Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Usage |
Need to bring your own test equipment 1. Microplate reader (can measure the absorption value of 450nm detection wavelength and the absorption value of 540nm or 570nm correction wavelength) 2. High-precision liquid dispenser and disposable tip 3. Distilled water or deionized water 4. Bottle washing (spray bottle), multi-channel plate washer or automatic plate washer 5. 500mL measuring cylinder 1. Preparation before the experiment 1. Sample collection and storage ① Cell culture supernatant: particulate matter should be removed by centrifugation; Test the sample immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator at-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). ② Serum: Use a serum separation tube (SST) to collect samples, and place the samples at room temperature for 30 minutes. Centrifuge for 15 minutes at a rotation speed of 1000 g. The serum was removed immediately and tested immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator ≤-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). ③ Plasma: Plasma was collected using EDTA, heparin or citric acid as anticoagulant, centrifuged for 15 minutes within 30 minutes after collection, rotated at 1000g, and detected immediately. If the sample is not tested in time after collection, it is recommended to pack it according to the one-time usage amount and store it in a refrigerator ≤-20 ℃ to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. Samples may need to be diluted with diluent (1 ×). 2. Reagent preparation (Please place all reagents and samples at room temperature before use and let them stand15Minutes. All experimental samples and standards are recommendedDo repeat hole detection) ① Preparation of 1 × washing liquid: The concentrated washing liquid in the kit is 20 × mother liquid, which needs to be diluted into 1 × working liquid with distilled water before use.Example:Take 10mL of concentrated washing solution + 190mL of distilled water and make the volume to 200mL. In actual operation, the amount used can be calculated first, and then prepared. ② Preparation of 1 × dilution buffer: The concentration and dilution buffer in the kit is 10 × mother liquor, which should be diluted to 1 × working solution with distilled water before use.Example:Make up to 30 mL with 3 mL of concentration and dilution buffer + 27 mL of distilled water. In actual operation, the required amount of dilution buffer solution can be calculated according to the sample dilution factor, and then prepared. ③ Antibody detection: centrifuge the dry powder to the bottom of the tube, dissolve it with 110uL dilution buffer (1 ×), and let it stand at room temperature for 5 minutes to obtain 100 × mother liquor; Dilute to 1 × working solution before use. Calculate the required volume according to the dosage of 100uL per well.Example:After 10 wells were used, 10 uL of the detection antibody having a working concentration of 100 times was taken, and the volume was diluted to 1 mL using a dilution buffer (1 ×) to obtain 1 mL of the detection antibody having a working concentration of 1 ×. ④ SA-HRP: SA-HRP is 40 × mother liquor, which needs to be diluted with dilution buffer (1 ×) before use to prepare 1 × working solution, and the required amount per well is 100uL.Example:After 10 wells were used, 25 uL of 40 × mother liquor + 975 uL of dilution buffer (1 ×) was diluted to 1 mL to obtain 1 mL of detection antibody having a 1 × working concentration. ⑤ Color development solution: According to 100uL per well, calculate the dosage required for the current test, take out the corresponding volume of color development solution, and protect it from light; The chromogenic solution removed is for the same day only. ⑥ Standard: The freeze-dried standard is re-dissolved with dilution buffer (1 ×), and the re-dissolving volume is 1000uL to obtain the standard mother liquor with a concentration of 1200pg/mL. Gently shake for at least 5 minutes and it dissolves well. 300 uL of dilution buffer (1 ×) was added to each dilution tube. Make serial dilutions of the standard mother liquor according to the figure below (3 times dilution), and each tube must be thoroughly mixed before pipetting to the next tube. The standard mother solution without dilution can be used as the highest point of the standard curve (1200 pg/mL), and the dilution buffer (1 ×) can be used as the zero point of the standard curve (0 pg/mL).  2. Operation steps 1. Prepare all required reagents and standards; 2. Take out the microplate from the sealed bag that has been balanced to room temperature. Please put the unused slats back into the aluminum foil bag and reseal them; 3. Add 300uL of washing liquid to the microplate, let it stand and soak for 30 seconds, discard the washing liquid and pat the microplate dry on absorbent paper. Please use it immediately and do not let the microplate dry; 4. Add different concentration standards, experimental samples or quality control products to the corresponding wells, 100uL per well. Sealing the reaction hole with plate sealing adhesive paper and incubating at room temperature for 2 hours; 5. Suck off the liquid in the plate and wash the plate with a bottle washer, a multi-channel plate washer or an automatic plate washer. 300 uL of washing solution was added to each well, and then the washing solution in the plate was aspirated off. Repeat the operation 3 times. Trying to absorb the residual liquid as much as possible every time you wash the plate will help to get good experimental results. At the end of the last plate washing, please suck all the liquid in the plate or turn the plate upside down, and pat all the residual liquid dry on absorbent paper; 6. Add 100 uL of detection antibody to each well. Seal the reaction wells with plate sealing tape and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours; 7. Repeat the plate washing operation in step 5; 8. Add 100 uL of SA-HRP to each well and incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. Be careful to avoid light; 9. Repeat the plate washing operation in step 5; 10. Add 100uL of chromogenic solution to each microwell, incubate at room temperature for 5-30 minutes, and avoid light; 11. Add 50uL of stop solution to each microwell, and the color of the solution in the well will change from blue to yellow. If the color of the solution changes to green or the color changes are inconsistent, pat the microplate gently to mix the solution evenly; 12. Within 30 minutes after adding the stop solution, measure the absorbance value of 450nm using a microplate reader, and set 540nm or 570nm as the calibration wavelength. If dual-wavelength correction is not used, the accuracy of the results may be affected; 13. Calculation Results: Average the corrected absorbance values (OD450-OD540/OD570), multiple well readings for each standard and sample, and then subtract the average zero standard OD value. Four-parameter logic (4-PL) curve fitting was performed using computer software to create the standard curve. Alternatively, a curve can be generated by plotting the logarithm of the standard concentration versus the logarithm of the corresponding OD value, and the best fit line can be determined by regression analysis. This process can generate a data fit that is sufficiently useful but less accurate. If the sample is diluted, the concentration should be calculated by multiplying the dilution factor. 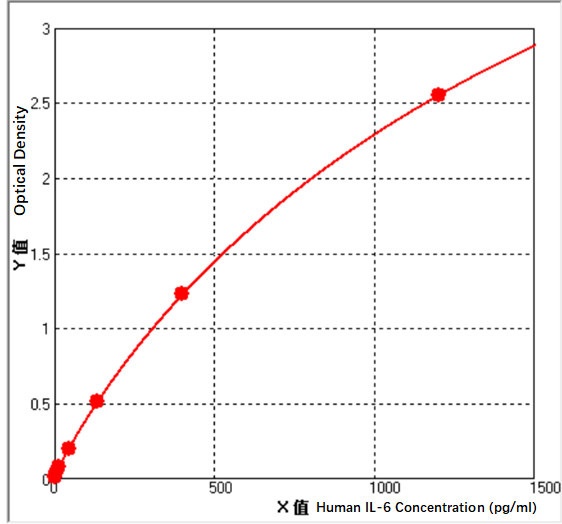 3. Kit parameters 1. Recovery rate: Different levels of human IL-6 were spiked into cell culture medium samples, and the recovery rate was determined. The recoveries ranged from 93 to 101%, with an average recovery of 98%. 2. Sensitivity: The lowest measurable dose (MDD) of human IL-6 is generally less than 1.56 pg/mL. The lowest measurable value is the corresponding concentration calculated from the mean of the zero-point absorbance values of 20 standard curves plus two standard deviations. 3. Linearity: 4 different samples were spiked with high concentrations of human IL-6, and then the samples were diluted to the detection range with diluent (1 ×) to determine their linearity.
4. Specificity: This ELISA method can detect natural and recombinant human IL-6 protein. The following factors were formulated with diluent (1 ×) at a concentration of 50 ng/mL to detect cross-reactivity with human IL-6. Interference with human IL-6 was detected by incorporating 50 ng/mL of the interfering factor into the mid-range recombinant human IL-6 control. No significant cross-reactivity or interference was observed.
