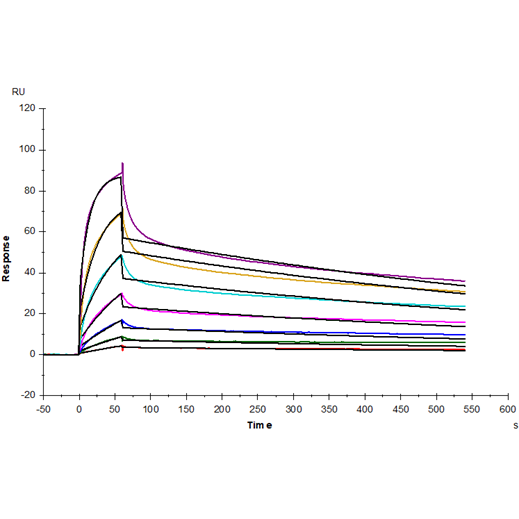
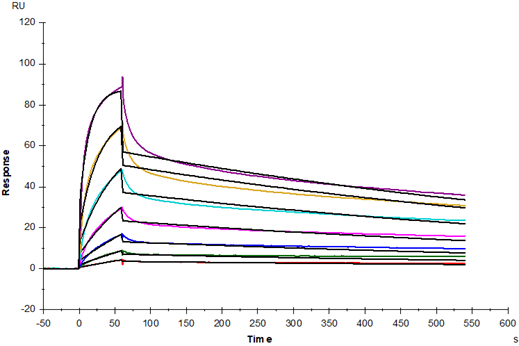
Anti-His antibody Immobilized on CM5 Chip captured CD7 Ligand/SECTM1 His Tag, Mouse (Cat. No. UA010323), can bind CD7 Fc Chimera, Mouse (Cat. No. UA010333) with an affinity constant of 31.54nM as determined in SPR assay.
Product Details
Product Details
Product Specification
| Species | Mouse |
| Antigen | CD7 Ligand |
| Synonyms | CD7 Ligand, SECTM1, K12 |
| Accession | NP_663348 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | Gln28-Thr165, with C-terminal 8*His QNKSWDNPICTEGILSVPRGNPAVMTCNISNTFTDVTIQLSANGKDKTIFDKKPQGNFSWRGWELQVQGGLAQLVIKDTQDDHTGIYLWQLHGRQRCYKNITLNILEPSNEDKVPDTTLFTSFPDHAKSSPIEGKPGTGGGSHHHHHHHH |
| Expression System | HEK293 |
| Molecular Weight | 25-35kDa |
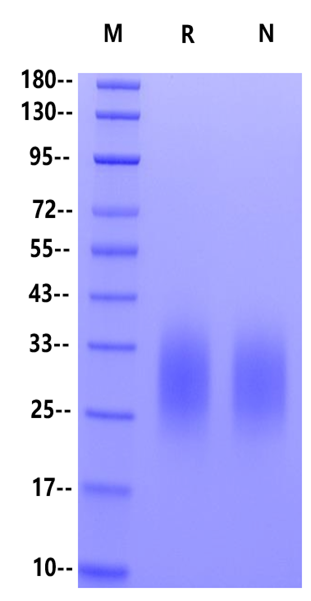
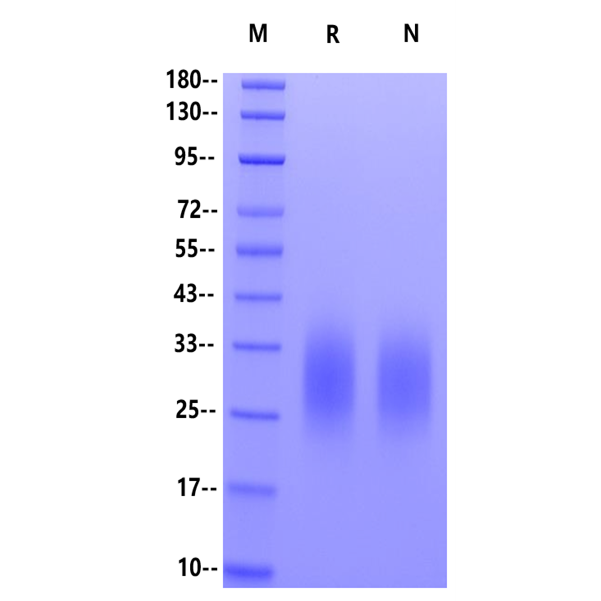
| Purity | >95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1EU/μg |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Tag | His Tag |
| Physical Appearance | Lyophilized Powder |
| Storage Buffer | PBS, pH7.4 |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation. |
| Stability & Storage | · 12 months from date of receipt, lyophilized powder stored at -20 to -80℃. · 3 months, -20 to -80℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · 1 week, 2 to 8℃ under sterile conditions after reconstitution. · Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reference |
1、Lyman S D. et al. (2000) Identification of CD7 as a cognate of the human K12 (SECTM1) protein. J Biol Chem. 275(5): 3431-3437. 2、Lam G K. et al. (2005) Expression of the CD7 ligand K-12 in human thymic epithelial cells: regulation by IFN-gamma. J Clin Immunol. 25(1): 41-49. |
Background
SECTM1 (secreted and transmembrane 1), also called K12, is either found as an approximately 27 kDa intracellular type I transmembrane protein that shows a perinuclear, Golgi‑like staining pattern, or as a 20 kDa soluble, secreted form. SECTM1 is expressed on thymic epithelial and fibroblast cells, breast cancer and leukemia cell lines, and neutrophils but not in peripheral lymphocytes. SECTM1 is expressed on cytomembrane, which is identified as a CD7 ligand.CD7 is expressed in T and natural killer (NK) cells, which could be activated by its ligand SECTM1, thus promoting the proliferation of T and NK cells. SECTM1 strongly costimulates CD4 and CD8 T cell proliferation and induces IFN-γ production, likely via a CD7-dependent mechanism. In addition, SECTM1 synergizes with suboptimal anti-CD28 to strongly augment T cell functions. A robust induction of IL-2 production when SECTM1 and anti-CD28 signals were present with TCR ligation.
Picture
Picture
Bioactivity
SDS-PAGE