported that p54 is one of the most important ASFV proteins and plays a key role in virus morphogenesis and viral infection. Anti-p54 sera were found to inhibit ASFV attachment to susceptible cells, suggesting its role in virus entry. Similarly, p54/E183L gene plays an essential role in virus viability and recruitment of envelop precursors to assembly sites. Most importantly, E183L gene is crucial for virus particle transporting to perinuclear factory via direct binding to light chain 8 (LC8) of the dynein. A short p54 peptide (149–161 aa) near to its C-terminus is enough to bind to dynein light chain 8 (DLC8) and act as a cargo transport for virus particle.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE