Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Human |
| Synonyms | Epidermal growth factor receptor 5; EGFR-5; EGFR 5; EGFR5; C14orf27; |
| Accession | Q86T13 |
| Amino Acid Sequence |
Glu22-Ala397, with C-terminal 8*His EHPTADRAGCSASGACYSLHHATMKRQAAEEACILRGGALSTVRAGAELRAVLALLRAGPGPGGGSKDLLFWVALERRRSHCTLENEPLRGFSWLSSDPGGLESDTLQWVEEPQRSCTARRCAVLQATGGVEPAGWKEMRCHLRANGYLCKYQFEVLCPAPRPGAASNLSYRAPFQLHSAALDFSPPGTEVSALCRGQLPISVTCIADEIGARWDKLSGDVLCPCPGRYLRAGKCAELPNCLDDLGGFACECATGFELGKDGRSCVTSGEGQPTLGGTGVPTRRPPATATSPVPQRTWPIRVDEKLGETPLVPEQDNSVTSIPEIPRWGSQSTMSTLQMSLQAESKATITPSGSVISKFNSTTSSATPQAFDSSSAHHHHHHHH |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
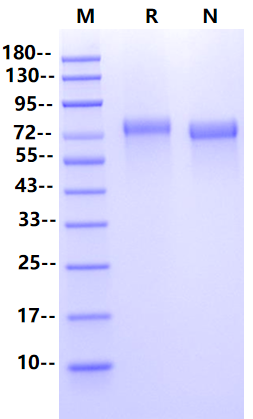
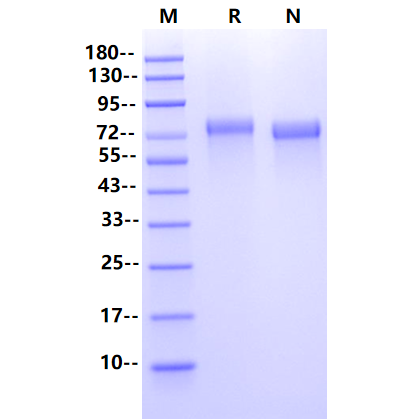
| Molecular Weight | 72-80kDa (Reducing) |
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
Background
C-type lectin domain family 14 member A (CLEC14A), also known as epidermal growth factor receptor 5 (EGFR-5), is an approximately 52-kDa member of the C-type lectin domain family that plays a role in angiogenic functions including cell-cell adhesion, endothelial cell migration, and tube formation. This tumor endothelial marker is a type I transmembrane protein whose extracellular domain (ECD) domain consists of a 141 amino acid (aa) C-type lectin domain, a 43 aa EGF-like domain, and a sushi-like domain. Within the ECD, human CLEC14A shares 67% and 68% sequence identity with mouse and rat CLEC14A, respectively. In endothelial cells, CLEC14A forms a complex with VEGFR-3. Failure in the formation of this complex has been observed to result in the enhanced expression and activity of VEGFR-2 and the downstream signaling. By its interaction with VEGFR-3, CLECA4 appears to regulate developmental angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and pathological angiogensis. CLEC14A acts in vascular homeostasis by fine-tuning VEGF R2 and VEGF R3 signaling in ECs, suggesting its relevance in the pathogenesis of angiogenesis-related human disorders.
Picture
Picture
SDS-PAGE