4. Solutions to common problemsanalysis 1. Whiteboard (after the color development is completed, no color appears)
2. Flower plate (blank and negative positive controls are normal, but the OD value of specimen wells is obviously higher)
5. Experimental flow chart  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Theory | This kit adopts double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent detection technology. Specific anti-human IL-6 antibodies were pre-coated on high affinity plates. The standard substance, the sample to be tested and the biotinylated detection antibody are added to the well of the enzyme label plate, and after incubation, IL-6 present in the sample binds to the solid phase antibody and the detection antibody to form an immune complex. After washing to remove unbound material, horseradish peroxidase-labeled Streptavidin-HRP was added. After washing, a chromogenic substrate is added to protect the color from light. A stop solution was added to stop the reaction, and the absorbance value was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm (reference calibration wavelength of 540 nm or 570 nm). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Composition |
Please use within the expiration date of the kit
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Background | Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a multifunctional cytokine with α-helix structure, 22-28kDa phosphorylation and varying degrees of glycosylation. It plays an important role in the acute phase of disease response, inflammation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism and cancer exacerbation. Mature human IL-6 has 183 amino acids and 41% homology to mouse and rat IL-6. Alternative splicing within IL-6 produces a variety of isomers, some of which exhibit antagonistic properties. Cells known to express IL-6 include CD8 + T cells, fibroblasts, synoviocytes, adipocytes, osteoblasts, megakaryocytes, endothelial cells (under the influence of endotheliin), sympathetic neurons, cerebral cortical neurons, adrenal medullary chromaffin cells, retinal pigment cells, mast cells, keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, fetal and adult glial cells, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, colonic epithelial cells, B1B cells, and islet beta cells. IL-6 production is usually controlled by glucocorticoids, catecholamines, and secondary sex steroids, and is generally associated with cellular activation. IL-6 in normal human blood is in the range of 1 pg/mL, slightly increased during menstrual period, severely increased in the middle and late stages of some cancers, and significantly increased after major surgery. IL-6 elicits cellular signaling through a cell surface receptor, which is a heterodimeric complex consisting of a ligand-binding subunit (IL-6 receptor) and a signal-transferring subunit gp130. Binding of IL-6 to the IL-6 receptor triggers binding of the IL-6 receptor to gp130 and dimerization of gp130. gp130 is also a component of CLC, CNTF, CT-1, IL-11, IL-27, LIF, and OSM receptors. Soluble IL-6 receptors are produced by alternative splicing and protease cleavage. Through trans-signaling mechanisms, soluble IL-6 and IL-6 receptor complexes can elicit responses in cells that lack IL-6 receptors on their surface but express gp130. The expression of IL-6 receptor is mainly restricted to hepatocytes, monocytes, lymphocytes and resting lymphocytes. Since the gp130 molecule is very widely expressed, trans-signaling enables a wider range of cell types to respond to IL-6. The soluble gp130 spliceosome prevents trans-signaling of IL-6/IL-6R, but not signaling by other cytokines using the gp130 molecule as a co-receptor. Together with tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and IL-1, the acute inflammatory response caused by IL-6 plays an almost unique role in fever and acute inflammatory response of the liver. It also plays an important role in the transformation of acute inflammation to acquired immunity or chronic inflammatory diseases. IL-6 dysregulation can promote chronic inflammation, such as obesity, insulin resistance, inflammatory bowel disease, inflammatory arthritis, and sepsis, often involving trans-signaling of IL-6. In the presence of transforming growth factor TGF-β, IL-6 plays an important role in the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th17 inflammatory cells. IL-6 regulates bone resorption and is a major contributor to inflammatory joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis by promoting the activity of Th17 inflammatory cells. IL-6 is involved in the formation and instability of atherosclerotic plaques. However, IL-6 also has anti-inflammatory effects, such as skeletal muscle secretion of IL-6 during physical exercise. As a growth factor of hematopoietic stem cells, it promotes and induces B cells to mature into plasma cells and immortality of multiple myeloma cells. IL-6 also promotes, but may not initiate, other inflammation-related carcinogenesis, such as colitis-related cancers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Notes | 1. Please use the kit within the validity period. 2. The components of different kits and different batch kits cannot be mixed. 3. If the sample value is greater than the highest value of the standard curve, the sample should be diluted with diluent (1 ×) and re-tested; If the cell culture supernatant sample needs to be distributed and diluted, cell culture medium can be used for other intermediate dilutions except dilution with diluent in the last step. 4. Differences in test results can be caused by a variety of factors, including the operation of the experimenter, the use of the pipette, the plate washing technique, the reaction time or temperature, the storage of the kit, etc. 5. The terminating solution in the kit is an acidic solution. Please protect your glasses, hands, face and clothes when using it. 6. For scientific research only, not for in vitro diagnosis. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Storage Temp. | Kit unopened, stored at 2-8 ℃. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test Range | 1.65pg/mL-1200pg/mL |